1) heat radiation


热辐射,辐射换热
2) radiative heat transfer


辐射换热
1.
Analysis and calculation on the characteristics for radiative heat transfer of flue gas with high carbon dioxide concentration
高浓度二氧化碳烟气辐射换热特性分析与计算
2.
Finite element diffusion-synthetic acceleration for radiative heat transfer in participating medium
介质辐射换热有限元法的扩散综合加速算法
3.
An improved Monte Carlo ray tracing approach has been developed, which combines the space division and the directional solidification features in production of turbine blades, the view factor calculation which is a key step and takes too much time in traditional radiative heat transfer approaches can be avoided so that the time consuming is greatly shortened.
提出改进型Monte Carlo射线追踪法进行辐射换热计算,通过子空间的划分,并结合定向凝固的特点回避了传统辐射换热计算中角系数的直接计算,节省了计算时间。
3) radiation heat transfer


辐射换热
1.
Discussion of convection heat transfer and radiation heat transfer of annealing coil;


退火钢卷辐射换热及对流换热的讨论
2.
Engineering Application and Numerical Analysis of Radiation Heat Transfer in Complex Geometry;
复杂结构辐射换热工程应用及数值计算
3.
In view of the characteristic of VGF (Vertical Gradient Freeze) technique, the radiation heat transfer model of the VGF furnace is established, and detailed simulations of the radiation heat transfer in the VGF system using a finite difference method under the varying temperature condition is presented.
根据VGF结晶技术的特点,建立了结晶炉内的辐射换热模型,并利用有限差分法对变温条件下砷化镓晶体表面的辐射换热进行了数值求解。
4) radiant heat transfer


辐射换热
1.
Coupling with heat conduction differential equation of the workpiece,the mathematical model of heat transfer is established in the forge furnace by zone method for making the model of radiant heat transfer .
分析了锻造炉内的热工特性,采用区域法建立炉内辐射换热数学模型,并与炉内工件的导热方程相耦合,建立炉内传热数学模型;通过求解数学模型分析了不同的两工件间距离对被加热工件温度分布的影响。
2.
Coupling with heat conduction differential equations of the thin slab and the furnace lining,the mathematical model of heat transfer is established in the long one dimension furnace by using zone method for making the model of radiant heat transfer.
通过分析CSP工艺中直通式辊底加热炉的热工及结构特性 ,采用区域法建立炉内辐射换热数学模型 ,与加热炉内连铸坯及炉衬的一维导热方程相耦合 ,建立长一维直通式辊底加热炉炉内传热数学模型 通过对数学模型的求解 ,研究分析了不同的薄板坯移动速度及钢种对加热炉炉内温度分布的影
3.
Three dimensional radiant heat transfer is usually calculated even in the case of those with two dimensional characteristics.
辐射换热通常按三维方法计算。
5) radiative heat exchange


辐射换热
1.
The gas radiation network units under the general gas radiative conditions is established,and the calculating formula of radiative heat exchange guantity between gas and aroud wall is derived by radiation network units and network analysis.
建立了一般气体辐射条件下气体辐射网络单元 ,并由此用网络分析法导出了气体与围壁间的辐射换热量计算公式 ,结果与传统法导出的完全一样。
2.
This paper shows us the deficiency on finding the solution of radiative heat exchange problem in a flame hearth by radiation network unit advanced by Hu Chang Gou in the literature.
指出了用文献 [1]提出的辐射网络单元求解火焰炉膛内辐射换热问题的不足之处 ,提出了更具普遍性的新的辐射网络单元。
6) radiant heat exchange


辐射换热
1.
Analyses of radiant heat exchange in an enclosure with homogeneous scattering media;


均匀散射介质参与体系辐射换热分析
2.
Based on the calculation of radiant heat exchange with 2-D heat flux method in paper 1, a computer program has been developed in 3-D rectangular coordinate system for calculating the temperature profile on radiant heat transfer with the flux mathematical model in paper 2.
本文在文献〔1〕二维热流法计算辐射换热的基础上,运用文献〔2〕提出的热流数学模型,在三维直角坐标系下开发了用热流法计算高温炉内辐射换热的温度场分布的计算程序,用该程序可以计算一般情况下纯辐射作用时炉内的温度分布,通过计算得到了炉内的温度分布,为全面研究高温炉热状态提供了依据和前提条件,同时得出在一般简化计算中二维模型的可靠性结论。
3.
Accoording to the new heat flux method which is discussed in liberature 4, we developed a computer program containing heat flux equations and an energy equation in a two-dimensional rectangular coordinate system in this article, Using this program we calcu- lated the radiant heat exchange and obtained the temperature profile in a high-temperature furnace.
用该程序计算了高温炉内的辐射换热,得到了高温炉内的温度分布。
补充资料:热辐射
| 热辐射 thermal radiation 物体由于具有温度而辐射电磁波的现象。热量传递的3种方式之一。一切温度高于绝对零度的物体都能产生热辐射,温度愈高,辐射出的总能量就愈大,短波成分也愈多。热辐射的光谱是连续谱,波长覆盖范围理论上可从0直至∞,一般的热辐射主要靠波长较长的可见光和红外线。由于电磁波的传播无需任何介质,所以热辐射是在真空中唯一的传热方式。物体在向外辐射的同时,还吸收从其他物体辐射来的能量。物体辐射或吸收的能量与它的温度、表面积、黑度等因素有关。但是,在热平衡状态下,辐射体的光谱辐射出射度(见辐射度学和光度学)r(λ,T)与其光谱吸收比a(λ,T)的比值则只是辐射波长和温度的函数,而与辐射体本身性质无关,即 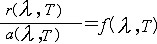 上述规律称为基尔霍夫辐射定律,由德国物理学家G.R.基尔霍夫于1859年建立。式中吸收比a 的定义是:被物体吸收的单位波长间隔内的辐射通量与入射到该物体的辐射通量之比。该定律表明,热辐射辐出度大的物体其吸收比也大,反之亦然。 上述规律称为基尔霍夫辐射定律,由德国物理学家G.R.基尔霍夫于1859年建立。式中吸收比a 的定义是:被物体吸收的单位波长间隔内的辐射通量与入射到该物体的辐射通量之比。该定律表明,热辐射辐出度大的物体其吸收比也大,反之亦然。黑体是一种特殊的辐射体,它对所有波长电磁辐射的吸收比恒为1。黑体在自然条件下并不存在,它只是一种理想化模型,但可用人工制作接近于黑体的模拟物。即在一封闭空腔壁上开一小孔,任何波长的光穿过小孔进入空腔后,在空腔内壁反复反射,重新从小孔穿出的机会极小,即使有机会从小孔穿出,由于经历了多次反射而损失了大部分能量 。对空腔外的观察者而言,小孔对任何波长电磁辐射的吸收比都接近于1,故可看作是黑体。将基尔霍夫辐射定律应用于黑体,有 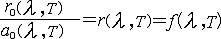 可见,基尔霍夫辐射定律中的函数f(λ,T)即黑体的光谱辐射出射度。 可见,基尔霍夫辐射定律中的函数f(λ,T)即黑体的光谱辐射出射度。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条