1) infimal convolution


卷积下确界
2) greatest lower bound


精确下界
1.
The thesis demonstrated the function dependency and the greatest lower bound ofλ-spiral function and proved the inclusion relation of the two functions.
对λ-螺旋形函数的从属性及星函数实部的精确下界给出了证明,并证明了两族函数的包含关系,给出了特殊情况的系数估计。
2.
Based on function An、function families Sλn,m(A,B)、the dependency of f(z) to g(z) and the definition of λ-spirial function,the depedency of function and the greatest lower bound of Re[(Dmf(z)/z)βeiλ] were demonstrated,and some conclusions were drawn i.
基于函数An、函数族Sn,mλ(A,B)、f(z)从属于g(z)以及λ-螺旋形函数的定义,给出了某些实数对函数的从属性,并证明了Re[(Dmf(z)/z)βeiλ]的精确下界,得出了几个推论,即:若f(z)是α阶星函数,则Re(f(z)/z)β>2-2β(1-α);若f(z)是α阶凸函数,则有Re(f′(z))β>2-2β(1-α)(0<β<2(1-α)-1)。
3) infimum
[in'faiməm]


下确界
1.
Supremum and Infimum of Order Bounded Sets of Fuzzy n-cell Numbers;


序有界模糊n-方体数集的上确界与下确界(英文)
2.
On metric description of supremum and infimum of the space of fuzzy numbers;


模糊数空间上下确界的度量刻划
3.
Researches on infimum of Hilbert space quantum effect


关于Hilbert空间量子效应下确界的研究
4) sets/infimum


集/下确界
5) greatest lower bound


下确界
1.
Let rn be the ratio of the maximum distance to the minimum distance, and Rn be the greatest lower bound for rn .
运用数学软件几何画板(TheGeometer'sSketchpad)研究以下的Heilbronn型问题:平面上有n个不同的点,它们之间的最大距离和最小距离的比记作出rn、rn的下确界设为Rn,试求Rn或给出Rn的上下界估计。
2.
Let r\-n be the ratio of the maximum distance to the minimum distance, and R\-n be the greatest lower bound for r\-n .
运用数学软件几何画板 (The Geometer' s Sketchpad)研究以下的 Heilbronn型问题 :平面上有 n个不同的点 ,它们之间的最大距离和最小距离的比记作出 rn,rn的下确界设为 Rn,试求 Rn或给出 Rn的上下界估计 。
3.
Let rn be the ratio of the maximum distance to the minimum distance,and Rn be greatest lower bound for rn.
平面上n个不同的点间的最大距离和最小距离的比记作r_n,r_n的下确界设为R_n。
6) the Fouque infimum


Fouque下确界
1.
For example: the Fouque infimum of two sub strong stopping points is still a sub strong stopping point.
探讨另外几种停点的过去 ,从而得到了亚强停点的 Fouque下确界仍是亚强停点 ,最后举 2个反例说明它的几何下确界不一定仍是亚强停
补充资料:卷积
| 卷积 convolution 分析数学中一种重要的运算。设f(x), g(x)是R1上的两个可积函数,作积分: 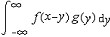 可以证明,关于几乎所有的x∈(-∞,∞) ,上述积分是存在的。这样,随着x的不同取值 ,这个积分就定义了一个新函数h(x),称为f与g的卷积,记为h(x)=(f *g)(x)。容易验证,(f *g)(x)=(g *f)(x),并且(f *g)(x)仍为可积函数。这就是说,把卷积代替乘法,L1(R1)1空间是一个代数,甚至是巴拿赫代数。 可以证明,关于几乎所有的x∈(-∞,∞) ,上述积分是存在的。这样,随着x的不同取值 ,这个积分就定义了一个新函数h(x),称为f与g的卷积,记为h(x)=(f *g)(x)。容易验证,(f *g)(x)=(g *f)(x),并且(f *g)(x)仍为可积函数。这就是说,把卷积代替乘法,L1(R1)1空间是一个代数,甚至是巴拿赫代数。卷积与傅里叶变换有着密切的关系。以 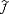 (x) , (x) , (x)表示L1(R)1中f和g的傅里叶变换,那么有如下的关系成立:(f *g)∧(x)= (x)表示L1(R)1中f和g的傅里叶变换,那么有如下的关系成立:(f *g)∧(x)=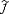 (x)· (x)· (x),即两函数的傅里叶变换的乘积等于它们卷积后的傅里叶变换。这个关系,使傅里叶分析中许多问题的处理得到简化。 (x),即两函数的傅里叶变换的乘积等于它们卷积后的傅里叶变换。这个关系,使傅里叶分析中许多问题的处理得到简化。由卷积得到的函数(f *g)(x),一般要比f,g都光滑。特别当g为具有紧支集的光滑函数,f 为局部可积时,它们的卷积(f *g)(x)也是光滑函数。利用这一性质,对于任意的可积函数 , 都可以简单地构造出一列逼近于f 的光滑函数列fs(x),这种方法称为函数的光滑化或正则化。 卷积的概念还可以推广到数列 、测度以及广义函数上去。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
 专业词汇(按中图法分类)
专业词汇(按中图法分类)