1) magnetohydrodynamic approximation


磁流体动力学近似
2) hydrostatic approximation


流体静力学近似
3) hydrodynamic approximation


流体动力近似
4) Magnetohydrodynamics
[mæɡ,ni:tə,haidrəudai'næmiks]


磁流体动力学
1.
Stripping Voltammetric Detection of Cadmium in Small Volume Samples Based on the Magnetohydrodynamics;
磁流体动力学用于镉的溶出伏安检测
2.
On the other hand, the magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is always the focus in electrochemistry.
另外,电化学中的磁流体动力学效应也一直是人们所关注的焦点。
5) magnetic fluid dynamics


磁流体动力学
1.
Analysis of nugget formation process in resistance spot welding based on magnetic fluid dynamics theory;
电阻点焊熔核形成过程磁流体动力学分析
2.
Using magnetic fluid dynamics and thermodynamics theory,a study on the results of axial bearing pressure ability of rotation axis magnetic fluid static seals was introduced.
介绍了利用磁流体动力学、热力学理论,研究旋转轴磁流体静密封轴向承压能力的结果。
3.
A mathematic model was developed according to the theory of magnetic fluid dynamics.


以TIG焊接电弧为对象,依据磁流体动力学理论构建电弧的数学模型,运用ANSYS有限元分析软件对二维稳态下轴对称的、氩氮混合气体保护的TIG焊接电弧进行了数值分析,得到了30%N2+70%Ar(体积分数)混合气体保护下焊接电弧的温度场、速度场的形态分布特征。
6) MHD


磁流体动力学
1.
The dispersion equations involing the overstability of axisymmetric oscillation are derived by using MHD equations for the Perturbations.
从磁流体动力学方程组出发,用微扰法得出吸积盘径向振荡超稳定性的色散方程,并在7种情况下详细讨论了磁场、径向粘滞力和修正的α型粘滞对吸积盘不稳定性的影响。
2.
Starting from MHD,the dispersion equation of the instability of thin accertion disks with magnetic fields is derived from by using the perturbation method.
从磁流体动力学方程组出发,用微扰法得出含有能量方程和因果性修正α型粘滞吸积盘径向不稳定性色散方程。
3.
Starting from the magneto-hydrodynamic(MHD) equations,the computing formulas for magnetic anomaly induced by underwater vehicle s motion in geomagnetic field have been derived by use of order analysis.
本文从磁流体动力学基本方程出发,通过对各物理量进行量级分析,导出了水下航行体诱导海流在地磁场中引起磁异常的计算公式,给出了计算方法。
补充资料:流体静力学
| 流体静力学 hydrostatics 主要研究静止或相对静止流体中压力、密度、温度等参数的分布以及流体对器壁或物体的作用的流体力学分支。流体静力学的基本方程是欧拉静平衡方程,在直角坐标系中表示为 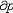 / /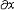 =ρX, =ρX,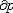 / /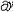 =ρY和 =ρY和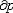 /¶z=ρZ,式中X、Y、Z为x、y、z3个坐标方向流体所受的单位质量力,p为压力,ρ为密度。通常情况,质量力仅为重力。液体一般是不可压缩流体,密度为常数,上述方程可积分为p=p0+γh,式中p0为液体表面压力,γ为重度,h为自表面铅垂向下的深度。但在有些情况如海洋深处,应考虑液体密度随压力而增大的影响,可导出p=p0-Eln( /¶z=ρZ,式中X、Y、Z为x、y、z3个坐标方向流体所受的单位质量力,p为压力,ρ为密度。通常情况,质量力仅为重力。液体一般是不可压缩流体,密度为常数,上述方程可积分为p=p0+γh,式中p0为液体表面压力,γ为重度,h为自表面铅垂向下的深度。但在有些情况如海洋深处,应考虑液体密度随压力而增大的影响,可导出p=p0-Eln(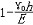 )。式中γ0为液表面重度,E为液体弹性模量,这里视为常数。气体(如大气情况)密度是变化的,若引入状态方程及给定的温度条件,可导出压力、密度等随高度变化的关系。在一般工程中使用的有限体积容器(如储气罐、气瓶)中压力可视为常数。沿浸入流体中的器壁或物体表面积分流体压力,可求出流体对其作用的总压力和压力中心(或铅垂方向为浮力和浮力中心),并可分析各种浮体、潜体的平衡和稳定性。流体静力学的研究在航空、航运、海洋工程、液压驱动装置、测压仪器及水坝、闸门、高压容器的设计方面有广泛应用。 )。式中γ0为液表面重度,E为液体弹性模量,这里视为常数。气体(如大气情况)密度是变化的,若引入状态方程及给定的温度条件,可导出压力、密度等随高度变化的关系。在一般工程中使用的有限体积容器(如储气罐、气瓶)中压力可视为常数。沿浸入流体中的器壁或物体表面积分流体压力,可求出流体对其作用的总压力和压力中心(或铅垂方向为浮力和浮力中心),并可分析各种浮体、潜体的平衡和稳定性。流体静力学的研究在航空、航运、海洋工程、液压驱动装置、测压仪器及水坝、闸门、高压容器的设计方面有广泛应用。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条