1) Magnetic Induction Tomography


磁感应成像
1.
Magnetic Induction Tomography is a new functional imaging technology.


磁感应成像是一种交换机型功能性成像技术。
2) magnetic induction tomography


磁感应断层成像
1.
Precise synchronous phase measurement method in magnetic induction tomography


磁感应断层成像中的一种高精度同步相位测量方法
2.
Simulated Image Reconstruction of Magnetic Induction Tomography on Simple Head Model


在简单头模型上的磁感应断层成像仿真图像重建
3.
Objective To solve the eddy current problem or the forward problem in magnetic induction tomography(MIT).
目的为了求解磁感应断层成像(magnetic induction tomography,MIT)技术中的涡流问题,以获得MIT正问题的有效解法。
3) brain magnetic induction tomography


脑磁感应成像
1.
AIM: To realize digital phase detection methods in brain magnetic induction tomography (MIT) system and to find a phase detection method with high accuracy.
目的:为实现用于脑磁感应成像系统中的数字鉴相方法,寻求一种高精度的相位检测手段。
4) MIT
[mit]


磁感应断层成像
1.
Magnetic induction tomography(MIT)is a new imaging technique of conductivitytomography.


磁感应断层成像(Magnetic induction tomography,MIT)是一种新的电阻抗断层成像技术。
5) magnetoacoustic tomography with magnetic induction


感应式磁声成像
1.
Three dimensional electromagnetic forward/inverse problems in magnetoacoustic tomography with magnetic induction;
感应式磁声成像中的三维电磁场正逆问题研究
6) magnetic resonance magnetic induction tomography(MRMIT)


磁共振磁感应成像
1.
A theoretical study on 3-D reconstruction algorithm of magnetic resonance magnetic induction tomography(MRMIT) was given in this paper.
对三维磁共振磁感应成像技术进行原理性研究。
补充资料:磁感应强度
| 磁感应强度 magnetic induction 描述磁场强弱和方向的基本物理量。是矢量,常用符号B表示。 点电荷q以速度v在磁场中运动时受到力f 的作用。在磁场给定的条件下,f的大小与电荷运动的方向有关 。当v 沿某个特殊方向或与之反向时,受力为零;当v与此 特殊方向垂直时受力最大,为fm。fm与|q|及v成正比,比值 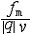 与运动电荷无关,反映磁场本身的性质,定义为磁感应强度的大小,即 与运动电荷无关,反映磁场本身的性质,定义为磁感应强度的大小,即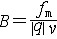 。B的方向定义为:由正电荷所受最大力fm的方向转向电荷运动方向 v 时 ,右手螺旋前进的方向 。定义了B之后,运动电荷在磁场 B 中所受的力可表为 f = qv×B,此即洛伦兹力公式。 。B的方向定义为:由正电荷所受最大力fm的方向转向电荷运动方向 v 时 ,右手螺旋前进的方向 。定义了B之后,运动电荷在磁场 B 中所受的力可表为 f = qv×B,此即洛伦兹力公式。除利用洛伦兹力定义B外,也可以根据电流元Idl在磁场中所受安培力df=Idl×B来定义B,或根据磁矩m在磁场中所受力矩M=m×B来定义B,三种定义,方法雷同,完全等价。 在国际单位制(SI)中,磁感应强度的单位是特斯拉,简称特(T)。在高斯单位制中,磁感应强度的单位是高斯(Gs ),1T=104Gs。由于历史的原因,与电场强度E对应的描述磁场的基本物理量被称为磁感应强度B,而另一辅助量却被称为磁场强度H,名实不符,容易混淆。通常所谓磁场,均指的是B。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条