1) Inflation
[英][ɪn'fleɪʃn] [美][ɪn'fleʃən]


通货膨胀;通胀
2) currency inflation


通货膨胀
1.
Since 1993, our country has been carrying out macroscopic adjustment and control, and the rate of unemployment has been rising steadily year by year, the rate of currency inflation has experienced the the course of climbing high firstly, and then falling backward steadily.
1993年国家实行宏观调控以来,我国失业率逐年上升,通货膨胀率则经历了先攀升后稳步回落的过程。
2.
This paper points out the defect of traditional curing currency inflation, gives an interest---money model curing currency inflation and calculates its effect.
指出了我国传统的治理通货膨胀方法的缺陷,提出了使用利率──货币价格治理通货膨胀的数学模型,并具体测算了其作用效应的大小。
3.
In recent times,the growth of the CPI in China has exceeded 5% for 8 months;this puts the government under a great stress of currency inflation and consumers feel the stress too.
我国居民消费价格指数(CPI)的涨幅已连续8个月超过5%,居民对此已有切身感受,政府也面临通胀压力,但还不能就此认为通货膨胀已经来临。
3) Inflation
[英][ɪn'fleɪʃn] [美][ɪn'fleʃən]


通货膨胀
1.
Empirical study of the relationship between inflation and housing prices;


通货膨胀与商品住宅价格关系的实证分析
2.
An inventory model with inflation induced demand and partial backlogging;


通货膨胀影响需求且短缺量部分补足的库存模型(英文)
4) disinflation
[英][,disin'fleiʃən] [美][,dɪsɪn'fleʃən]


滞胀;反通货膨胀
5) inflation rate


通货膨胀率
1.
The empirical analysis on consumer s risk expectation and the inflation rate;


消费者风险预期与通货膨胀率关系的实证分析
2.
Regime division and regime switching in the process of inflation rates of China's economy


我国通货膨胀率过程区制状态划分与转移分析
3.
This paper examines the relationship between inflation rate and economic growth rate in China by using the methods of regression and coefficient test.
通过回归和系数检验实证,分析了我国通货膨胀率与经济增长率之间的关系。
6) inflation
[英][ɪn'fleɪʃn] [美][ɪn'fleʃən]


通货膨胀率
1.
The relationship between stock returns and inflation can be either negative or positive.


股票收益率和通货膨胀率之间既可以正相关,也可以负相关。
2.
By studying the relationship between stock real returns and inflation, we could find the correlation between stock market volatility and macroeconomic conditions.
我们检验发现,通货膨胀率的波动能够影响股票实际收益率的变化,这说明价格水平变化不仅影响消费品之间的替代,也影响投资品之间的替代。
补充资料:通货膨胀
| 通货膨胀 inflation 纸币的发行量超过商品流通中所需要的货币量而引起的货币贬值、物价上涨的状况。通货膨胀是纸币流通条件下特有的一种社会经济现象。 原因 纸币是一种纯粹的货币符号,没有价值,只是代替金属货币执行流通手段的职能;纸币的发行量应以流通中需要的金属货币量为限度,如果纸币的发行量超过了流通中需要的金属货币量,纸币就会贬值,物价就要上涨。因此,纸币发行量过多引起的货币贬值、物价上涨,是造成通货膨胀的直接原因。 特点 ①纸币因发行过多而急剧贬值。在流通中所需的金属货币量已定的情况下,纸币发行越多,单位纸币所能代表的金属货币量就越少,纸币的贬值程度就越大。纸币的贬值程度即纸币贬值率的计算公式是:纸币贬值率=(1-  )×100%例如,一个国家某个时期流通中所需要的金属货币量是100亿元,实际发行的纸币是200亿元,纸币贬值率 )×100%例如,一个国家某个时期流通中所需要的金属货币量是100亿元,实际发行的纸币是200亿元,纸币贬值率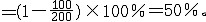
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|
|
| ©2011 dictall.com | |