1) heterogeneous knowledge


异性知识
2) heterogeneity knowledge


异质性知识
1.
Transdisciplinary as an important form of the sci-tech innovation, from the perspective of activities, the nature of it is a coupling of heterogeneity knowledge, that is a coupling of sci-tech knowledge, theoretical methods, organizational and cultural knowledge.
跨学科作为科技创新的重要形式之一,从活动的角度看,其本质在于异质性知识的耦合,即不同学科科技知识、理论方法、组织知识以及文化知识的耦合;从团队的层面看,跨学科创新团队就是由若干异质Agent构成的"多Agent系统",并对应一个较大的知识空间。
4) variation knowledge


变异知识
1.
The approximate precision degree of variation rough sets and the properties of variation knowledge;
变异粗集近似精度与变异知识特性
2.
By using concept of variation rough sets,this paper presents the concept of filter degree of variation knowledge,the characters about granulation and filter of variation knowledge are also discussed.
利用变异知识的概念,提出了变异知识过滤度的概念,对变异知识[α/R]的颗粒特征、过滤特征进行了讨论。
3.
Presents the dependency concept of variation knowledge, advances transfer theorem of variation knowledge dependence, dependency finite extension theorem of variation knowledge and application of variation knowledge in knowledge mining.
给出变异知识的依赖概念 ,提出变异知识依赖的传递性定理 ,变异知识的依赖有限扩张定理 ,给出变异知识依赖在知识挖掘中的应
5) Isomeric knowledge


异构知识
1.
Based on this description, the process and integration of the isomeric knowledge is realized by building an .
在此基础上,通过建立基于异构知识的智能性管理决策系统的体系结构,来实现对异性知识的处理与集成,以达到使多种异性知识有机结合与集成利用。
2.
This papers discusses the integrated reason and application of isomeric knowledge based on management decision problems.
探讨了基于管理决策问题异构知识的集成推理及应用 ,在异构 (混合 )知识的面向对象表示的基础上 ,构建了一个在推理策略控制下 ,以元推理机为核心 ,四种功能推理机协调工作的推理系统。
3.
The concept of isomeric knowledge is introduced, the isomeric knowledge management based on XML is discussed, and a new architecture of isomeric knowledge-based IDSS is proposed.
介绍了异构知识的基本概念,探讨了基于 XML 的异构知识管理,进而提出基于异构知识的 IDSS 新结构框架。
6) knowledge alienation


知识异化
补充资料:板料冲压性能及测试--厚向异性系数
厚向异性系数r(也叫塑性应变比r,简称r值)是评定板料压缩类成形性能的一个重要参数。r值是板料试件单向拉伸试验中宽度应变εb与厚度应变εt之比,即
r=εb/εt
板料r值的大小,反映板平面方向与厚度方向应变能力的差异。r=1时,为各向同性;r≠1时,为各向异性。当r>1,说明板平面方向较厚度方向更容易变形,或者说板料不易变薄。r值与板料中晶粒的择优取向有关,本质上是属于板料各向异性的一个量度。
r值与冲压成形性能有密切的关系,尤其是与拉深成形性能直接相关。板料的r值大,拉深成形时,有利于凸缘的切向收缩变形和提高拉深件底部的承载能力。图1示出拉深时的应力状态,对照各向异性板料的屈服椭圆(图2)知;拉深件凸缘的应力状态类似于屈服椭圆第二象限区的情况,而底部的应力状态则类似于第一象限区的情况。r值增加,会同时使底部的强度增加和凸缘的变形抗力减小,这对拉深是非常有利的。大型覆盖件成形,基本上是一咱拉深与胀形相结合的复合成形,当拉深变形的成分占主导地位时,板材r值大,成形性能好。
板平面中最主要的三个方向是与轧制方向呈0°、45°和90°,相应地用r0、r45和r90表示。由于不同方向上测得的数值是变化的(图3),板料的厚向异性系数常用平均值r表示。

板平面内各向异性的差别用△r表示。
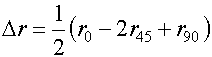
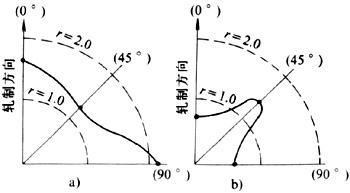
图1 拉深时的应力状态
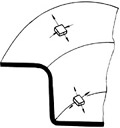

图3 r值在板平面内的变化
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条