2) aerodynamic tilting-pad journal bearing


可倾瓦空气动压轴承
1.
A computational scheme is presented to evaluate the dynamic stiffness and damping coefficients of the aerodynamic tilting-pad journal bearings by combining the partial derivative method with the equivalent coefficient method.
提出将偏导数法和折合系数法相结合来计算可倾瓦空气动压轴承的动态刚度和阻尼系数。
3) Hybrid Tilting Pad bearing


动静压可倾瓦轴承
4) tilting pad journal bearing


可倾瓦滑动轴承
1.
Rotor bearing system is the heart of large-scale rotating machinery, as a major way to support, the dynamic problem of tilting pad journal bearing (TPJB) growing concern by the people.
转子—轴承系统是大型旋转机械的核心部件,作为主要支承方式的可倾瓦滑动轴承支承,它的动力学特性日益被人们所关注。
2.
As the major way to support the main structure, the dynamic character of tilting pad journal bearing (TPJB) are being more and more concerned today.
作为主要支承方式的可倾瓦滑动轴承支承,其动力学特性日益被人们所关注。
5) tilting-pad bearing


可倾瓦轴承
1.
The calculating method and its solution on tilting-pad bearing are discussed,and the program is designed.
讨论了可倾瓦轴承的设计计算方法和求解过程。
2.
In the process of overhauling a power plant,after anatomizing some existent faults of tilting-pad bearings,the methods to deal with the faults are put forward to ensure the stable operation of steam turbine.
通过某电厂检修过程中可倾瓦轴承出现的一些故障,经仔细分析,找出了处理这些故障的办法,从而保证了汽轮机组的稳定运行。
6) tilting pad journal bearing


可倾瓦轴承
1.
Abnormal vibration was occurred in tilting pad journal bearing of Banshan No.


