1) electron spin double resonance


电子自旋双共振
3) Electron spin resonance(ESR)


电子自旋共振
1.
Electron spin resonance(ESR)spectroscopy is one of the most effective technique for detection of ir- radiated food containing bone.
电子自旋共振(Electron spin resonance,ESR)波谱测定是检测含骨类食品自由基的有效方法之一。
2.
The production of ·OH radicals was investigated by using the electron spin resonance(ESR) method with 5,5-dimethyl-1-1pyrroline-1-oxide(DMPO) as spin trap reagent.
利用电子自旋共振-自旋捕集技术(ESR)研究了不同条件下Fenton和类Fenton反应中羟基自由基的变化规律。
3.
Electron spin resonance(ESR)technique was used to measure the reactive oxygen species(ROS)in lung tissue,meanwhile,the malondialdehyde(MDA)contents,superoxide dismutase(SOD)activity in plasma,and the lung dry weight,lung wet weight,lung coefficient and pathological examination on lung were performed too.
方法经股静脉注射油酸复制大鼠ARDS模型,应用电子自旋共振(ESR)技术观察大鼠肺内活性氧(ROS)自由基的生成情况,同时检测血浆丙二醛(MDA)含量和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性的变化,进行肺湿干重、肺系数测定及肺组织病理学检查,并与使用丹参组大鼠结果进行比较。
5) electron spin resonance


电子自旋共振
1.
Accurate measurement of g factor in electron spin resonance experiment;


电子自旋共振实验g因子的准确测量方法
2.
Based on the free radical reaction mechanism of spontaneous combustion of coal,the parameters of coal free radicals,including Lande factor,concentration,line width and line height were measured using an electron spin resonance(ESR) spectrograph during the processes of being crushed and oxidated at low temperature.
基于煤炭自燃的自由基作用机理,采用电子自旋共振(ESR)测谱仪,测定煤体在破碎和低温氧化过程中的自由基朗德因子,浓度,线宽和线高。
3.
Electron spin resonance (ESR) method was used for studying radicals generated in low and high density polyethylene (LDPE and HDPE) by gamma ray irradiation.
研究了几种类型的聚乙烯膜在不同辐照气氛下生成的自由基的电子自旋共振(ESR)谱。
6) ESR


电子自旋共振
1.
ESR STUDIES OF RADIOPROTECTION MECHANISM ON DNA BY SINAPIC ACID AND ITS DERIVATIVE;


芥子酸及其衍生物辐射保护DNA的电子自旋共振研究(英文)
2.
STUDY ON THE HEAT STABILITY OF HEAT TRANSFER OILS WITH ELECTRON SPIN RESONANCE(ESR);


用电子自旋共振研究导热油的热稳定性
3.
ESR Studies on 2-Methyl-3-Acetyl Quinoxaline N, N-Dioxide and Its Cyclodextrin Inclusion Compounds;
MAQO和它的环糊精包结物的电子自旋共振研究
补充资料:电子自旋
| 电子自旋 electron,spin of 电子的基本性质之一。电子内禀运动或电子内禀运动量子数的简称。1925年G.E.乌伦贝克和S.A.古兹密特受到泡利不相容原理的启发,分析原子光谱的一些实验结果,提出电子具有内禀运动——自旋,并且有与电子自旋相联系的自旋磁矩。由此可以解释原子光谱的精细结构及反常塞曼效应 。电子的自旋角动量为 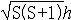 ,式中电子自旋S= 1/2。1928年P.A.M.狄拉克提出电子的相对论波动方程,方程中自然地包括了电子自旋和自旋磁矩。电子自旋是量子效应,不能作经典的理解,如果把电子自旋看成绕轴的旋转,则得出与相对论矛盾的结果。 ,式中电子自旋S= 1/2。1928年P.A.M.狄拉克提出电子的相对论波动方程,方程中自然地包括了电子自旋和自旋磁矩。电子自旋是量子效应,不能作经典的理解,如果把电子自旋看成绕轴的旋转,则得出与相对论矛盾的结果。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条