1) Bernoulli process


伯努利过程
2) Bernoulli equation


伯努利方程
1.
The Application of Bernoulli Equation in Judging the Direction of Air Flow after Laneway Perforation;
伯努利方程在判定巷道贯通后风流方向中的应用
2.
This paper systematically expounds the basic principles of hydrodynamics and gives a kind of theoretical estimate on the necessity of safety and protection in large train-acceleration by the application of Bernoulli Equation and its principle of pressure reduction from fluid velocity increment.
对流体力学的基本原理进行了系统表述,应用伯努利方程及其流速增加压强降低原理,对铁路提速中安全防护的必要性提供了一项理论估算。
3.
The formula for penetration resistance of a slender projectile is gained using Bernoulli equation and the equivalent plane solution is also obtained for penetration resistance of a cone-shaped warhead.
根据伯努利方程推得了细长杆弹侵彻阻抗力的公式,进而求出锥形弹头侵彻阻抗力的等效平面解,得到了弹体的侵彻深度。
4) Bernoulli equation


伯努利方程式
1.
Deduction of Bernoulli equation at non-inertial reference frame;


非惯性参照系下的伯努利方程式的推导
5) Quasi-Bernolli equation


准伯努利方程
6) Bernoulli's equation of fluid


流体伯努利方程
补充资料:伯努利方程
| 伯努利方程 Bernoulli's equation 理想正压流体在有势彻体力作用下作定常运动时,运动方程(即欧拉方程)沿流线积分而得到的表达运动流体机械能守恒的方程。因D.伯努利于1738年提出而得名。对于重力场中的不可压缩均质流体 ,方程为 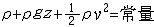 ,式中p、ρ、v 分别为流体的压强、密度和速度;z为铅垂高度;g为重力加速度。 上式各项分别表示单位体积流体的压力能p、重力势能ρg z和动能 ,式中p、ρ、v 分别为流体的压强、密度和速度;z为铅垂高度;g为重力加速度。 上式各项分别表示单位体积流体的压力能p、重力势能ρg z和动能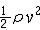 ,在沿流线运动过程中,总和保持不变,即总能量守恒。但各流线之间总能量(即上式中的常量值)可能不同。对于气体,可忽略重力,方程简化为 ,在沿流线运动过程中,总和保持不变,即总能量守恒。但各流线之间总能量(即上式中的常量值)可能不同。对于气体,可忽略重力,方程简化为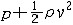 =常量(p0),各项分别称为静压、动压和总压。显然 ,流动中速度增大,压强就减小;速度减小, 压强就增大;速度降为零,压强就达到最大(理论上应等于总压)。飞机机翼产生举力,就在于下翼面速度低而压强大,上翼面速度高而压强小 ,因而合力向上。 据此方程,测量流体的总压、静压即可求得速度,成为皮托管测速的原理。在无旋流动中,也可利用无旋条件积分欧拉方程而得到相同的结果但涵义不同,此时公式中的常量在全流场不变,表示各流线上流体有相同的总能量,方程适用于全流场任意两点之间。在粘性流动中,粘性摩擦力消耗机械能而产生热,机械能不守恒,推广使用伯努利方程时,应加进机械能损失项。 =常量(p0),各项分别称为静压、动压和总压。显然 ,流动中速度增大,压强就减小;速度减小, 压强就增大;速度降为零,压强就达到最大(理论上应等于总压)。飞机机翼产生举力,就在于下翼面速度低而压强大,上翼面速度高而压强小 ,因而合力向上。 据此方程,测量流体的总压、静压即可求得速度,成为皮托管测速的原理。在无旋流动中,也可利用无旋条件积分欧拉方程而得到相同的结果但涵义不同,此时公式中的常量在全流场不变,表示各流线上流体有相同的总能量,方程适用于全流场任意两点之间。在粘性流动中,粘性摩擦力消耗机械能而产生热,机械能不守恒,推广使用伯努利方程时,应加进机械能损失项。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条