1) binomial distribution


二项分布
1.
Several empirical Bayes Estimations on binomial distribution;


二项分布的几种经验Bayes估计方法
2.
Improvement of Stirling s formula and approximate calculation of probability of binomial distribution;
Stirling公式的改进及二项分布概率的近似计算
3.
Hypothesis test in the judgement on a binomial distribution and a Poisson distribution;


二项分布与泊松分布判别的假设检验
2) binominal distribution


二项分布
1.
Result The index of distribution of carcinoma of the stomach from 44 clans in wuwei is well above the probability space in binominal distribution (χ 2=15.
方法 :用二项分布 (p +q)n数学模型拟合 ,用 χ2 进行配合适度检验。
2.
But concerning the probability of the number of core damage under the condition of multiple reactor years,it follows the binominal distribution.
概率安全分析可得出单个反应堆的堆芯损坏频率,而在多堆年情况下发生堆芯损坏次数的概率则可由概率论中的二项分布来计算。
3) Binomial distribution


二项式分布
1.
005, the paper asserts that the cipher bit-stream follows the binomial distribution B(n, 0.
5的二项式分布 ,可见 Rijndael算法的频数具有良好的随机特性。
2.
The vehicle routing problems(VRP)in the stochastic demand is studied in this paper,where the demand at service nodes is subjected to the binomial distribution.
本文主要研究随机需求的 VRP问题 ,其中服务需求量满足二项式分布 ,根据期望值的大小我们提出了在一条路线上理想最大服务点数的新概念 ,并在此基础上建立了三种 VRP问题的新模型 ,由于允许服务失败两次和部分服务使得模型能适应多种实际问题 ,以模拟退火思想为基础的两阶段方法经修正后用于解新模型并取得较好的数值结果。
3.
Utilized the characteristic of the binomial distribution and the normal distribution of the analytical errors, meanwhile, according to the domain of the allowed analytical errors between 2 tests, we can make out the accurate inner-enterprise product.
探讨利用平行试验数据间的服从二项式分布特性x~(N,σ2),及试验误差的正态分布及计算公式Φ(z)=∫z-∞1/2πe-u2/2dμ,依据分析方法的重复性、再现性要求满足P(-Z,Z)的运算规律,经计算讨论得出产品的内控指标。
4) Negative binomial distribution


负二项分布
1.
The Biparametric Additive Theorem of Conditional Negative binomial distribution;


条件负二项分布的双参数加法定理
2.
Empirical Bayesian estimation for negative binomial distribution reliability


负二项分布可靠度的经验Bayes估计
3.
Method: The response variable is fitted with Poisson and negative binomial distributions,and the coefficient is estimated with IGLS.
方法:分布函数采用Poisson分布和负二项分布,参数估计为迭代广义最小二乘法。
5) β·distribution


β·二项分布
6) Bivariate binomial distribution.


二变量二项分布
补充资料:二项分布
| 二项分布 binomial distribution 概率论中最常用的一种离散型概率分布。若随机变量遵从二项分布,则这个随机变量只取有限个值,即取0,1,2,…,n共n+1个整数值,取k值的概率为 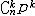 (1-p)n-k(k=0,1,2,…,n; (1-p)n-k(k=0,1,2,…,n;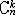 = =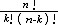 )。记二项分布为B(n,p)。因为 )。记二项分布为B(n,p)。因为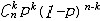 恰好是〔(1-p)+p〕n的二项式展开的第k+1项,所以二项分布由此得名。从不合格率为p的产品中独立地抽取n个产品(每次抽一个,抽取后又放回),其中恰有k个不合格品的概率就是 恰好是〔(1-p)+p〕n的二项式展开的第k+1项,所以二项分布由此得名。从不合格率为p的产品中独立地抽取n个产品(每次抽一个,抽取后又放回),其中恰有k个不合格品的概率就是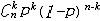 ,所以这n个产品中不合格品数是一个随机变量,它遵从二项分布。类似的例子在生产实践和科学实验中是常见的,将这类问题模型化,假设每一次试验只有两个可能结果:事件A出现或者不出现,A出现的概率为p,不出现的概率为1-p。这种只有两个可能结果的随机试验就称为伯努利试验,将这种试验独立地重复进行n次所组成的随机试验称为n重伯努利试验,其中事件A出现的次数Z是一个服从二项分布B(n,p)的随机变量。二项分布有两个参数n和p,n代表试验的总次数,p代表每次试验事件A出现的概率。二项分布B(n,p)的数学期望为np,方差为np(1-p)。当p固定,n充分大时,二项分布B(n,p)近似于正态分布,当p很小而n较大时,二项分布也可以用泊松分布来近似。 ,所以这n个产品中不合格品数是一个随机变量,它遵从二项分布。类似的例子在生产实践和科学实验中是常见的,将这类问题模型化,假设每一次试验只有两个可能结果:事件A出现或者不出现,A出现的概率为p,不出现的概率为1-p。这种只有两个可能结果的随机试验就称为伯努利试验,将这种试验独立地重复进行n次所组成的随机试验称为n重伯努利试验,其中事件A出现的次数Z是一个服从二项分布B(n,p)的随机变量。二项分布有两个参数n和p,n代表试验的总次数,p代表每次试验事件A出现的概率。二项分布B(n,p)的数学期望为np,方差为np(1-p)。当p固定,n充分大时,二项分布B(n,p)近似于正态分布,当p很小而n较大时,二项分布也可以用泊松分布来近似。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条