1) Beta-binomial distribution


贝塔-二项分布
2) beta distribution


贝塔分布
1.
Making full use of knowledge in manufacturing tolerance analysis combined with the beta distribution model is introduced and applied.
所用分析方法充分利用制造环境知识 ,把贝塔分布应用于公差设计 。
2.
Considering the step by step improvement in the related knowledge and information, a dynamic and recurring method is advocated of assessing the containment with Bayes theorem and the solution is obtained to the problem in its practical application: how to set forth a prior Beta distribution.
解决了贝叶斯方法实用中难题:如何简易地确定先验的贝塔分布。
3.
The 8087 s instructions are estimated with beta distribution and normal distribution separately, the whole program s execution time is approximated with normal distribution after adding instruction.
分别用贝塔分布和正态分布模拟8087指令的运行时间,进行指令叠加后用正态分布模拟整个程序的运行时间;实验结果表明,基于分布函数的程序执行时间预估方法是可行的;最后对估计出来的时间区间作了调整。
3) Beta-binomial model


贝塔二项模型
4) binomial distribution


二项分布
1.
Several empirical Bayes Estimations on binomial distribution;


二项分布的几种经验Bayes估计方法
2.
Improvement of Stirling s formula and approximate calculation of probability of binomial distribution;
Stirling公式的改进及二项分布概率的近似计算
3.
Hypothesis test in the judgement on a binomial distribution and a Poisson distribution;


二项分布与泊松分布判别的假设检验
5) binominal distribution


二项分布
1.
Result The index of distribution of carcinoma of the stomach from 44 clans in wuwei is well above the probability space in binominal distribution (χ 2=15.
方法 :用二项分布 (p +q)n数学模型拟合 ,用 χ2 进行配合适度检验。
2.
But concerning the probability of the number of core damage under the condition of multiple reactor years,it follows the binominal distribution.
概率安全分析可得出单个反应堆的堆芯损坏频率,而在多堆年情况下发生堆芯损坏次数的概率则可由概率论中的二项分布来计算。
6) mixed Beta distribution


混合贝塔分布
1.
In order to avoid that a small amount of field test information would be obliterated by a large amount of prior information,a Bayesian method with mixed Beta distribution was used.
为避免少量的现场试验信息被大量的先验信息淹没,使用了以混合贝塔分布为先验分布的贝叶斯方法。
补充资料:二项分布
| 二项分布 binomial distribution 概率论中最常用的一种离散型概率分布。若随机变量遵从二项分布,则这个随机变量只取有限个值,即取0,1,2,…,n共n+1个整数值,取k值的概率为 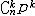 (1-p)n-k(k=0,1,2,…,n; (1-p)n-k(k=0,1,2,…,n;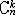 = =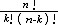 )。记二项分布为B(n,p)。因为 )。记二项分布为B(n,p)。因为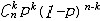 恰好是〔(1-p)+p〕n的二项式展开的第k+1项,所以二项分布由此得名。从不合格率为p的产品中独立地抽取n个产品(每次抽一个,抽取后又放回),其中恰有k个不合格品的概率就是 恰好是〔(1-p)+p〕n的二项式展开的第k+1项,所以二项分布由此得名。从不合格率为p的产品中独立地抽取n个产品(每次抽一个,抽取后又放回),其中恰有k个不合格品的概率就是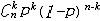 ,所以这n个产品中不合格品数是一个随机变量,它遵从二项分布。类似的例子在生产实践和科学实验中是常见的,将这类问题模型化,假设每一次试验只有两个可能结果:事件A出现或者不出现,A出现的概率为p,不出现的概率为1-p。这种只有两个可能结果的随机试验就称为伯努利试验,将这种试验独立地重复进行n次所组成的随机试验称为n重伯努利试验,其中事件A出现的次数Z是一个服从二项分布B(n,p)的随机变量。二项分布有两个参数n和p,n代表试验的总次数,p代表每次试验事件A出现的概率。二项分布B(n,p)的数学期望为np,方差为np(1-p)。当p固定,n充分大时,二项分布B(n,p)近似于正态分布,当p很小而n较大时,二项分布也可以用泊松分布来近似。 ,所以这n个产品中不合格品数是一个随机变量,它遵从二项分布。类似的例子在生产实践和科学实验中是常见的,将这类问题模型化,假设每一次试验只有两个可能结果:事件A出现或者不出现,A出现的概率为p,不出现的概率为1-p。这种只有两个可能结果的随机试验就称为伯努利试验,将这种试验独立地重复进行n次所组成的随机试验称为n重伯努利试验,其中事件A出现的次数Z是一个服从二项分布B(n,p)的随机变量。二项分布有两个参数n和p,n代表试验的总次数,p代表每次试验事件A出现的概率。二项分布B(n,p)的数学期望为np,方差为np(1-p)。当p固定,n充分大时,二项分布B(n,p)近似于正态分布,当p很小而n较大时,二项分布也可以用泊松分布来近似。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条