|
|
|
说明:双击或选中下面任意单词,将显示该词的音标、读音、翻译等;选中中文或多个词,将显示翻译。
|
|
|
1) On the Consideration

论对价
2) consideration theory

对价理论
3) Discussion of the Consideration in Negotiable Instrument

论票据对价
4) relativity of music value

音乐价值相对论
1.
The article reviewed on the historical process of argument, sorted out the different ideas, and proposed the writer s opinions on the relativity of music value, criticism of post colonial, the musical view of people foremost and music foremost, as well as how to deal with the relationship between China and the West in the situation of the multicultural in the contemporary era.
本文在回顾论战的历史过程、对各家观点进行梳理的基础上,就论战中涉及到的“音乐价值相对论”、“后殖民”批评、人本与乐本的音乐观以及在当代世界文化多样性格局中如何看待和处理中西音乐关系等问题发表了作者的见解[本文(上)发表在《黄钟》2006年第二期上]。
2.
The article reviewed on the historical process of argument,sorted out the different ideas,and proposed the writer s opinions on the relativity of music value,criticism of post colonial,the musical view of people foremost and music foremost,as well as how to deal with the relationship between China and the West in the situation of the multicultural in the contemporary era.
本文在回顾论战的历史过程、对各家观点进行梳理的基础上,就论战中涉及到的“音乐价值相对论”、“后殖民”批评、人本与乐本的音乐观以及在当代世界文化多样性格局中如何看待和处理中西音乐关系等问题发表了作者的见解。
5) VSEPR

价层电子对互斥理论
1.
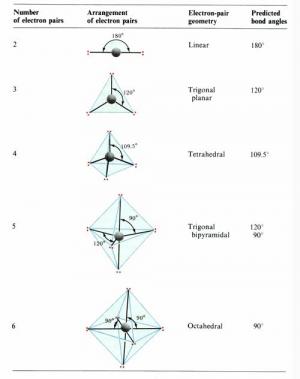
The VSEPR theory is mainly applied to predict the geometries of molecules and ions and it is surprisingly useful, but its rules appear somewhat arbitary and its deduction to the relation between VP and the geometry of the electron pairs is troublesome and hard to justify in a rigorous quantum-mechanical formulation, and it cannot expla.
在分子结构理论中,杂化轨道理论在多原子分子的空间构型被实验确定后,能够根据一定的假设给出合理的解释;价层电子对互斥理论主要用于预测分子或离子的空间构型,但其假设有些生硬、推理不够严密,对VP与电子对空间构型之间关系的推导比较繁琐,不易理解,也不能很好地解释一些多原子分子(如PF5、IF7等分子)中存在键长不等的现象。
6) valence-shell electron pair repulsion theory

价电子对互斥理论
补充资料:价层电子对互斥理论
一个分子的中心原子究竟采取哪种类型的轨道杂化,直接可以预测整个分子的空间构型。 杂化轨道理论成功地解释了部分共价分子杂化与空间构型关系,但是,仅用杂化轨道理论预测有时是难以确定的。1940年美国的sidgwick nv等人相继提出了价层电子对互斥理论(valence shell electron pair repulsion theory),简 称vsepr法,该法适用于主族元素间形成的abn型分子或离子。该理论认为,一个共价分子或离子中,中心原子a周围所配置的原子b(配位原子)的几何构型,主要决定于中心原子的价电子层中各电子对间的相互排斥作用。这些电子对在中心原子周围按尽可能互相远离的位置排布,以使彼此间的排斥能最小。所谓价层电子对,指的是形成σ键的电子对和孤对电子。孤对电子的存在,增加了电子对间的排斥力,影响了分子中的键角,会改变分子构型的基本类型。根据此理论,只要知道分子或离子中的中心原子上的价层电子对数,就能比较容易而准确地判断 abn 型共价分子或离子的空间构型。 价层电子对理论预测分子空间构型步骤为: 1.确定中心原子中价层电子对数 中心原子的价层电子数和配体所提供的共用电子数的总和除以2,即为中心原子的价层电子对数。 规定:(1)作为配体,卤素原子和h 原子提供1个电子,氧族元素的原子不提供电子;(2)作为中心原子,卤素原子按提供7个电子计算,氧族元素的原子按提供6个电子计算;(3)对于复杂离子,在计算价层电子对数时,还应加上负离子的电荷数或减去正离子的电荷数;(4)计算电子对数时,若剩余1个电子,亦当作 1对电子处理。(5) 双键、叁键等多重键作为1对电子看待。 2.判断分子的空间构型 根据中心原子的价层电子对数,从表9-4中找出相应的价层电子对构型后,再根据价层电子对中的孤对电子数,确定电子对的排布方式和分子的空间构型。 实例分析:试判断pcl5 离子的空间构型。 解:p离子的正电荷数为5,中心原子p有5个价电子,cl原子各提供1个电子,所以p原子的价层电子对数为(5+5)/2 = 5,其排布方式为三角双锥。因价层电子对中无孤对电子,所以pcl5 为三角双锥构型。 实例分析:试判断h2o分子的空间构型。 解 :o是h2o分子的中心原子,它有 6个价电子,与o化合的2个h原子各提供1个电子,所以o原子价层电子对数为(6+2)/2 = 4,其排布方式为 四面体,因价层电子对中有2对孤对电子,所以h2o分子的空间构型为v形。 表9-5 理想的价层电子对构型和分子构型 实例分析:判断hcho分子和hcn分子的空间构型 解分子中有1个c=o双键,看作1对成键电子,2个c-h单键为2对成键电子,c原子的价层电子对数为3,且无孤对电子,所以hcho分子的空间构型为平面三角形。 hcn分子的结构式为h—c≡n∶,含有1个c≡n叁键,看作1对成键电子,1个ch单键为1对成键电子,故c原子的价层电子对数为2,且无孤对电子,所以hcn分子的空间构型为直线。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|