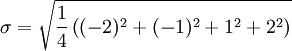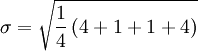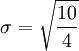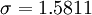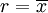|
|
|
说明:双击或选中下面任意单词,将显示该词的音标、读音、翻译等;选中中文或多个词,将显示翻译。
|
|
|
1) standard deviation

标准差
1.
Relativity analysis between half peak and standard deviation of track irregularity;

轨道不平顺半峰值和标准差的相关性分析
2.
Power quality disturbance classification based on standard deviation of multi-resolution analysis and self-organizing feature mapping;
基于多分辨率标准差及自组织映射网络的电能质量扰动分类识别
3.
Algorithm of 3D terrain digital surface model based on standard deviation;

基于标准差的地形三维表面模型建立方法
2) standard difference

标准差
1.
Utilizing the random uncertainity of steady line precision index to calculate the standard difference,analyzes the big or the abnormal survey point,devide regulation relationship curve shape and the suitable operation method to make relationship curve satisfy the precision index,then to improve the flow precision.
利用定线精度指标的随机不确定度推算标准差 ,分析偏大或异常测点 ,确定调整关系曲线线型及处理方式 ,使关系曲线满足精度指标 ,进而提高推求的流量精度。
2.
The construction practice and statistic analysis of high-strength concrete in the Xiaolangdi Project show that when the average concrete strength f cr is over 30?MPa, the standard difference of concrete strength σ obviously increases with f cr , thus σ cannot be considered as a constant.
通过小浪底工程高强混凝土施工实践和统计分析 ,验证了当混凝土配制强度fcr大于 30MPa时 ,混凝土强度标准差σ随fcr增大而递增仍然比较明显 ,因此不可视σ为常数 ,在进行配制强度计算时 ,应按不同混凝土设计标号采用不同的σ值 ,这样既可保证满足设计要求 ,又能取得较好的经济效益 。
3.
This paper pressents “The Test Score Gaussian Distribution ” when Χ 2 Compatibility Test is used in the test, points out that the students score should be tested by Χ 2 and its mean value and standard difference should be limited as well.
提出Χ2 适合性检验中的“成绩正态分布”吻合检验问题 ,指出在对学生成绩这一特殊总体除了进行Χ2 检验外 ,还要对其均值和标准差作适当限制 ,从而使检验法更加完善 ,更具有实际意义 。
3) Standard error

标准差
1.
The slope standard error and correlation coefficient of zero-crossing linear fitting;

过原点直线拟合的斜率标准差与相关系数
2.
It has a bigger warp when the method of absolute value is used to analyse error of digital electronic blood-pressure meter s dynamic pressure, so the method of standard error is employed here to acquire a real warp level.
用绝对值方法分析数字式血压计动态血压误差存在较大偏差,而用标准差方法能较好反应真真实偏差水平。
3.
Testing the standard error of horizontal direction with a equi-spaced scale and processing the tested data with the method of relitive adjustment,we obtain that the testing error of leveling angle is less than one third of the error of leveling angle, which testifies the validity and feasibility of the method.
针对全站仪精度,采用等间隔标尺检测的方法测定水平方向标准差,用相关参数平差的方法对检测数据进行处理,求取全站仪水平测角精度,得到水平角测定误差小于水平角误差的三分之一,实验证明该方法的正确性和可行性。
4) standerd deviation