对国内首台GE公司生产的9F单轴燃机发生在可倾瓦轴承上异常振动进行了介绍、分析和诊断。
2.
The elastic and thermal deformations of tilting pad journal bearings subjected to various pressures and temperatures are calculated rapidly using a twenty node finite element method.
用20节点有限元快速计算径向可倾瓦轴承瓦块,在任意压力分布和温度分布下的弹性变形和热变形,并验证了所编程序的正确性和精确
3.
The finite element method and finite difference method are employed to establish the model for considering the three dimensional elastic deformations of pad and thermal effects in a tilting pad journal bearing.
用有限元素法和有限差分法建立了可倾瓦轴承瓦块三维弹性变形及热效应的计算模型。
补充资料:机械零件:液体动压轴承
液体动压轴承
靠液体润滑剂动压力形成的液膜隔开两摩擦表面并承受载荷的滑动轴承。液体润滑剂是被两摩擦面的相对运动带入两摩擦面之间的。產生液体动压力的条件是﹕两摩擦面有足够的相对运动速度﹔润滑剂有适当的黏度﹔两表面间的间隙是收敛的(这一间隙实际很小﹐在图1 油楔承载 中是夸大画的)﹐在相对运动中润滑剂从间隙的大口流向小口﹐构成油楔。这种支承载荷的现象通常称为油楔承载(见润滑)。
油楔承载 中是夸大画的)﹐在相对运动中润滑剂从间隙的大口流向小口﹐构成油楔。这种支承载荷的现象通常称为油楔承载(见润滑)。
机械加工后的两摩擦表面微观是凹凸不平的﹐如图1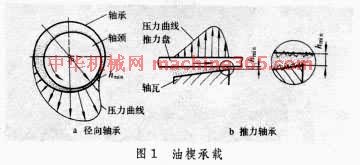 油楔承载 中局部放大图。在正常运输的液体动压轴承中﹐油膜最薄(即通称最小油膜厚度)处两表面的微观凸峰不接触﹐因而两表面没有磨损。这时的摩擦完全属於油的内摩擦﹐摩擦係数可小至0.001。油的黏度越低﹐摩擦係数越小﹐但最小油膜厚度也越薄。因此﹐油的最低黏度受到最小油膜厚度的限制。当最小油膜厚度处两表面的微观凸峰接触时﹐油膜破裂﹐摩擦和磨损都增大。摩擦功使油发热而降低油的黏度。为使油的黏度比较稳定﹐一般採用有冷却装置的循环供油系统或在油中加入能降低油对温度敏感的添加剂(见润滑剂)。液体动压轴承在啟动和停车过程中﹐因速度低不能形成足够隔开两摩擦表面的油膜﹐容易出现磨损﹐所以製造轴瓦或轴承衬须选用能在直接接触条件下工作的滑动轴承材料。液体动压轴承要求轴颈和轴瓦表面几何形状正确而且光滑﹐安装时精确对中。
油楔承载 中局部放大图。在正常运输的液体动压轴承中﹐油膜最薄(即通称最小油膜厚度)处两表面的微观凸峰不接触﹐因而两表面没有磨损。这时的摩擦完全属於油的内摩擦﹐摩擦係数可小至0.001。油的黏度越低﹐摩擦係数越小﹐但最小油膜厚度也越薄。因此﹐油的最低黏度受到最小油膜厚度的限制。当最小油膜厚度处两表面的微观凸峰接触时﹐油膜破裂﹐摩擦和磨损都增大。摩擦功使油发热而降低油的黏度。为使油的黏度比较稳定﹐一般採用有冷却装置的循环供油系统或在油中加入能降低油对温度敏感的添加剂(见润滑剂)。液体动压轴承在啟动和停车过程中﹐因速度低不能形成足够隔开两摩擦表面的油膜﹐容易出现磨损﹐所以製造轴瓦或轴承衬须选用能在直接接触条件下工作的滑动轴承材料。液体动压轴承要求轴颈和轴瓦表面几何形状正确而且光滑﹐安装时精确对中。
液体动压轴承分液体动压径向轴承和液体动压推力轴承。液体动压径向轴承又分单油楔和多油楔两类(见表 液体动压径向轴承类型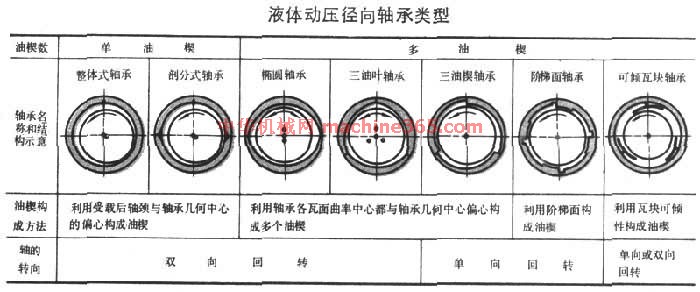 )。
)。
单油楔液体动压径向轴承 轴颈周围只有一个承载油楔的轴承。图2 单油楔轴承的几何参数 中是剖分式的单油楔轴承。O 为轴承几何中心﹐O 为承受载荷F 后的轴颈中心。这两中心的连线称为连心线。连心线与载荷作用线所夹锐角称为偏位角。受载瓦面包围轴颈的角度称为轴承包角。O 与O 之间的距离称为偏心距。轴承孔半径R 与轴颈半径之差称为半径间隙。与之比称为相对间隙。与之比称为偏心率。最小油膜厚度=-=(1-)﹐所在方位由确定。轴承宽度B (轴向尺寸)与轴承直径之比称为宽径比。
