1) steering pose


转向位姿
1.
The manipulator\'s acceleration and load quality have influence on steering pose of the forklift robot in its operation.
执行器的加速度和负载质量会影响叉车式机器人的转向位姿。
2) Pose of steering wheel


转向轮姿态
3) pose
[英][pəʊz] [美][poz]


位姿
1.
Three-point Method on Pose Measurement of Microstructure Stage Based on Machine Vision;


基于机器视觉的微工作台位姿三点法测量
2.
Novel pose measurement for agricultural vehicle guided by machine vision;


视觉导航农用车辆相对位姿测量新方法(英文)
3.
Analysis and Synthesis of Robot Pose Errors;


机器人位姿误差的分析与综合
4) Position and pose


位姿
1.
By means of the precise position and pose measured by visual system,the nonlinear kinematics anti-calculated should be substituted utilizing the Euler angles.
在视觉提供手爪的精确位姿条件下,利用欧拉角特性代替非线性的运动学反解计算,不仅简化了控制环节、提高了控制鲁棒性,同时也符合人类视觉操作的工作模式。
5) Position and orientation


位姿
1.
This paper describes the theory and implementation of a system that determines position and orientation of a parallel 6-DOF electrohydraulic servo platform, or a 6-DOF platform for short, in a reference coordinate system called the world coordinate system.
位姿是六自由度平台的一项重要性能指标 ,其全方位、全行程的动态精确检测 ,对于六自由度平台的精确控制及广泛应用具有十分重要的意义。
2.
This thesis mainly study the spreadbands drive parallel robot\'s workspace when bearing a certain amount of load and the buckling critical load that varies with the strip\'s structure and size, the moving platform\'s position and orientation.
本文主要研究了钢带并联机器人的失稳力随钢带结构、尺寸、钢带并联机器人位姿的变化规律和一定负载时的工作空间,研究工作包括:1。
6) position and posture


位姿
1.
The drawing method which can reduce the work to solve the equation is applied in solving the posture, the description of position and posture is very clear.
针对作两圆柱相贯线运动的机器人提出了一种有效的轨迹规划方法 ;用作图法完成了空间位姿的描述 ,减少了因解代数方程而带来的大量计算 ,使位姿的描述形象、明了 ;利用运动学方程完成笛卡尔坐标空间与关节坐标空间的相互转换 ;利用变角速度实现稳定的运动效果 ;在比较多种插值函数的基础上 ,对关节变量作了多项式插值 ;提出了计算算法及具体情况的解决方法 ,并作了综合分
2.
The methodology for calculation of industrial robot moving position and posture during its visual navigation and motion is presented,the relations of car and camera coordinates are discussed, and the transform matrix between two coordinate systems is derived.
介绍了工业机器人视觉导航中的运动车体位姿的计算方法 ,论述了车体坐标系和摄像机坐标系之间的变化关系 ,推导出了车体坐标系和摄像机坐标系之间的变换矩阵 ,并进行了实验 。
补充资料:交通运轮机械:车辆转向机构
用以控制各类轮式或履带式车辆的行驶方向的机构。轮式车辆的转向机构一般由转向机和转向杆系组成。采用动力转向时﹐还需要装备液压泵﹑操纵阀﹑作用缸和贮油罐﹐合称液压助力机构。
转向方式 轮式车辆的转向机构有轴转向﹑轮转向和铰接式转向 3类。早期的汽车和现代某些全挂车上采用轴转向。这种转向方式虽然几个车轮轴线在转向时交于一点﹐但转向时车轮前后位移过大﹐转向阻力大﹐轮胎磨耗大﹐所以不适用于高速行驶的车辆。在艾克曼于19世纪末发明梯形连杆转向机构后﹐汽车已普遍采用轮转向。为使结构简单﹐大多数车辆用前轮转向。转向时尽量使全部车轮绕同一个瞬时转向中心作圆周运动
(见图 轮转向运动图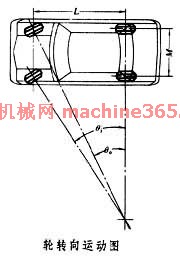 )﹐以保证转向轮不发生滑移。由于各转向轮的转弯半径不同﹐其转角也不相同﹐内外转向轮的转角之间应保持下列关系
)﹐以保证转向轮不发生滑移。由于各转向轮的转弯半径不同﹐其转角也不相同﹐内外转向轮的转角之间应保持下列关系

式中为外转向角﹐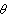 i为内转向角﹐L 为轴距﹐
i为内转向角﹐L 为轴距﹐ 为轮距。梯形连杆机构能近似地满足这一关系。与车辆悬架配合﹐连接车轮和转向机的转向杆系有整体式和各种分段式。杆系一般布置在前轴之后﹐有时也布置在前轴之前。有的车辆因前轴为驱动轴或载荷较重或对机动性有特殊要求而用后轮转向。等轴距3轴﹑4轴或多轴车辆也有用前﹑后轮同时转向的(有的4轮驱动拖拉机采用全轮转向﹐可根据情况随时以前轮﹑后轮转向或4轮同时转向﹐甚至可以蟹行)。
为轮距。梯形连杆机构能近似地满足这一关系。与车辆悬架配合﹐连接车轮和转向机的转向杆系有整体式和各种分段式。杆系一般布置在前轴之后﹐有时也布置在前轴之前。有的车辆因前轴为驱动轴或载荷较重或对机动性有特殊要求而用后轮转向。等轴距3轴﹑4轴或多轴车辆也有用前﹑后轮同时转向的(有的4轮驱动拖拉机采用全轮转向﹐可根据情况随时以前轮﹑后轮转向或4轮同时转向﹐甚至可以蟹行)。
铰接式车辆的转向动作类似于轴转向﹐即车轮无转向动作而用液压或气压机构推动车辆的铰接部分使车辆转向。铰接式车辆大都是行驶于松软地面的越野车辆或工程机械﹐车速也较低﹐可以用这种转向方式。
履带式车辆只要使左右侧履带的速度不同即可转向﹐因此﹐一侧制动就可以在原地转向。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条