1) atomic orbital graph


原子轨道图
2) graphical representation of atomic orbit


原子轨道图形
3) atomic orbital


原子轨道
1.
Drawing atomic orbital and electronic cloud using MATLAB;


使用MATLAB绘制原子轨道和电子云图形
2.
The Fission Results and Index System of Atomic Orbital and Atomic Spectrum in Various Symmetry Groups;
原子轨道和原子光谱项在各种对称环境中分裂结果及其检索系统的设计
3.
This article discusses the instability of some heavy atoms of higher oxidation states in P-block element and the various reasons of the inertial of the electrons,which in a 6s atomic orbital.
从原子轨道的结构特征及有效核电荷等方面讨论了P区重元素的高氧化态的不稳定性,说明造成6 s电子惰性的原因是多方面的。
4) atomic orbit


原子轨道
1.
Taking Li4(CH3)4 as an example,we describe the formation and bonding (linkage) effect of four -center,two-electron bond, and discuss the overlap of atomic orbital and bond order.
对四中心两电子键的原子轨道重叠和电子云的分布及键级等进行讨论分析并对Li4(CH3)4的结构数据做出理论解释。
2.
This paper has determined hybridized orbital patterns of atomic orbits in MX5 with the group theory method and calculated the linkage capabilities of the orbits and discussed relative stabilities of the molecules between space configurations.
用群论的方法,通过分子对称性的分析,确定了MX5型化合物的原子轨道的杂化形式,并计算了杂化轨道的成键能力,讨论了两种不同杂化类型分子空间构型的相对稳定性。
5) atom orbital energies


原子轨道能
1.
In this paper,the exceptional electron structure of transition elements is better expounded by concept of the atom orbital energies,Hund's rule and relativistic effects.
本文用原子轨道能、洪特规则、相对论性效应的概念较好地解释了过渡元素原子“例外”电子层结
6) Number of atomie orbitals


原子轨道数
补充资料:原子轨道
| 原子轨道 atomic orbit 描述原子中单电子处于真实的(如氢原子或类氢离子的单电子体系)或假定的(即有效的,如多电子原子的电子体系)中心势场中束缚态波函数的空间部分,即单电子薛定谔方程 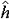 (1)ψ(1)=Eψ(1)的解ψ(1)称原子轨道。式中 (1)ψ(1)=Eψ(1)的解ψ(1)称原子轨道。式中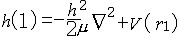 , , 为单电子哈密 顿 算符; μ=mM/(m+M),为约化质量;h=h/2π,h是普朗克常数;▽2是拉普拉斯算符;m、M分别是电子和原子核的质量;V(r)是单电子真实的或假定的有效势函数 ;h(1)和ψ(1)中的数字1表示单电子空间坐标(以核为参考点)。 氢原子和类氢离子是由一个电子和原子核组成的双粒子体系,引入质心坐标以后,求解电子相对于核的相对运动方程,得到电子的波函数ynlm(r,θ,  )=Rnl(r)Ylm(θ, )=Rnl(r)Ylm(θ, ),式中n=1,2,3,…,为主量子数;l=0,1,2,…,-1,为角量子数;m=0,±1,±2,…,±l ,为磁量子数;Rnl(r) 是原子轨道的径向部分;Ylm(θ, ),式中n=1,2,3,…,为主量子数;l=0,1,2,…,-1,为角量子数;m=0,±1,±2,…,±l ,为磁量子数;Rnl(r) 是原子轨道的径向部分;Ylm(θ, )是球谐函数 )是球谐函数,即原子轨道的角度部分。通常用符号s ,p ,d ,f,…等依次代表l=0,1,2,3,…,故 n=2 ,l=0 的状态的原子轨道可写为ψ2s,n=3,l=2的状态可写为ψ3d,余类推。多电子原子轨道通常用自洽场方法求解单电子函数满足的哈特里福克方程获得。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条