1) Total derivative term


全微分项
2) sequential differential


逐项微分
1.
This article presents several methods in calculating the unlimited progression,such as,extention of power progression,sequential differential and sequential differential,Fourier progression and Euler constant.
介绍了裂项相消法、利用已知的幂级数展式法、逐项微分与逐项积分法、傅立叶级数求和法和欧拉常数法这几种无穷级数的求和方法,这些方法为计算收敛数列极限提供了新的工具,使处理不同形式的极限具有更大的灵活性。
3) termwise differentiation


逐项微分
1.
In this article, the relation between covergence region of power series and the new covergence region of power series resulted from termuise integration and termwise differentiation is briefly discussed.
本文主要讨论了幂级数的收敛域与将幂级数逐项积分、逐项微分后所得的新的幂级数的收敛域之间的关系。
4) Linear homogeneous differential equation which coefficients are all multinomial


系数全为多项式的线性齐次微分方程
5) differential polynomial


微分多项式
1.
Values distribution of certain differential polynomials;


一类微分多项式的值分布
2.
Some theorems for linear differential polynomials;


线性微分多项式的几个定理
3.
On the meromorphic functions that their differential polynomials share one value;


微分多项式具有相同1值点的亚纯函数
6) Differential monomial


微分单项式
1.
On the value distribution of differential monomial of algebroid functions;


一类微分单项式的值分布
2.
Value distributions of the general differential monomials is discussed.


讨论了一般微分单项式的值分布 ,得到定理 :设 f 是平面上的超越亚纯函数 。
补充资料:全微分
| 全微分 complete differential 如果二元函数z=f(x,y)在P(x,y)点的增量Δz=f(x+Δx,y+Δy)-f(x,y) 能表示为Δz=AΔx+BΔy+0(ρ),其中 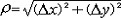 ,A、B,是与Δx和Δy无关的常数,0(ρ)表示当ρ→0时比ρ高阶的无穷小量, 即0(ρ)趋于0的速度比ρ趋于0的速度要快,AΔx+BΔy成为函数增量的主要部分,并且关于Δx、Δy是线性的,则说二元函数z=f(x,y)T赑点可微,称AΔx+BΔy为函数的全微分。记为dz=AΔx+BΔy,因自变量的微分等于改变量,所以dz=Adx+Bdy。与一元函数所不同之处是,在一元函数中,函数在P点可微与可导是等价的,但对二元函数来说,由可微可推出两个偏导数(见偏导数)存在,但光从两个偏导数存在还不能得出可微的结论。 ,A、B,是与Δx和Δy无关的常数,0(ρ)表示当ρ→0时比ρ高阶的无穷小量, 即0(ρ)趋于0的速度比ρ趋于0的速度要快,AΔx+BΔy成为函数增量的主要部分,并且关于Δx、Δy是线性的,则说二元函数z=f(x,y)T赑点可微,称AΔx+BΔy为函数的全微分。记为dz=AΔx+BΔy,因自变量的微分等于改变量,所以dz=Adx+Bdy。与一元函数所不同之处是,在一元函数中,函数在P点可微与可导是等价的,但对二元函数来说,由可微可推出两个偏导数(见偏导数)存在,但光从两个偏导数存在还不能得出可微的结论。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条