1) convolution(convolution root)


卷积(卷积根)
2) Convolution roots


卷积根
1.
While the closure of these distrbutions under convoltions and under convolution roots is one of the most important problems.
而其卷积与卷积根的封闭性又是最基本和最重要的问题之一。
3) convolution
[英][,kɔnvə'lu:ʃn] [美]['kɑnvə'luʃən]


卷积
1.
Application of hybrid convolution in statistical tolerance analysis;


混合卷积在统计公差分析中的应用
2.
convolution method in statistical tolerance analysis;


统计公差分析的卷积算法
3.
Numerical Deconvolution Method for Continuous Signals Processing and Its Application;


时幅连续信号数值反卷积方法及其应用
4) convolution integral


卷积
1.
Computation of symmetry descriptor convolution integral;


对称描述符中的卷积积分计算
2.
Simple analyzing the applied condition of the result from the differential and integral properties of convolution integral;
浅析由卷积微积分性质所得推论的应用条件
3.
The procedure may be first to get the unit impulse response of structure, then to make convolution integral convolution integral with the differential coefficient of load.
即先求出结构的单位冲激响应,再与载荷做卷积求得总的响应;或者先计算出单位阶跃响应,再与载荷的微分做卷积来求得总的响应。
5) convolution integral


卷积积分
1.
The main idea behind this method was firstly to utilize convolution integral to calculate pointwise curvature through resampling the contour in multiscale space, and then the feature points were selected.
该方法的基本思想是首先采用卷积积分的方法 ,在多尺度空间里通过对轮廓进行重采样来计算轮廓上每一点的曲率并选取特征点。
2.
There are two difficult points in convolution integral: how to determine the limit of the integral, and the integrands on the convolution integral.
确定卷积积分的积分限和在相应区间上的被积函数是计算卷积积分的两个难点。
3.
The zero state response to an arbitrary excitation in a fist order circuit can be solved by either the convolution integral or the three element method.
一阶电路在任意激励下的零状态响应,既可以用卷积积分法,也可以用三要素法进行分析与计算。
补充资料:卷积
| 卷积 convolution 分析数学中一种重要的运算。设f(x), g(x)是R1上的两个可积函数,作积分: 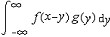 可以证明,关于几乎所有的x∈(-∞,∞) ,上述积分是存在的。这样,随着x的不同取值 ,这个积分就定义了一个新函数h(x),称为f与g的卷积,记为h(x)=(f *g)(x)。容易验证,(f *g)(x)=(g *f)(x),并且(f *g)(x)仍为可积函数。这就是说,把卷积代替乘法,L1(R1)1空间是一个代数,甚至是巴拿赫代数。 可以证明,关于几乎所有的x∈(-∞,∞) ,上述积分是存在的。这样,随着x的不同取值 ,这个积分就定义了一个新函数h(x),称为f与g的卷积,记为h(x)=(f *g)(x)。容易验证,(f *g)(x)=(g *f)(x),并且(f *g)(x)仍为可积函数。这就是说,把卷积代替乘法,L1(R1)1空间是一个代数,甚至是巴拿赫代数。卷积与傅里叶变换有着密切的关系。以 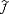 (x) , (x) , (x)表示L1(R)1中f和g的傅里叶变换,那么有如下的关系成立:(f *g)∧(x)= (x)表示L1(R)1中f和g的傅里叶变换,那么有如下的关系成立:(f *g)∧(x)=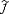 (x)· (x)· (x),即两函数的傅里叶变换的乘积等于它们卷积后的傅里叶变换。这个关系,使傅里叶分析中许多问题的处理得到简化。 (x),即两函数的傅里叶变换的乘积等于它们卷积后的傅里叶变换。这个关系,使傅里叶分析中许多问题的处理得到简化。由卷积得到的函数(f *g)(x),一般要比f,g都光滑。特别当g为具有紧支集的光滑函数,f 为局部可积时,它们的卷积(f *g)(x)也是光滑函数。利用这一性质,对于任意的可积函数 , 都可以简单地构造出一列逼近于f 的光滑函数列fs(x),这种方法称为函数的光滑化或正则化。 卷积的概念还可以推广到数列 、测度以及广义函数上去。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条