1) heavy timber construction


大木建筑
2) slow burning heavy timber construction


缓燃大木建筑
5) civil construction


土木建筑
1.
Application of carbon fiber composites in infrastructure and civil construction;


碳纤维复合材料在基础设施和土木建筑上的应用
2.
The thinking about the reform of graphics serial courses of civil construction;


关于土木建筑图学系列课程改革的思考
3.
In this paper the application of carbon fiber composites(CFC) in infrastructure and civil construction was introduced, including advantages of applying CFC, technologies for reinforcing and rehabilitation infrastructure and research and development plans as well as standards and codes for using CFC in infrastructure and civil constructio
本文介绍碳纤维复合材料在基础设施和土木建筑上的应用 ,包括在基础设施和土木建筑上采用复合材料的优点 ,用碳纤维复合材料修复补强技术与应用 ,碳纤维复合材料应用在基础设施和土木建筑的研究推广计划和复合材料在基础设施和土木建筑上应用的标准和法
6) Wooden Building


木构建筑
1.
This paper mainly discusses the culture inherriation of the wooden buildings and the feature of the traditional wooden buildings.
论述木构建筑的文化传承以及传统木构建筑的特征,即取材方便,适应性强,有较强的搞震性能,便于修缮、搬迁。
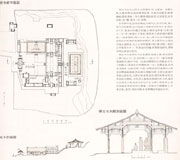
补充资料:最大的唐代木建筑-山西五台山佛光寺东大殿
最大的唐代木建筑-山西五台山佛光寺东大殿
五台山在唐代已是我国的佛教中心之一,建有许多佛寺。佛光寺位于台南豆村东北约五公里的佛光山腰,大殿建于唐大中十一年(公元857年),面阔七开间,进深八架椽,单檐四阿顶,虽然经过多次修葺,大体仍保持唐代原来面貌。
大殿建在低矮的砖台基上,平面柱网由内外二圈柱组成,这种形式在宋《营造法式》中称为“金厢斗底槽”。内外柱高相等,但柱径略有差别。柱身都是圆形直柱,仅上端略有卷杀。檐柱有侧脚及升起。阑额上无普拍枋。
大殿屋面坡度较平缓,举高约1/4.77。正脊及檐口都有升起曲线,屋面筒瓦虽是后代所铺,但鸱尾式样及叠瓦脊仍遵旧制。
柱高与开间的比例略呈方形,斗拱高度约为柱高的1/2。粗壮的柱身、宏大的斗拱再加上深远的出檐,都给人以雄健有力的感觉。
殿内的砖砌佛座和塑造佛像,都是唐代遗物。
佛光寺大殿是我国现存最大的唐代木建筑,已列入全国重点文物保护单位。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条