3) discontinuity spacings


结构面间距
1.
Research on two-parameter negative exponential distribution of discontinuity spacings in rock mass
岩体结构面间距的双参数负指数分布研究
4) large-space structure


大空间结构
1.
Studies on performance-based fire-resisting design method for large-space structures;


大空间结构防火性能化设计方法研究
2.
Simplified temperature calculation methods of steel roof members of large-space structures under fire conditions have not been studied systematically.
为了研究大空间结构屋面钢构件火灾下温度场的简化计算方法,把国内外现有用于“室内火灾”温度场的简化计算公式和方法,应用于典型尺寸的大空间结构模型,并与数值模拟结果进行比较。
3.
The results show that the fiber and multi-spring elements are not suited for simulating the continuous wall of large-space structures under strong motions.
建立了大空间砖-混凝土组合结构弹塑性分析模型,分别采用纤维单元、多弹簧单元和斜撑单元模型模拟大空间结构的墙体完成结构弹塑性地震反应计算,研究了大空间结构计算模型和计算方法的适用性,提出了结构计算倒塌概念,认为纤维单元与多弹簧单元模型不适合用于模拟强震下大空间结构的连续墙体。
5) large space structure


大空间结构
1.
Several measures of moving technique for buildings are introduced,based on different structures,such as large space structure,buildings with settlement joints,thermo joints or aseismic joints,buildings with different basal elevations,basement or elevator well,and the towering structure.
针对较为常见的大空间结构、带“三缝”结构、基底标高不同或带地下室、电梯井结构和高耸结构的迁移,提出了具体的处理措施,高耸结构迁移的关键是防止倾覆,其它结构迁移技术的关键是托换加固方法和支撑措施。
2.
By researching the design and engineering practice of the typical solar buildings completed in recent 10 years at home and abroad, analysis is carried out on the development tendency of solar building and its existing problems, and discussion given to its application prospect in high-rise building and large space structure.
通过对近10年来国内外的代表性的太阳能建筑的工程实践、设计进行研究,分析了太阳能建筑的发展趋势及存在的问题,并探讨了太阳能在高层建筑和大空间结构中应用前景。
6) long-span spatial structure


大跨度空间结构
1.
Influence of wave travelling effect on random seismic responses of long-span spatial structures;
行波效应对大跨度空间结构随机地震响应的影响
2.
Wind vibration coefficient of long-span spatial structures with self-oscillating of roof and fluid-structure coupling effect;
考虑屋面板自振效应和流固耦合效应的大跨度空间结构风振系数
3.
The non-stationary random seismic analysis of long-span spatial structures under multi-support excitations of three-dimensional orthogonal earthquake motion was performed.
对大跨度空间结构进行三向正交地震动多点激励下的非平稳随机地震反应分析。
补充资料:抽芯成型高差大的滑块多级锁紧结构
在压铸模设计中, 常常会遇到同一抽芯而各成型高度相差较大的零件, 如果采用斜拉杆或弯销抽芯, 习惯上采取的措施是增加滑块的高度,以满足滑块的退位空间,其结果是滑块的重量增加,模框的强度降低。
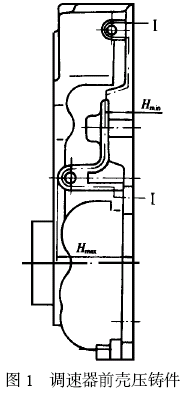
图1 是汽车油泵调速器前壳压铸件示意图, Ⅰ- Ⅰ分型面需用抽芯才能完成脱模,其最低抽芯高度Hmin 为17mm, 最大抽芯高度Hmax为45mm, 为了保证滑块有足够的退位空间而不发生自锁, 滑块的高度必须大于或等于45mm。为避免抽芯距离过大造成滑块体积增加, 在设计中采用了局部增高多级锁紧结构,如图2 所示。P 是高于17mm低于45mm的面,N是高于45mm的面,M面是与N面同高且保证N 面受力平衡的辅助结构。α为抽芯角,β1 、β2 为锁紧角,β1 、β2 不仅具有锁紧作用,而且在开模抽芯时还具有让位的作用,所以β1 、β2 必须大于α, 而且β2 应大于β1 , 否则开模时, 滑块会出现自锁。锁紧角β2 也可以等于β1 , 但由于制造时有误差, 如果误差大, 则β1和β2 形成的锁紧面会出现干涉。在压铸件调速器前壳模具设计中, α取23°, β1 取26°, β2取30°,实现了安全生产。

总之, 对于那些抽芯高度相差大的滑块,采用多级锁紧结构,对减小滑块的重量、延长模具寿命,节约模具材料具有重要的作用。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条