1) fractal and fractal dimension
分形和分维
2) fractal
分形
1.
Numerical simulation of pore fractal dimension evolution during coal pyrolysis;
煤颗粒热解过程中孔隙分形维数变化的数值模拟
2.
The Application of Fractal Theory in the Catalysts Research;
分形理论在催化剂研究中的应用
3.
The fractal characteristics of the pore texture in low porosity and low permeability reservoir;
低孔低渗储层孔隙结构分形特征
3) fractals
分形
1.
Study on Corrosion and Fractals of O'-Sialon ZrO_2-SiC Composites;
O'-Sialon-ZrO_2-SiC复合材料的侵蚀及界面分形研究
2.
Using fractals to study microstructural fracture of Dual-phase Steel;
双相钢显微结构断裂的分形分析
3.
Chaos & fractals optimization method and its application;
混沌分形优化方法及其应用
4) fractal theory
分形
1.
3D terrain generation based on fractal theory and elevation map control;
基于分形和高度图控制的三维地形生成技术研究
2.
Fitting irregular curves by using the fractal theory;
应用分形技术进行不规则曲线模拟
3.
Several methods for image generation based on fractal theory;
几种基于分形思想的图像生成技术
5) Fractal dimension
分形
1.
Study of effective diffusion coefficient of Chryseobacterium sp. in saturated soil using membrane cell and fractal dimension model;
应用隔膜池及分形方法测算金黄杆菌在土壤中的有效扩散系数
2.
Analyzing the information entropy and fractal dimension of urban land use spatial evolving process from 1900 to 2004 in Changchun City;
长春市百年城市土地利用空间结构演变的信息熵与分形机制研究
3.
Attrition indices and fractal dimensions were determined.
应用分形理论研究了砂状氧化铝表面形貌和强度的关系。
6) Fractal geometry
分形
1.
The expansion mechanism of hardened cement paste with double expansion sources of entringite and brucite was studied by using theory of fractal geometry and viscoelasticity.
应用分形学与粘弹性力学对含钙矾石和水镁石膨胀源的水泥硬化浆体的膨胀机理进行了研究与分析。
2.
These methods include statistical prediction,theory of grey system,fuzzy mathematics,fractal geometry,geostatistics,pattern recognition, GIS and so on.
主要包括矿床统计预测方法、灰色系统方法、模糊数学方法、分形几何方法、地质统计学方法、模式识别方法和地理信息系统等,并简述和评价了某些方法的基本应用。
3.
In the paper,the application of fractal geometry in the study of surface structure of coal has been introduced.
介绍了分形理论在煤表面结构研究中的应用。
参考词条
补充资料:分形维数
| 分形维数 fractal dimension 描述分形最主要的参量。简称分维。通常欧几里德几何中,直线或曲线是1维的,平面或球面是2维的,具有长、宽、高的形体是 3 维的;然而对于分形如海岸线、科赫曲线、射尔宾斯基海绵等的复杂性无法用维数等于 1、2、3 这样的数值来描述。科赫曲线第一次变换将1英尺的每边换成4个各长4英寸的线段,总长度变为 3×4/3=4 英尺;每一次变换使总长度变为乘以4/3,如此无限延续下去,曲线本身将是无限长的。这是一条连续的回线,永远不会自我相交,回线所围的面积是有限的,它小于一个外接圆的面积。因此科赫曲线以它无限长度挤在有限的面积之内,确实是占有空间的 ,它比1维要多,但不及2维图形,也就是说它的维数在1和2之间,维数是分数。同样,谢尔宾斯基海绵内部全是大大小小的空洞,表面积是无限大,而占有的 3 维空间是有限的,其维数在2和3之间。 计算分形维数的公式是 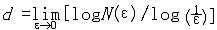 ,式中ε是小立方体一边的长度, N (ε)是用此小立方体覆盖被测形体所得的数目,维数公式意味着通过用边长为ε的小立方体覆盖被测形体来确定形体的维数。对于通常的规则物体 ,覆盖一根单位 长度的线 段所需 的数目要 N (ε)=1/ε2,覆盖一个单位边长的正方形,N(ε)=(1/ε)2 ,覆盖单位边 长的立方体,N (ε)=(1/ε)3。从这三个式子可见维数公式也适用于通常的维数含义。利用维数公式可算得科赫曲线的维数 d=1.2618,谢尔宾斯基海绵的维数d= 2.7268。对于无规分形,可用不同的近似方法予以计算,也可用一定的适当方法予以测定。 ,式中ε是小立方体一边的长度, N (ε)是用此小立方体覆盖被测形体所得的数目,维数公式意味着通过用边长为ε的小立方体覆盖被测形体来确定形体的维数。对于通常的规则物体 ,覆盖一根单位 长度的线 段所需 的数目要 N (ε)=1/ε2,覆盖一个单位边长的正方形,N(ε)=(1/ε)2 ,覆盖单位边 长的立方体,N (ε)=(1/ε)3。从这三个式子可见维数公式也适用于通常的维数含义。利用维数公式可算得科赫曲线的维数 d=1.2618,谢尔宾斯基海绵的维数d= 2.7268。对于无规分形,可用不同的近似方法予以计算,也可用一定的适当方法予以测定。分维反映了复杂形体占有空间的有效性,它是复杂形体不规则性的量度。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。