1) river-crossing trigonometric leveling


跨江三角高程
1.
With massive measured data of the river-crossing trigonometric leveling survey,the change rule of atmospheric refraction coefficient is calculated and analyzed in elevation transmission region of a bridge,and some beneficial conclusions are obtained.
从三角高程测量的原理出发,推导了利用对向三角高程测量计算大气折光系数的公式,并利用跨江三角高程测量的大量实测数据,计算分析了某大桥跨江高程传递区域大气折光系数的变化规律,得出一些有意义的结论。
2) trigonometric levelling


三角高程
1.
Analysing the features of the advanced measurement instrument — the total station,the measurement principle of the trigonometric levelling and the error,the paper puts forward to use the total station trigonometric levelling in the mining area has advantages such as free from landform,small error,high precision,great efficiency,etc.
通过对先进的测量设备——全站仪的特点、三角高程测量原理及其误差的分析,提出在矿区采用全站仪进行三角高程测量,不受地形限制,具有误差小、精度高、效率快等优点,可代替四等水准测量。
3) triangle elevation


三角高程
1.
Substitute of the leveling measurement of crossing rivers with EDM triangle elevation;


用EDM三角高程代替跨河水准测量
2.
Precision analysis of triangle elevation survey of total station instrument to replace fourth-grade-leveling survey;
全站仪三角高程替代四等水准测量精度分析
3.
Quick Triangle Elevation with Total-Station;


快速全站仪三角高程测量方法及应用
4) trigonometric leveling


三角高程
1.
Survey and precision analysis of tree height by trigonometric leveling.;


三角高程法树高测量与精度分析
2.
Discussing the issue of the EDM trigonometric leveling again;


EDM三角高程测量问题再讨论
3.
Analysis on accuracy in trigonometric leveling with total station and its applied study;


全站仪三角高程测量精度分析及应用研究
5) triangle elevation network


三角高程网
1.
A question discussion of the triangle elevation network elevation begins reckoning;


三角高程网高程起算点探析
6) trigonometric leveling


三角高程测量
1.
Precise analysis for EDM trigonometric leveling;


EDM三角高程测量精度分析
2.
Research on the Atmospheric Research Correction in Trigonometric Leveling;


三角高程测量中大气折光改正的教学研究
3.
The selection of station position in short distance trigonometric leveling;


短距离三角高程测量中测站位置的选择
补充资料:三角高程测量
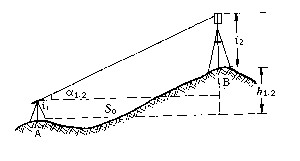
| 三角高程测量 trigonometric leveling 通过观测两点间的水平距离和天顶距(或高度角)求定两点间高差的方法。它观测方法简单,不受地形条件限制,是测定大地控制点高程的基本方法。 三角高程测量的基本原理如图,A、B为地面上两点,自A点观测B点的竖直角为α1.2,S0为两点间水平距离,i1为A点仪器高,i2为B点觇标高,则A、B两点间高差为 h1.2=S0tga1.2+i1-i2
上式是假设地球表面为一平面,观测视线为直线条件推导出来的。在大地测量中,因边长较长,必须顾及地球弯曲差和大气垂直折光的影响。 为了提高三角高程测量的精度,通常采取对向观测竖直角,推求两点间高差,以减弱大气垂直折光的影响。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条