1) derivative
[英][dɪ'rɪvətɪv] [美][də'rɪvətɪv]


导数
1.
Determination of trace selenium by flow injection-hydride generation-derivative atomic absorption spectrometry;
流动注射—氢化物发生—导数原子吸收光谱法测定水中痕量硒(英文)
2.
Direct determination of Ho~(3+) by derivative spectra in presence of Ce~(4+);


铈存在下导数光谱直接测定钬
3.
Fractional Derivative Combined Fourier Least Square Fitting to Process Noised Overlapped Signal;
分数导数结合傅里叶最小二乘拟合处理含噪音的重迭信号
2) derivatives
[英][dɪ'rɪvətɪvz] [美][də'rɛvətɪvz]


导数
1.
Equivalence characterization for derivatives of Bernstein-Durrmeyer operators;


Bernstein-Durrmeyer算子导数的等价刻划
2.
Self-tuning observing derivatives of various orders of an uncertain system output;


不确定性系统输出各阶导数的自校正观测
3.
Consistency of kernel estimation of the derivatives of regression functionin variable bandwidth;
变窗宽下回归函数导数核估计的相合性
3) differential coefficient


导数
1.
Application of differential coefficient in inequation verification;


导数知识在不等式证明中的应用
2.
It also elaborates what should be pay attention to while making use of this method to obtain differential coefficient.
本章给出了由分段函数直接求导数再取极限求函数在分段点处导数的方法,并就利用该方法求导数时需要注意的问题进行了说明。
3.
NormaIly we use the definition of differential coefficient to seek the differential coefficient of the independent variable point in differential coefficient of subsection funtion,which is very complicated in some cases.
对于分段函数自变量分界点处的导数,一般使用导数定义去求,有时很繁琐。
4) derivation
[英][,derɪ'veɪʃn] [美]['dɛrə'veʃən]


导数
1.
Study and Application on a few Properties of Derivation;


导数几个性质的探究与应用
2.
The approach utilizes 2-level derivation of secondary current and a 3-sample fitting calculation for decaying DC component depress as well as the sample data identifying.
该方法采用微分电路和三采样值运算法,以电流的二阶导数深度抑制非周期分量并提高对采样值的甄别。
3.
In order to solve the derivation of power exponent function,this paper has studied the derivation regulations on power function from the perspective of the differentiation of multi-variable function and in accordance with the derivation laws on multi-variable complex function.
为解决幂指函数的求导问题,从多元函数微分法的角度出发,根据多元复合函数的求导法则,探索幂指函数求导的规律,并揭示了幂指函数与幂函数及指数函数导数间的关系,给出了幂指函数求导的另一种方法。
5) Derivate
[英]['deriveit] [美]['dɛrə,vet]


导数
1.
Give examples to show that the derivate of elementary function may be unelementary function.
给出实例说明初等函数的导数可以是非初等函数。
6) A-derivatives


A导数
补充资料:导数
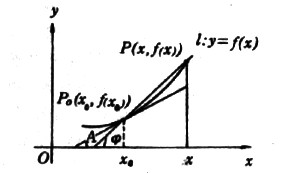
| 导数 derivative 由速度问题和切线问题抽象出来的数学概念。又称变化率。如一辆汽车在10小时内走了 600千米,它的平均速度是60千米/小时,但在实际行驶过程中,是有快慢变化的,不都是60千米/小时。为了较好地反映汽车在行驶过程中的快慢变化情况,可以缩短时间间隔,设汽车所在位置x与时间t的关系为x=f(t),那么汽车在由时刻t0变到t1这段时间内的平均速度是 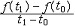 ,当 t1与t0很接近时,汽车行驶的快慢变化就不会很大,平均速度就能较好地反映汽车在t0 到 t1这段时间内的运动变化情况 ,自然就把极限 ,当 t1与t0很接近时,汽车行驶的快慢变化就不会很大,平均速度就能较好地反映汽车在t0 到 t1这段时间内的运动变化情况 ,自然就把极限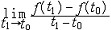 作为汽车在时刻t0的瞬时速度,这就是通常所说的速度。一般地,假设一元函数 y=f(x )在 x0点的附近(x0-a ,x0 +a)内有定义,当自变量的增量Δx= x-x0→0时函数增量 Δy=f(x)- f(x0)与自变量增量之比 作为汽车在时刻t0的瞬时速度,这就是通常所说的速度。一般地,假设一元函数 y=f(x )在 x0点的附近(x0-a ,x0 +a)内有定义,当自变量的增量Δx= x-x0→0时函数增量 Δy=f(x)- f(x0)与自变量增量之比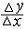 的极限 的极限 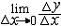 存在且有限,就说函数f在x0点可导,记作 存在且有限,就说函数f在x0点可导,记作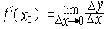 ,称之为f在x0点的导数(或变化率)。若函数f在区间I 的每一点都可导,便得到一个以I为定义域的新函数,记作 f′,称之为f的导函数,简称为导数。函数y=f(x)在x0点的导数f′(x0)的几何意义: ,称之为f在x0点的导数(或变化率)。若函数f在区间I 的每一点都可导,便得到一个以I为定义域的新函数,记作 f′,称之为f的导函数,简称为导数。函数y=f(x)在x0点的导数f′(x0)的几何意义: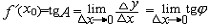 ,表示曲线l 在P0[x0,f(x0)] 点的切线斜率。 ,表示曲线l 在P0[x0,f(x0)] 点的切线斜率。
|
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条