1) superfinishing
[,sju:pə'finiʃiŋ]


超精加工
1.
This paper analyzed the superfinishing principle of engineering ceramic material, studied the effect of superfinishing process parameters, such as the pressure, amplitude and frequency of grinding head, the rotate speed of workpiece, and the machining time, on the workpiece surface roughness, and obtained a group of optimized superfinishing process parameters.
本文分析了陶瓷材料超精加工机理 ,试验研究了用超精加工工艺参数如磨头压力、振幅、振动频率、工件转速、加工时间等对工件表面粗糙度的影响 ,得到了一组较优的超精加工工艺参数值。
2.
Dissertating the five very important aspects that must be considered when we select whetstone before doing superfinishing of bearing parts.
论述了油石选择需要考虑的五个方面的重要因素,详细介绍了轴承零件超精加工中有关油石的规格和油石运动参数的选择方法,分析了各种参数之间的相互关系。
2) ultra-precision machining


超精加工
1.
Mechanism and application of ultra-precision machining using loose abrasive grains


游离磨粒超精加工机理和应用
2.
The successful applications of diamond cutting tool in the ultra-precision machining micro-optical structure elements(such as fresnel mirror,diffraction mirror,prism and micro-morror arrays,etc.
从金刚石的机械物理特性和金刚石刀具几何构成出发,分析研究了超精金刚石刀具的特点,并以加工实例介绍了金刚石刀具在超精加工微光学结构元件(如菲涅耳镜,衍射镜,三棱镜和微反射阵列等)时的成功应用。
3) superfinish
[,sju:pə'finiʃ]


超精加工
1.
By this way, the effects of current density and superfinish on the corrosion resistance of piston rods in Santana shock absorbers were investigated and established.
通过不同电镀工艺参数条件下对减振器连杆进行镀铬处理 ,用盐雾试验和电解腐蚀试验评价其耐腐蚀性能 ,研究了电流密度和超精加工对桑塔纳轿车减振器连杆耐蚀性的影响 。
4) ultraprecision machining


超精密加工
1.
Application of SPM in ultraprecision machining;


扫描探针显微镜在超精密加工中的应用
2.
Study on the degenerative layer in ultraprecision machining of aluminium composites;


超精密加工铝基复合材料的切削变质层
3.
According to the requirements of development plan- ning in the future,we positively probe into the technology of precision and ultraprecision machining at home and overseas, and analyze its present status as well as propose the imple- mental methods and the considered problems.
根据未来工艺发展规划要求,积极探索国内外精密超精密加工技术,对该项技术的现状进行了分析,作出综述,并提出了实施该项技术的具体途径及所要考虑的问题。
5) super-grinding machining


超精磨加工
6) ultra precision machining


超精密加工
1.
Study on the technology of the ultra precision machining for the optical components in laser nuclear fusion;
激光核聚变光学元件超精密加工技术的研究
2.
The technology of single point diamond turning(SPDT) is a new technique widely used in the world since 1980’s, it is very useful for ultra precision machining.
单点金刚石切削(SPDT)技术是上世纪80年代以来国际上推广应用的一项新技术,是实现超精密加工的有效技术途径。
3.
The ultra precision machining aims at obtaining the designed surface functions through the surface quality controlling.
超精密加工的目标是通过表面质量控制获得预定的表面功能。
补充资料:超精加工
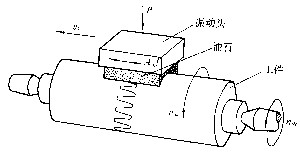
| 超精加工 superfinishing 用细粒度的磨条以一定的压力压在旋转的工件上,并在轴向作往复振荡进行微量切削的光整加工方法。超精加工一般安排在精磨工序之后进行,其加工余量很小(一般为5~8微米),常用于加工各种内外圆柱面、圆锥面、平面、球面等,如曲轴、轧辊、滚动轴承套圈和各种精密零件等。工件经超精加工后,表面粗糙度可达R0.08~0.01微米,表面加工纹路由波纹曲线相互交叉形成,从而易于形成油膜,提高润滑效果,因此耐磨性较好。由于切削区温度较低,表面层有轻度塑性变形,所以表面带有低残余压应力。超精加工常用的磨条粒度一般为W0.5~W28;常用的切削液为80%左右的煤油加20%左右的机油,并经严格过滤;磨条压力一般为0.05~0.3兆帕;磨条振幅一般为1~6毫米;工件圆周速度一般不超过700米/分。若需要提高零件的形状精度及去掉磨削变质层,必须去掉余量0.03毫米左右,此时采取将超精加工分为粗精两阶段,粗加工时用较粗粒度的磨条、较大转速和磨条压力,精加工时取较小的值。
|
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条