1) Lebesgue Integral


勒贝格积分
1.
Firstly,the article theoretically expounds the superiority of Lebesgue Integral,then through the detailed cases analyzes its superiority shown in the practical application compared to Riemann Integral.
文章首先从理论上阐明勒贝格积分的优越性,然后通过具体实例详细探讨勒贝格积分相对于黎曼积分,在实际应用中体现出的巨大优越性。
2.
Their properties and the connection with Lebesgue integral sum and integral are studied.


基于粗糙集理论的知识库,定义了知识积分和与知识积分,研究了它们自身的性质及与勒贝格积分和、勒贝格积分的关系。
3.
The paper states the distinctions between Riemann integral and Lebesgue integral from the aspects of the definition of integral,the continuity of integrable function,the additivity of integral,integral limitation theorems and Newton-Leibnitz formula.
从积分的定义,可积函数的连续性,积分的可加性,积分极限定理,牛顿-莱布尼兹公式五个方面阐述了黎曼积分与勒贝格积分的区别。
2) lebesgue area


勒贝格面积
3) L-S integral


勒贝格-斯蒂阶积分
5) Lebesgue Integral


勒贝革积分
1.
On the Extending of Integral Conditions of Riemann Function According to the Foundation and Development of Lebesgue Integral
从勒贝革积分理论的建立和发展看函数黎曼可积条件的推广
6) Lebesgue Decomposition


勒贝格分解
补充资料:勒贝格积分
| 勒贝格积分 Lebesgue integral 分析数学中普遍使用的工具。1902年由法国数学家H.L.勒贝格建立。它是黎曼积分(简记为(R)积分)的重要推广,它克服了(R)积分的许多局限性。一个在[a,b]上(R)可积的有界函数一定在[a,b]上勒贝格可积〔简记为(L)可积〕,但反之不然。典型的例子是狄利克雷函数D(x),它在[0,1]中的有理数上取值为1,在其余点取值为0,则D(x)在[0,1]上有界,(R)不可积,但(L)是可积的,积分值为0。 (L)积分除了具有与(R)积分相似的性质(例如线性性质、对积分区域的有限可加性、单调性等)外,还有其特有的性质:对积分区域的可列可加性、唯一性、绝对可积性、绝对连续性,以及有关交换积分与极限次序的三大定理:单调收敛定理、法都引理、勒贝格控制收敛定理等。正是这些基本性质使得(L)积分具有广泛的应用。例如:利用单调收敛定理及(L)积分与(R)积分间的关系,可以很容易地进行逐项积分,得到 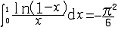
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|
|
| ©2011 dictall.com | |