单油楔轴承的几何参数 中是剖分式的单油楔轴承。O 为轴承几何中心﹐O 为承受载荷F 后的轴颈中心。这两中心的连线称为连心线。连心线与载荷作用线所夹锐角称为偏位角。受载瓦面包围轴颈的角度称为轴承包角。O 与O 之间的距离称为偏心距。轴承孔半径R 与轴颈半径之差称为半径间隙。与之比称为相对间隙。与之比称为偏心率。最小油膜厚度=-=(1-)﹐所在方位由确定。轴承宽度B (轴向尺寸)与轴承直径之比称为宽径比。
靠液体润滑剂动压力形成的液膜隔开两摩擦表面并承受载荷的滑动轴承。液体润滑剂是被两摩擦面的相对运动带入两摩擦面之间的。產生液体动压力的条件是﹕两摩擦面有足够的相对运动速度﹔润滑剂有适当的黏度﹔两表面间的间隙是收敛的(这一间隙实际很小﹐在图1
 油楔承载 中是夸大画的)﹐在相对运动中润滑剂从间隙的大口流向小口﹐构成油楔。这种支承载荷的现象通常称为油楔承载(见润滑)。
油楔承载 中是夸大画的)﹐在相对运动中润滑剂从间隙的大口流向小口﹐构成油楔。这种支承载荷的现象通常称为油楔承载(见润滑)。 机械加工后的两摩擦表面微观是凹凸不平的﹐如图1
 油楔承载 中局部放大图。在正常运输的液体动压轴承中﹐油膜最薄(即通称最小油膜厚度)处两表面的微观凸峰不接触﹐因而两表面没有磨损。这时的摩擦完全属於油的内摩擦﹐摩擦係数可小至0.001。油的黏度越低﹐摩擦係数越小﹐但最小油膜厚度也越薄。因此﹐油的最低黏度受到最小油膜厚度的限制。当最小油膜厚度处两表面的微观凸峰接触时﹐油膜破裂﹐摩擦和磨损都增大。摩擦功使油发热而降低油的黏度。为使油的黏度比较稳定﹐一般採用有冷却装置的循环供油系统或在油中加入能降低油对温度敏感的添加剂(见润滑剂)。液体动压轴承在啟动和停车过程中﹐因速度低不能形成足够隔开两摩擦表面的油膜﹐容易出现磨损﹐所以製造轴瓦或轴承衬须选用能在直接接触条件下工作的滑动轴承材料。液体动压轴承要求轴颈和轴瓦表面几何形状正确而且光滑﹐安装时精确对中。
油楔承载 中局部放大图。在正常运输的液体动压轴承中﹐油膜最薄(即通称最小油膜厚度)处两表面的微观凸峰不接触﹐因而两表面没有磨损。这时的摩擦完全属於油的内摩擦﹐摩擦係数可小至0.001。油的黏度越低﹐摩擦係数越小﹐但最小油膜厚度也越薄。因此﹐油的最低黏度受到最小油膜厚度的限制。当最小油膜厚度处两表面的微观凸峰接触时﹐油膜破裂﹐摩擦和磨损都增大。摩擦功使油发热而降低油的黏度。为使油的黏度比较稳定﹐一般採用有冷却装置的循环供油系统或在油中加入能降低油对温度敏感的添加剂(见润滑剂)。液体动压轴承在啟动和停车过程中﹐因速度低不能形成足够隔开两摩擦表面的油膜﹐容易出现磨损﹐所以製造轴瓦或轴承衬须选用能在直接接触条件下工作的滑动轴承材料。液体动压轴承要求轴颈和轴瓦表面几何形状正确而且光滑﹐安装时精确对中。 液体动压轴承分液体动压径向轴承和液体动压推力轴承。液体动压径向轴承又分单油楔和多油楔两类(见表 液体动压径向轴承类型
 )。
)。 单油楔液体动压径向轴承 轴颈周围只有一个承载油楔的轴承。图2
 单油楔轴承的几何参数 中是剖分式的单油楔轴承。O 为轴承几何中心﹐O 为承受载荷F 后的轴颈中心。这两中心的连线称为连心线。连心线与载荷作用线所夹锐角称为偏位角。受载瓦面包围轴颈的角度称为轴承包角。O 与O 之间的距离称为偏心距。轴承孔半径R 与轴颈半径之差称为半径间隙。与之比称为相对间隙。与之比称为偏心率。最小油膜厚度=-=(1-)﹐所在方位由确定。轴承宽度B (轴向尺寸)与轴承直径之比称为宽径比。
单油楔轴承的几何参数 中是剖分式的单油楔轴承。O 为轴承几何中心﹐O 为承受载荷F 后的轴颈中心。这两中心的连线称为连心线。连心线与载荷作用线所夹锐角称为偏位角。受载瓦面包围轴颈的角度称为轴承包角。O 与O 之间的距离称为偏心距。轴承孔半径R 与轴颈半径之差称为半径间隙。与之比称为相对间隙。与之比称为偏心率。最小油膜厚度=-=(1-)﹐所在方位由确定。轴承宽度B (轴向尺寸)与轴承直径之比称为宽径比。 说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条