1) minimal propositional calculus


极小命题演算
2) propositional calculus


命题演算
1.
To meet the application needs of the incomplete information database,based on original connectives ∧,∨,→, and μ,a new three-valued logic propositional calculus system M.
构造了一种新的三值逻辑命题演算系统M PM和三值逻辑谓词演算系统M FM,证明了其可靠性和完备性,并给出了在查询优化方面的应用。
2.
Methods At first,through the study of the common characteris ties of fuzzy proposi- tional calculus systems,a reasoning operator is obtained on the powerset of fomula set which is satisfied by general fuzzy propositional calculus system;Secondly,with the aid of the thought of cstablishing topological space with to- pological closure operator,the theory of reasoning closure space i.
方法通过对命题演算系统的共同特征的研究,在公式集的幂集格上得到了一般命题演算系统共同满足的一个推理闭包算子,再借助通过拓扑闭包算子建立拓扑空间的思想提出了推理闭包空间理论。
3.
The formal deductive system L * for fuzzy propositional calculus and the revised Kleene logic systems ,W,W k , that are relevant to the former in semantics, has been studied, both of them are first proposed by professor Guo jun Wang.
研究了王国俊教授建立的模糊命题演算的形式演绎系统 L*以及在语义上相关的修正的 Kleene逻辑系统 W,W,Wk,给出了 L*系统的一种改进系统 L*0 ,并证明了二者之间的等价性 ,为形式演绎系统 L* 的研究和应用提供了一个有益的途
3) sentential calculus


命题演算
1.
The authors give a brief introduction to Hilbert s type intuitionistic system of first order sentential calculus,and prove some theorems of this system by logical deduction method.
简要介绍了一阶命题演算的希尔伯特型直觉主义系统 ,运用逻辑演绎的方法证明了此系统的一些定理 ,其目的在于加深对直觉主义系统中概念的理解 ,便于对此系统的进一步研究及应用 。
2.
Two intuitionistic systems of firstorder sentential calculus, Hilbert s type(HSI) and natural deduction type(NDSI), were introduced.
介绍了一阶命题演算的两个直觉主义系统 :希尔伯特型 (HSI)及自然演绎型 (NDSI) ,并证明了这两个系统的等价性 ,揭示了直觉主义逻辑的内涵及与其他非经典逻辑的关
4) propositional logic calculation


命题逻辑演算
1.
This paper introduces a method for propositional logic calculation.


介绍了命题逻辑演算方法。
5) Propositional calculus system


命题演算系统
1.
MP~M is a 3-valued logic propositional calculus system which is based on the medium logic system,and it is used to deal with the incomplete information in the database.
MP~M系统是在中介逻辑系统的基础上建立起来的,用于处理数据库中不完全信息的三值逻辑命题演算系统。
6) Fuzzy Propositional Calculus


