2) utterance interpretation


话语理解
1.
In view of utterance interpretation, this paper carries out a comparative study on Relevance Theory and the Theory of Conversational Implicature.
从话语理解的角度对关联理论和会话含意理论的语用解释作了一定的探讨。
2.
In terms of intentionality theory, utterance interpretation and inference of implicatives are seen as a kind of interpretation of the speaker s intentions.
在意向性理论的视野下,话语理解和含意推导是一种意向性解释。
3) discourse understanding


话语理解
1.
Cognitive context plays an important role in discourse understanding,restricting language interpretation.
认知语境在话语理解中占有十分重要的地位,制约着对语言的理解。
2.
The relevance theory of Sperber & Wilson illustrates the influences of contexts to discourse understanding.
话语理解是一种特殊的认知活动,理解话语需借助语境。
3.
It reveals the base of the cognitive psychology of discourse understanding,confines the understanding and the expression of discourse.
认知语境在话语理解中占有十分重要的地位,它揭示了话语理解的认知心理依据,制约着对语言的理解。
4) discourse comprehension


话语理解
1.
In the course of discourse comprehension, the matter of context is apt to be neglected in classroom teaching.
在话语理解方面,语境识别是课堂教学中最容易忽视的问题。
2.
Cognitive process of metaphor plays a critical part in discourse comprehension.


隐喻的认知过程为话语理解中的关键环节。
3.
Relevance Theory is a cognitive theory referring to the human communication and discourse comprehension.
关联理论是一种有关人类交际与话语理解的认知理论。
5) utterance understanding


话语理解
1.
This paper analyzes the differences be- tween the traditional context and cognitive context,and analyzes the important role cognitive context plays in the utterance understanding through specific language phenomenon.
对比分析了传统语境和认知语境,通过具体语言现象分析了认知语境在话语理解中的重要作用。
2.
Generally speaking there are three main factors that affect the final result of utterance understanding,i.
影响话语理解的因素概括起来主要有三个,即话语的接收和识别、具体语境和特定的文化背景。
6) comprehension process


理解过程
1.
The effect of reading beliefs in the comprehension process;


阅读信念在阅读理解过程中的作用
2.
The comprehension process is vital to the grasp of accurate and complete meanings of the source language (SL) discourse and hence reformulation of the messages in the target language (TL).
但是,人类大脑就像一个“黑匣子”,我们无法从外部对其内部信息处理的复杂过程直接进行观察,而单纯的语言学也无法对具有深刻认知心理本质的理解过程进行充分解释。
补充资料:理解锡膏的回流过程
当锡膏至于一个加热的环境中,锡膏回流分为五个阶段,
首先,用于达到所需粘度和丝印性能的溶剂开始蒸发,温度上升必需慢(大约每秒3°C),以限制沸腾和飞溅,防止形成小锡珠,还有,一些元件对内部应力比较敏感,如果元件外部温度上升太快,会造成断裂。
助焊剂活跃,化学清洗行动开始,水溶性助焊剂和免洗型助焊剂都会发生同样的清洗行动,只不过温度稍微不同。将金属氧化物和某些污染从即将结合的金属和焊锡颗粒上清除。好的冶金学上的锡焊点要求“清洁”的表面。
当温度继续上升,焊锡颗粒首先单独熔化,并开始液化和表面吸锡的“灯草”过程。这样在所有可能的表面上覆盖,并开始形成锡焊点。
这个阶段最为重要,当单个的焊锡颗粒全部熔化后,结合一起形成液态锡,这时表面张力作用开始形成焊脚表面,如果元件引脚与PCB焊盘的间隙超过4mil,则极可能由于表面张力使引脚和焊盘分开,即造成锡点开路。
冷却阶段,如果冷却快,锡点强度会稍微大一点,但不可以太快而引起元件内部的温度应力。
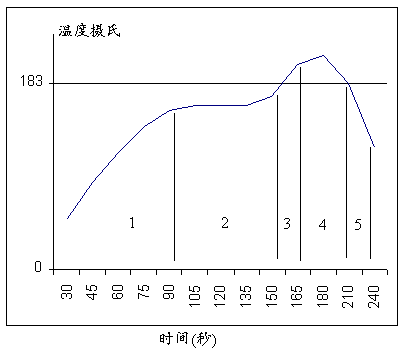
回流焊接要求总结:
重要的是有充分的缓慢加热来安全地蒸发溶剂,防止锡珠形成和限制由于温度膨胀引起的元件内部应力,造成断裂痕可靠性问题。
其次,助焊剂活跃阶段必须有适当的时间和温度,允许清洁阶段在焊锡颗粒刚刚开始熔化时完成。
时间温度曲线中焊锡熔化的阶段是最重要的,必须充分地让焊锡颗粒完全熔化,液化形成冶金焊接,剩余溶剂和助焊剂残余的蒸发,形成焊脚表面。此阶段如果太热或太长,可能对元件和PCB造成伤害。
锡膏回流温度曲线的设定,最好是根据锡膏供应商提供的数据进行,同时把握元件内部温度应力变化原则,即加热温升速度小于每秒3°C,和冷却温降速度小于5° C。
PCB装配如果尺寸和重量很相似的话,可用同一个温度曲线。
重要的是要经常甚至每天检测温度曲线是否正确。
首先,用于达到所需粘度和丝印性能的溶剂开始蒸发,温度上升必需慢(大约每秒3°C),以限制沸腾和飞溅,防止形成小锡珠,还有,一些元件对内部应力比较敏感,如果元件外部温度上升太快,会造成断裂。
助焊剂活跃,化学清洗行动开始,水溶性助焊剂和免洗型助焊剂都会发生同样的清洗行动,只不过温度稍微不同。将金属氧化物和某些污染从即将结合的金属和焊锡颗粒上清除。好的冶金学上的锡焊点要求“清洁”的表面。
当温度继续上升,焊锡颗粒首先单独熔化,并开始液化和表面吸锡的“灯草”过程。这样在所有可能的表面上覆盖,并开始形成锡焊点。
这个阶段最为重要,当单个的焊锡颗粒全部熔化后,结合一起形成液态锡,这时表面张力作用开始形成焊脚表面,如果元件引脚与PCB焊盘的间隙超过4mil,则极可能由于表面张力使引脚和焊盘分开,即造成锡点开路。
冷却阶段,如果冷却快,锡点强度会稍微大一点,但不可以太快而引起元件内部的温度应力。

回流焊接要求总结:
重要的是有充分的缓慢加热来安全地蒸发溶剂,防止锡珠形成和限制由于温度膨胀引起的元件内部应力,造成断裂痕可靠性问题。
其次,助焊剂活跃阶段必须有适当的时间和温度,允许清洁阶段在焊锡颗粒刚刚开始熔化时完成。
时间温度曲线中焊锡熔化的阶段是最重要的,必须充分地让焊锡颗粒完全熔化,液化形成冶金焊接,剩余溶剂和助焊剂残余的蒸发,形成焊脚表面。此阶段如果太热或太长,可能对元件和PCB造成伤害。
锡膏回流温度曲线的设定,最好是根据锡膏供应商提供的数据进行,同时把握元件内部温度应力变化原则,即加热温升速度小于每秒3°C,和冷却温降速度小于5° C。
PCB装配如果尺寸和重量很相似的话,可用同一个温度曲线。
重要的是要经常甚至每天检测温度曲线是否正确。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条