1) hybridization of atomic orbits


原子轨道的杂化
2) hybridized molecular orbits


杂化分子轨道
3) Hybrid orbital


杂化轨道
1.
Equivalent and nonequivalent of hybrid orbitals;


杂化轨道的等性与不等性
2.
On the basis of hybrid orbital theory and valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory that anticipate and judge the configuration of covalent polyatomic molecule or iron(not including complexes),a simple and convenient method to calculate the type of the central atomic hybrid orbital directly is deduced by the valence shell electron pairs.
根据用杂化轨道理论和价层电子对互斥理论预测和判断共价多原子分子或离子 (不包括配合物 )空间构型的原理 ,导出了一种用价层电子对数直接预测中心原子轨道杂化类型的简便方
3.
In this paper,the nip angle formula between hybrid orbitals is introduced.


介绍了杂化轨道间夹角公式。
4) orbital hybridization


轨道杂化
1.
In this paper, we discuss the reason of the negative resistance phenomenon(NRP) existing in a MIM(metal insulator metal)light emission tunnel junction s I V character by using orbital hybridization theory for the first time.
首次从轨道杂化的角度探讨了 MIM隧道结负阻特性的成因 ,结合化学上的计算 ,并与实际测量结果进行对比分析 ,提出了 MIM隧道结负阻特性的理论解
5) hybridization
[英][,haibridai'zeiʃən] [美][,haɪbrɪdə'zeʃən]


轨道杂化
1.
An anomalously large up\|shift of 9?cm -1 between 20?K and room temperature for the pinch Ag(2) mode suggests the existence of hybridization between the C 60 molecules and the intercalants.
径向Ag(2 )模的频率在 2 0K到室温之间有一个反常大的向高频漂移 (9cm-1) ,这表明在C60 分子和掺杂离子之间存在着轨道杂化 。
2.
Also,more emphysises have been placed on the effects of the sp-d hybridization of Co atom on the stabilities and magnetism.
N≥8时,Co原子陷入主团簇内部,体系的对称性降低,稳定性增强;轨道杂化增强了体系的稳定性,但减小了双重态和三重态体系中Co原子的磁矩;N=3,8,10是团簇CoAlN(N=2-11)的幻数。
6) hybridized orbital


杂化轨道
1.
Based on the hybridized orbital theory and electron partnership theory,a method for predicting molecular geometries is proposed Using it ,the geometries of molecules with AB_n can be predicted simply and correctly.
本文研究的预测分子空间构型的方法是以杂化轨道理论为基础 ,根据电子配对原理 ,简明、准确地预测ABn 型分子的空间构型。
补充资料:原子轨道
| 原子轨道 atomic orbit 描述原子中单电子处于真实的(如氢原子或类氢离子的单电子体系)或假定的(即有效的,如多电子原子的电子体系)中心势场中束缚态波函数的空间部分,即单电子薛定谔方程 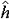 (1)ψ(1)=Eψ(1)的解ψ(1)称原子轨道。式中 (1)ψ(1)=Eψ(1)的解ψ(1)称原子轨道。式中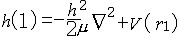 , , 为单电子哈密 顿 算符; μ=mM/(m+M),为约化质量;h=h/2π,h是普朗克常数;▽2是拉普拉斯算符;m、M分别是电子和原子核的质量;V(r)是单电子真实的或假定的有效势函数 ;h(1)和ψ(1)中的数字1表示单电子空间坐标(以核为参考点)。 氢原子和类氢离子是由一个电子和原子核组成的双粒子体系,引入质心坐标以后,求解电子相对于核的相对运动方程,得到电子的波函数ynlm(r,θ,  )=Rnl(r)Ylm(θ, )=Rnl(r)Ylm(θ, ),式中n=1,2,3,…,为主量子数;l=0,1,2,…,-1,为角量子数;m=0,±1,±2,…,±l ,为磁量子数;Rnl(r) 是原子轨道的径向部分;Ylm(θ, ),式中n=1,2,3,…,为主量子数;l=0,1,2,…,-1,为角量子数;m=0,±1,±2,…,±l ,为磁量子数;Rnl(r) 是原子轨道的径向部分;Ylm(θ, )是球谐函数 )是球谐函数,即原子轨道的角度部分。通常用符号s ,p ,d ,f,…等依次代表l=0,1,2,3,…,故 n=2 ,l=0 的状态的原子轨道可写为ψ2s,n=3,l=2的状态可写为ψ3d,余类推。多电子原子轨道通常用自洽场方法求解单电子函数满足的哈特里福克方程获得。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条