模糊命题演算
1.
The formal deductive system L * for fuzzy propositional calculus and the revised Kleene logic system 、W、W k, that are relevant to the former in semantics, have been studied, both of which are first proposed by Professor Guo jun Wang.
研究了模糊命题演算的形式演绎系统L 以及在语义上相关的修正的Kleene逻辑系统 W ,W ,Wk 和R0 代数 ,讨论了算子 :F(S)×F(S)→F(S)的一些基本性质 ,给出了L 系统中的模糊演绎定理 。
补充资料:命题演算
| 命题演算 propositional calculus 一种最简单的逻辑演算。又称命题逻辑。命题演算中组成命题的最基本的成分是简单命题,可以回答"真"或"假"的一个陈述叫命题。例如"今天下雨"就是一个命题,而且是不再包含更小命题的所谓简单命题。简单命题可以联结成复合命题,命题演算中常用符号 p,q,r, …表示命题变元。命题变元可以代表任意一个简单命题,也可以代表任意一个命题。命题联结符号有:否定连词“  ”表示“非” ,合取连词“∧”表示“并且”,析取连词“∨”表示“或者”,蕴涵连词“ ”表示“非” ,合取连词“∧”表示“并且”,析取连词“∨”表示“或者”,蕴涵连词“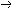 ”表示“如果…那么…”,等价连词“«”表示“当且仅当”。用命题变元和命题连词按一定方式联结就可以组成命题公式,例如用p表示“今天下雨”,q表示“有客人来”,r表示“去商店” 。 则一个命题公式 ”表示“如果…那么…”,等价连词“«”表示“当且仅当”。用命题变元和命题连词按一定方式联结就可以组成命题公式,例如用p表示“今天下雨”,q表示“有客人来”,r表示“去商店” 。 则一个命题公式 (p∧q) (p∧q)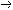 r表示“如果今天不下雨且有客人来那么就去商店”。一个命题公式中的每个命题变元都取定真假值时,这个公式的真假值也就确定了。因此,一个命题公式也就是一个真值函数。命题公式的真假值的取法可以列表给出,这种表叫做真值表。 r表示“如果今天不下雨且有客人来那么就去商店”。一个命题公式中的每个命题变元都取定真假值时,这个公式的真假值也就确定了。因此,一个命题公式也就是一个真值函数。命题公式的真假值的取法可以列表给出,这种表叫做真值表。不论命题变元取什么值,命题公式都取真值,这样的公式叫做恒真式,也叫重言式,不论命题变元怎么取值,两个命题公式A,B的取值永远相同,就称 A ,B 逻辑等价。记作A  B。实际上,A B。实际上,A B当且仅当A B当且仅当A B是恒真式,一些基本的等价式,例如 B是恒真式,一些基本的等价式,例如  p p p , p , (p∧q) (p∧q)  p∨ p∨ q ,(p q ,(p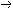 q) q)  p∨q,( p∨q,( p p  q) q) q q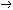 p,都可以用作命题公式等价变换的代数规则。这些规则可以把任何一个命题公式变换成与之等价的有标准形式的命题公式。这种标准形公式反映出一定的性质,取值的规律。 p,都可以用作命题公式等价变换的代数规则。这些规则可以把任何一个命题公式变换成与之等价的有标准形式的命题公式。这种标准形公式反映出一定的性质,取值的规律。命题演算还研究命题公式的自然推演,从一些条件出发,根据一定的法则可以推理出结论,给定命题变元的取值,如果条件都真。则结论一定也真,常见的法则有: ①附加 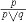 ,②化简 ,②化简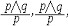 p 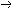 q qp  q③假言推理 q③假言推理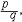 ,④拒取式 ,④拒取式 ⑤析取三段论式 ⑤析取三段论式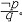 式中横线上的是条件,横线下的是结论。 式中横线上的是条件,横线下的是结论。p∨q 命题演算可以公理化。例如取下列命题公式作为公理: A×1 A 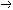 (B (B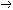 A)。 A)。A×2 (A 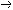 (B (B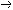 C)) C))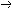 ((A ((A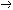 B) B)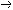 (A (A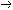 C))。 C))。A×3 (  A A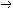  B) B)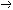 (B (B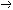 A)。推演法则:由A A)。推演法则:由A B和A得B,以上A,B,C 都代表任意一个命题公式。这是命题演算的一个完全的公理系统,在这个系统中,从公理出发按推演规则得到的都是恒真式,而且每一个恒真的命题公式都可以从公理出发按规则推演出来。命题演算中每一个公式都可以通过真值表来判定是否恒真式,因此可以判定是否可以从公理推演出来。 B和A得B,以上A,B,C 都代表任意一个命题公式。这是命题演算的一个完全的公理系统,在这个系统中,从公理出发按推演规则得到的都是恒真式,而且每一个恒真的命题公式都可以从公理出发按规则推演出来。命题演算中每一个公式都可以通过真值表来判定是否恒真式,因此可以判定是否可以从公理推演出来。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条