1) theory of visceral basis of affections


脏腑说
2) theory of zang-fu organs


脏腑学说
3) Theory of visceral


中医脏腑学说
4) theories of zangfu and meridians


脏腑经络学说
1.
The theories of primordial-qi,yin-yang and five phases are the theoretical basis for Chinese medicine and the concept of harmony has a direct manifestation in theories of zangfu and meridians.
元气论和阴阳五行学说都是中医学的理论基础,"和谐观"在脏腑经络学说中有直接表现。
5) entrails
[英]['entreɪlz] [美]['ɛntrəlz]


脏腑
1.
The article summarized the vital movement periodicity in Qi and blood, entrails and color and pulses, and expounded the effect of vital movement periodicity to body and raised the life-cultivation and therapeutic principle of accustomization nature and concordance period.
《内经》从多方面论述了生命运动的周期性,包括日周期、十日周期、月周期、年周期等,笔者以气血、脏腑、色脉为纲对其进行总结,阐述生命运动周期性对人体的影响,凸显生命运动周期的重要性,并提出顺应自然、协调周期的养生、治疗原则。
2.
The treatment combined ocular acupuncture therapy with the relation of entrails and meridian could investigate senile dementia coursed by the variation of organ and meridian.
结合眼针疗法与中医脏腑和经络的关系,可以更深入地研究由于部分脏器和经络发生变化而引发的老年性痴呆这一病症。
6) internal organs


脏腑
1.
Progress of study on relative effect between meridians and internal organs;


经脉(穴)与脏腑相关效应规律的研究进展
补充资料:脏腑
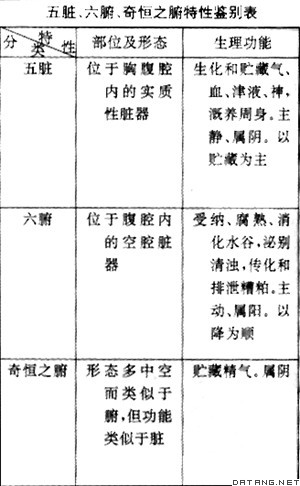
| 脏腑 中医学对人体内脏的总称。从部位、形态及生理功能上可划分为五脏、六腑和奇恒之腑三类。五脏,即心、肝、脾、肺、肾,有时加上心包,又称六脏。六腑,即胆、胃、大肠、小肠、三焦、膀胱。奇恒之腑,即脑、髓、骨、脉、胆、女子胞。一般而言,五脏是位于胸腹腔内的实质性脏器,主要生理功能是生化和贮藏精、气、血、津液、神;六腑,是位于腹腔内的空腔器官,主要生理功能是受纳和消化饮食,泌别清浊,排泄废物;奇恒之腑的形态类似于腑,但功能却类似于脏。脏腑之间通过经络相互络属,构成密切的表里关系,它们在生理功能上相互依存,密不可分;在病理变化上相互影响。
|
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条