标准偏差(标准差)
5) standard deviation

标准偏差,标准差
6) error to standard deviation

误差标准差
补充资料:标准差
标准差概述 标准差是一种表示分散程度的统计观念,主要是根据基金净值于一段时间内波动的情况计算而来的。标准差已广泛运用在股票以及共同基金投资风险的衡量上,主要是根据基金净值于一段时间内波动的情况计算而来的。一般而言,标准差愈大,表示净值的涨跌较剧烈,风险程度也较大。实务的运作上,您可进一步运用单位风险报酬率的概念,同时将报酬率的风险因素考虑在内。所谓单位风险报酬率是指衡量投资人每承担 一单位的风险,所能得到的报酬,以夏普指数最常为投资人运用。 标准差是一组数值自平均值分散开来的程度的一种测量观念。一个较大的标准差,代表大部分的数值和其平均值之间差异较大;一个较小的标准差,代表这些数值较接近平均值。 例如,两组数的集合 {0, 5, 9, 14} 和 {5, 6, 8, 9} 其平均值都是 7 ,但第二个集合具有较小的标准差。 标准差可以当作不确定性的一种测量。例如在物理科学中,做重复性测量时,测量数值集合的标准差代表这些测量的精确度。当要决定测量值是否符合预测值,测量值的标准差占有决定性重要角色:如果测量平均值与预测值相差太远(同时与标准差数值做比较),则认为测量值与预测值互相矛盾。这很容易理解,因为值都落在一定数值范围之外,可以合理推论预测值是否正确。 [编辑] 标准差的简易计算公式 假设有一组数值 x1, ..., xN (皆为实数),其平均值为: 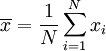 此组数值的标准差为: 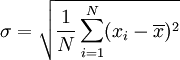 一个较快求解的方式为: 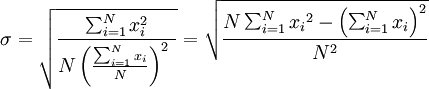 一随机变量X 的标准差定义为: 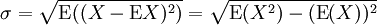 须注意并非所有随机变量都具有标准差,因为有些随机变量不存在期望值。 如果随机变量 X 为 x1,...,xN 具有相同机率,则可用上述公式计算标准差。从一大组数值当中取出一样本数值组合 x1,...,xn ,常定义其样本标准差: 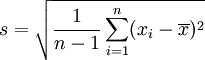 [编辑] 范例 这里示范如何计算一组数的标准差。例如一群孩童年龄的数值为 { 5, 6, 8, 9 } : 第一步,计算平均值 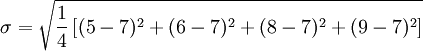 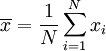 n = 4 (因为集合里有 4 个数),分别设为: 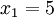 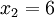 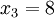 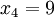  用 4 取代 N 用 4 取代 N 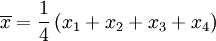 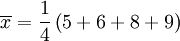 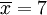 此为平均值。 此为平均值。 第二步,计算标准差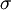 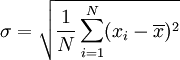 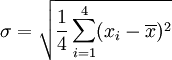 用 4 取代 N 用 4 取代 N 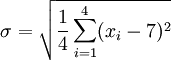 用 7 取代 用 7 取代 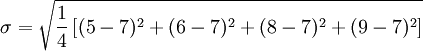 ![\sigma = \sqrt{\frac{1}{4} \left [ (x_1 - 7)^2 + (x_2 - 7)^2 + (x_3 - 7)^2 + (x_4 - 7)^2 \right ] }](/picture/bkimg/ch_90/90_6_85_20.jpg) ![\sigma = \sqrt{\frac{1}{4} \left [ (5 - 7)^2 + (6 - 7)^2 + (8 - 7)^2 + (9 - 7)^2 \right ] }](/picture/bkimg/ch_90/90_6_85_5.jpg) 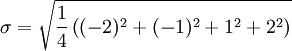 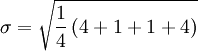 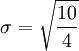 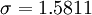 [编辑] 标准差与平均值之间的关系 一组数据的平均值及标准差常常同时做为参考的依据。在直觉上,如果数值的中心以平均值来考虑,则标准差为统计分布之一"自然"的测量。较确切的叙述为:假设 x1, ..., xn 为实数,定义其公式  使用微积分,不难算出 σ(r) 在下面情况下具有唯一最小值: 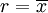
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|









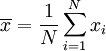
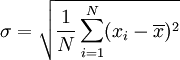
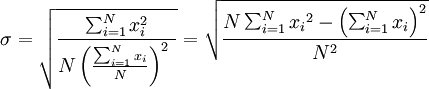
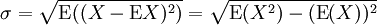
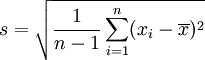
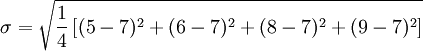
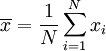
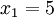
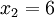
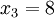
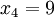
 用 4 取代 N
用 4 取代 N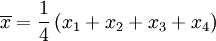
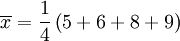
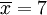 此为平均值。
此为平均值。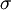
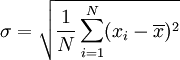
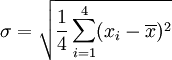 用 4 取代 N
用 4 取代 N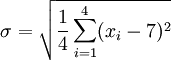 用 7 取代
用 7 取代 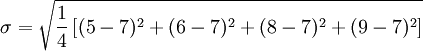
![\sigma = \sqrt{\frac{1}{4} \left [ (x_1 - 7)^2 + (x_2 - 7)^2 + (x_3 - 7)^2 + (x_4 - 7)^2 \right ] }](/picture/bkimg/ch_90/90_6_85_20.jpg)
![\sigma = \sqrt{\frac{1}{4} \left [ (5 - 7)^2 + (6 - 7)^2 + (8 - 7)^2 + (9 - 7)^2 \right ] }](/picture/bkimg/ch_90/90_6_85_5.jpg)