2) methods of torsional-balance


扭力秤法
3) torsional period


扭转周期
1.
According to the design of Xinyuan building, the problem, which the first structural period is torsional period in frame-corewall structure, has been solved through the adjustment of thickness of shear wall and the location of calculation holes.
针对信远大厦工程设计出现的问题 ,通过调整剪力墙厚度、开洞位置等手段解决了内筒外框结构第一周期为扭转周期这一不利影响 ;分析了温度应力对超长楼板的影响 ,并提出处理意见 ;从计算及构造上解决了楼板开洞过大问题。
4) oscillatory cycle


扭摆周期
5) torsion balance


扭秤
1.
It is significant for equivalence principle test for extended rotating bodies with a torsion balance to measure the internal friction torque of a gyroscope.
利用角动量定理对实验采用的电磁驱动机械陀螺的内部摩擦力矩进行测量,分析了这一摩擦力矩对宏观旋转物体等效原理扭秤方案检验的影响,并就此提出了几项改善措施。
2.
The theoretical background of equivalence principle is briefly given,and the experimental tests of the equivalence principle is discussed in detail,via free-fall method and torsion balance.
本文简要阐述等效原理的研究背景,通过对自由落体法和扭秤法检验等效原理的详细介绍来具体讨论等效原理的实验检验。
3.
This paper points out some imprecise statements on invention of torsion balance andgives a detailed explaination to the contribution to physical development by the invention andapplication of rorsion balance.
本文指出了关于扭秤发明的一些不确切的说法,全面论述了它的发明应用对物理学发展的重要贡献。
6) Torsion pendulum


扭秤
1.
Research on the Gravity Gradient in the Weak Equivalence Principle Based on the Torsion Pendulum;
扭秤弱等效原理实验中的引力梯度效应研究
补充资料:扭秤
| 扭秤 torsion balance 测量重力位二次导数的仪器。早在1791年H.卡文迪什用来测量重力常数的仪器就是扭秤的一种形式。1881年匈牙利物理学家厄缶为测定物质的引力质量发展了扭秤,1915年开始用于重力勘探。 扭秤的基本原理是在一根刚性杆的两端连结相距一定高度的两个相同质量的重物,通过秤杆的中心用一扭丝悬挂起来。秤杆可以绕扭丝自由转动,当重力场不均匀时,两个质量所受的重力不平行。这个方向上的微小差别在两个质量上引起小的水平分力,并产生一个力矩使悬挂系统绕扭丝转动,直到与扭丝的扭矩平衡为止。扭丝上的小镜将光线反射到记录相板上。当扭丝转动时,光线在相板上移动的距离标志着扭转角的大小。平衡位置与扭秤常数和重力位二次导数有关。在一个测点上至少观测3个方位,确定4个二次导数值,测量精度一般达几厄缶。 扭秤的测量结果用矢量图表示,用一短线表示曲率,矢量方向 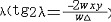 相应于最小曲率平面的方位,矢量长度 相应于最小曲率平面的方位,矢量长度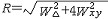 表示等位面曲率差大小 。在短线中心以箭头画出总梯度,指向重力增加的方向。 表示等位面曲率差大小 。在短线中心以箭头画出总梯度,指向重力增加的方向。扭秤的灵敏度很高并可测多个参数,但由于测量时间长,仪器笨重,受地形影响严重,几乎已完全被重力仪所取代,但在重力测量史上它曾起过重要作用。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条