1) metric space


2-度量空间
1.
Unique common fixed point of another contractive type commuting selfmaps in 2-metric spaces;
2-度量空间中另一类收缩可交换自映射族的唯一公共不动点(英文)
2.
A family of selfmaps having an unique common fixed point in 2-metric spaces;


2-度量空间中具有唯一公共不定点的自映射族(英文)
3.
A new common fixed point theorem in 2-metric spaces;


2-度量空间上的新的公共不动点定理(英文)
2) 2-metric spaces


2-度量空间
1.
A family of quasi-contractive type non-commutative self-maps having an unique common fixed point in 2-metric spaces;
2-度量空间上具有唯一公共不动点的拟收缩型非交换自映射族
2.
Unique common fixed point theorem for a family of contractive type non-commuting selfmaps in 2-metric spaces;
2-度量空间上一族收缩型非交换自映射族的唯一公共不动点定理
3) metric space


度量空间
1.
Iterative processes for generalized asymptotically non-expansive mapping in convex metric space;
度量空间中广义渐进非扩张映射Ishikawa迭代的收敛性问题
2.
Discussion on the sets both open and close in the metric space;


度量空间中既开又闭的集合探讨
3.
Chain recurrent points and ω-limiting points in metric space;


度量空间中的链回归点与ω-极限点
4) metric spaces


度量空间
1.
A rectifible property of sets in metric spaces;


关于度量空间中泛流的注记(英文)
2.
In this paper,internal characterizations onthe compact-covering cs-pi images of metric spaces and the compact-covering cs images of locally separable metric spacesare obtained.
给出了度量空间的紧覆盖cs-π映象和局部可分度量空间的紧覆盖cs映象的内在刻画。
3.
Internal Characterizations of CS?mapping images( Compact ? covering CS ? mapping images ) of metric spaces.
分别建立了度量空间在CS 映射和紧复盖CS 映射下的象空间的特征 。
5) spatial measure


空间度量
1.
This paper gives a definition of spatial measure on spatial data cube for multi-source data on "Digital City",and describes basic concept of aggregation on spatial measure,and explains aggregation process of point spatial measure,line spatial measure,area spatial measure by legend,and states basic aggregation principle of spatial measure,and expresses foundatio.
叙述了面向“数字城市”多源数据的空间数据立方体空间度量的基本定义;描述了空间度量的聚集概念,并结合具体的图例阐述了点状、线状、面状空间度量的聚集过程;解释了空间数据立方体维上钻、维下翻、维层次上钻、维层次下翻的空间度量聚集操作基本原理。
6) vacuity
[英][və'kju:əti] [美][və'kjuətɪ]


(1)真空[度](2)空间
补充资料:度量空间
| 度量空间 metric space 具有度量的抽象空间,设X是一个集合,若有定义在X×X上的非负实值函数d,满足①d(x,y)≥0,d(x,y)=0 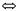 x=y; ②d(x,y)=d(y,x);③d(x,z)≤d(x,y)+d(y,z),则称(X,d)是度量空间,d称为距离或度量。这是最接近于欧几里得空间的抽象空间。利用度量可很自然地将欧几里得空间上点的邻域、开集、闭集,收敛序列以及连续映射等概念推广到一般度量空间,也能将一致连续的概念推广到度量空间。由于19世纪末集合论产生后,实变函数及泛函分析的发展,需要规定函数间的距离,因而抽象出度量、度量空间的概念,其创始人是M.R.弗雷歇。常见的度量空间有: x=y; ②d(x,y)=d(y,x);③d(x,z)≤d(x,y)+d(y,z),则称(X,d)是度量空间,d称为距离或度量。这是最接近于欧几里得空间的抽象空间。利用度量可很自然地将欧几里得空间上点的邻域、开集、闭集,收敛序列以及连续映射等概念推广到一般度量空间,也能将一致连续的概念推广到度量空间。由于19世纪末集合论产生后,实变函数及泛函分析的发展,需要规定函数间的距离,因而抽象出度量、度量空间的概念,其创始人是M.R.弗雷歇。常见的度量空间有:n维欧几里得空间(Rn,d):Rn={(x1,…,xn)|xi∈R,i=1,2,…,n },d(x,y)= 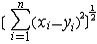 ,其中x=(x1,x2,…, xn),y=(y1,y2,…,yn)。 ,其中x=(x1,x2,…, xn),y=(y1,y2,…,yn)。希尔 伯特空 间(l2;d):l2={(x1,x2,…,xn…) 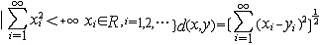 , 其中x =( x1,x2 ,…),y=(y1,y2,…)∈l2。 , 其中x =( x1,x2 ,…),y=(y1,y2,…)∈l2。函数空间(ρ[0,1],d):C[0,1]={f:f为[0,1]上的实值连续函数},对任意f,g∈C[0,1],d(f,g)=max{|f(x)-g(x)|}。 x∈[0,1] 对度量空间(X,d)可引进拓扑结构,即以包含开球B(x,r)={y∈X|d( x,y)<r }的集为邻域定义拓扑,称为d所诱导的拓扑。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条