2) interface anisotropy


界面各向异性
1.
Our theory holds for arbitrary external magnetic field,ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic interface exchange coupling and arbitrary easy axis(unaxial) volume and interface anisotropy.
结果发现,在三链系统中,有两种不同类型的光学界面自旋波,它们在不同界面各向异性条件下,均可存在0~2个自旋波
2.
Our theory holds for arbitrary external magnetic field,ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic interface exchange coupling,and arbitrary easy axis (unaxial) volume and interface anisotropy.
计入外磁场、铁磁和反铁磁层间耦合、体和界面各向异性后,研究了A-B-A 三链系统中的声学型界面自旋波及其存在条件。
3.
The model of a ferromagnetic bichain with arbitrary easy axsi unaxial volume and interface anisotropy,and ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic interface exchange coupling is investigated.
在考虑了外磁场、界面各向异性后,详细研究了铁磁和反铁磁层间耦合下自旋双链系统中的声-光型界面自旋波及其存在的充要条件。
4) capillary anisotropy


界面能各向异性
1.
Based on the adaptive finite element method,the phase-field model has been employed to simulate the free dendritic growth process governed by capillary anisotropy or kinetic anisotropy.
采用自适应有限元方法求解相场模型,分别对界面能各向异性和界面动力学各向异性条件下自由枝晶生长过程进行了模拟。
5) biphase interface


异相界面
1.
The valence electron structures of the biphase interfaces with V,Nb,Mo in α2 alloy were calculated with the empirical electron theory of solids and molecules and the improved Thomas-Fermi-Dirac theory.
利用合金相界面价电子结构信息-界面结合因子,即异相界面共价电子密度ρ、共价电子密度差Δρ,使界面电子密度保持连续的原子状态组数σ,分析了单相α2合金与多相α2合金相界面的价电子结构。
2.
The calculation model and method calculating the valence electron structures of biphase interface α2/γ of the lamellar structure in two-phase TiAl-alloy are advanced on the basis of the empirical electron theory of solids and molecules(EET) and the improved Thomas-Fermi-Dirac theory(TFD).
基于余氏固体与分子经验电子理论(EET)和程氏改进的 TFD 理论提出了计算双相 TiAl 合金层片状结构α2/γ界面电子结构的计算模型与方法,计算了含常用合金元素的单相 TiAl 合金与双相 TiAl 合金中的异相界面的电子结构,利用界面电子结构给出的信息?界面结合因子ρ, ?ρ, σ,以合金元素 Mn 为例初步分析讨论了双相 TiAl 合金层片状结构增加韧性的微观机制。
补充资料:板料冲压性能及测试--厚向异性系数
厚向异性系数r(也叫塑性应变比r,简称r值)是评定板料压缩类成形性能的一个重要参数。r值是板料试件单向拉伸试验中宽度应变εb与厚度应变εt之比,即
r=εb/εt
板料r值的大小,反映板平面方向与厚度方向应变能力的差异。r=1时,为各向同性;r≠1时,为各向异性。当r>1,说明板平面方向较厚度方向更容易变形,或者说板料不易变薄。r值与板料中晶粒的择优取向有关,本质上是属于板料各向异性的一个量度。
r值与冲压成形性能有密切的关系,尤其是与拉深成形性能直接相关。板料的r值大,拉深成形时,有利于凸缘的切向收缩变形和提高拉深件底部的承载能力。图1示出拉深时的应力状态,对照各向异性板料的屈服椭圆(图2)知;拉深件凸缘的应力状态类似于屈服椭圆第二象限区的情况,而底部的应力状态则类似于第一象限区的情况。r值增加,会同时使底部的强度增加和凸缘的变形抗力减小,这对拉深是非常有利的。大型覆盖件成形,基本上是一咱拉深与胀形相结合的复合成形,当拉深变形的成分占主导地位时,板材r值大,成形性能好。
板平面中最主要的三个方向是与轧制方向呈0°、45°和90°,相应地用r0、r45和r90表示。由于不同方向上测得的数值是变化的(图3),板料的厚向异性系数常用平均值r表示。

板平面内各向异性的差别用△r表示。
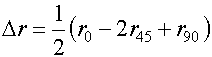
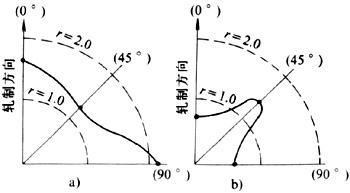
图1 拉深时的应力状态
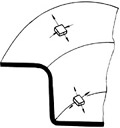

图3 r值在板平面内的变化
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条