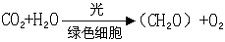
1) photosynthetic rate


光合作用率
2) Photosynthetic rate


光合作用速率
1.
The results showed that the root vigor and photosynthetic rate of flag leaf in hybrid wheat QCH-1 were higher than those of parent or the control especially during the senescence of root and flag leaf, the decreasing rate of either root vigor or photosynthetic rate was slower than that of parent or the control and the kernel filling rate was similar to the pat.
大田栽培条件下,对杂种小麦QCH-1与其亲本及对照的根系、旗叶与籽粒的生理特性及其产量构成进行了研究,结果表明:杂交小麦QCH-1的根系活力与旗叶光合作用速率表现超亲优势,特别是在根系与旗叶衰老过程中,根系活力与光合作用的衰减速率均显著低于其双亲;QCH-1的籽粒灌浆与高亲(父本Q98-7)相近,显著高于母本J17与对照L14;杂交种QCH-1的产量优势主要来源于穗粒数与千粒重的杂交优势,亩穗数的提高也起了一定的作用,而穗粒数的提高则是其穗长、可育小穗数具超亲优势而不育小穗数与低亲相近的结果。
2.
Seedling growth, ch1orophyll content, net photosynthetic rate and contents of soluble starch and soluble protein in leaves and roots of hybrid rice cv.
4mmol/LCa~(2+)能有效地促进杂交水稻幼苗的生长;提高叶片中的叶绿素含量和净光合作用速率,以及植株中的可溶性淀粉和蛋白质含量;降低叶片中的可溶性糖含量;增加植株的有效穗、结实率、千粒重和谷产量。
3) Photosynthesis rate


光合作用速率
1.
The results showed that after rice plants were infested by WBPH, photosynthesis rate and chlorophyll contents in leaves of susceptible rice varieties (TN1 and Shanyou 63) declined obviously compared to those of resistant rice variety (N22); activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) increased and of catalase(CAT) and peroxidase (POD) decreased in susceptible rice varieties, but activity.
结果表明 ,稻株受害后 ,感虫品种 (TN1和汕优 6 3)光合作用速率和叶绿素含量下降比抗虫品种 (N2 2 )明显 ;感虫品种超氧化物歧化酶 (SOD)活性增加 ,过氧化物酶 (POD)和过氧化氢酶 (CAT)活性下降 ,而抗虫品种 POD和 SOD均增加 ,CAT减少 ;感虫品种除丙氨酸含量下降外 ,其他氨基酸含量均上升 ,尤其是天门冬氨酸、苏氨酸、缬氨酸及蛋氨酸等含量增加很快 ,抗虫品种中天门冬氨酸、缬氨酸等含量增加也很快 ,但苏氨酸、蛋氨酸、丙氨酸的含量显著下
5) photosynthetic spectral efficiency


光合作用光谱效率
6) Light-saturated net photosynthetic rate


最大光合作用速率