1) Metazoa
[英][,metə'zəuə] [美][,mɛtə'zoə]


无脊椎后生动物
2) collagens,invertebrate


无脊椎动物生胶
3) invertebrates


无脊椎动物
1.
Application of Sequences of nrDNA ITS to Molecular Systematics of Invertebrates;


核rDNA ITS区序列在无脊椎动物分子系统学研究中的应用
2.
Study on feeding habits and food relationship of main economic invertebrates in Taiwan Strait and its adjacent areas;
台湾海峡及邻近海域主要无脊椎动物食性特征及其食物关系研究
3.
Metallothionein diversity and its ecological service functions of invertebrates: an overview;
无脊椎动物金属硫蛋白(MTs)多样性及其生态服务功能
4) invertebrate
[英][ɪn'vɜ:tɪbrət] [美][ɪn'vɝtəbrət]


无脊椎动物
1.
Antibacterial activities of epiphytic bacteria from the surfaces of seaweeds and invertebrates against fouling bacteria isolated from a net cage in coastal sea in Dalian;
大连海区海藻和无脊椎动物附生细菌对养殖网笼污损细菌的拮抗活性
2.
Structure and diversity of invertebrate resources in the Yellow Sea;


黄海无脊椎动物资源结构及多样性
3.
Diversity of Aboveground Invertebrates in Dinghushan and Its Correlation with Litter;


鼎湖山地表无脊椎动物多样性及其与凋落物的关系
6) aquatic invertebrate zoology


水生无脊椎动物学
补充资料:后生动物
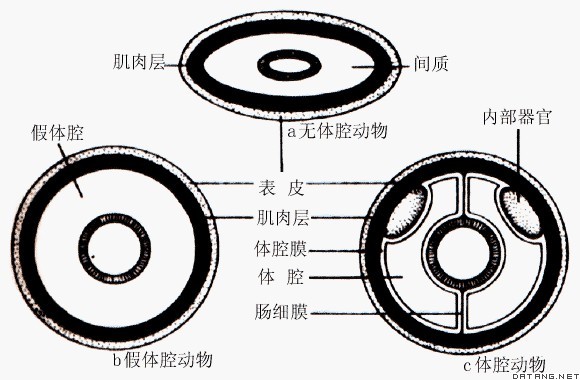
| 后生动物 Metazoa 原生动物门以外的所有多细胞动物门类的总称。包括多孔动物门、腔肠动物门、扁形动物门等(见无脊椎动物)。其特征是体躯由大量形态有分化、机能有分工的细胞构成;生殖细胞和营养细胞有明显的分化。 后生动物依体制形态的对称情况,可分为不对称动物、辐射对称动物和两侧对称动物;根据体腔的有无和结构可分为无体腔动物、假体腔动物和体腔动物。根据形态结构可分为实囊胚级水平、细胞水平、组织级水平和器官系统级水平。 古生物学、形态学和胚胎学的证据表明:多细胞的后生动物来自单细胞的原生动物。单细胞动物群体与多细胞动物之间并没有绝对的鸿沟。
|
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条