2) urban active fault


城市活断层
1.
The shallow seismic detection method for the urban active fault control;


城市活断层控制性浅层地震探测方法分析
2.
Exemplified by some results obtained from the electric imaging detection of active faults in Zibo City,this paper described the method for geological interpretation and analysis of images from the electric imaging technique,and studied the input impedance range of the instrument for urban active fault detection as well as some problems which deserve attention in data processing and inversion.
以淄博市活断层电成像探测的某些结果为例,阐述了电成像图像的地质解释和分析方法,探讨了用于城市活断层探测的仪器的输入阻抗范围以及数据处理和反演中需注意的问题。
3.
Seismic refraction method is tentatively used in the exploration of urban active faults where strong interference of surface waves exists and it is difficult to use seismic reflection survey.
在城市活断层勘探中,对于面波干扰大、地震反射波法难以开展工作的区域,可尝试利用地震折射波法进行探测,并对折射波法探测的原始记录采用时间项、差异时距曲线和有限差分成像等方法进行综合计算、分析,以探索折射波法在城市活断层勘探中的应用成效。
3) urban active faults


城市活断层
1.
The paper introduces aim and meaning of exploring urban active faults; researches the examples of exploring earthquake active faults at home and abroad.
巨大的城市地震灾害主要由隐伏于城市下边的活动断裂产生的地震造成的,因此城市活断层的探测工作是十分必要、紧迫的。
2.
To study canonical acquisition and processing technique of ultra-shallow seismic data for detecting urban active faults in Urumqi is provided with great typicality and applied value, and can support vital reference for detecting urban active faults in Urumqi and other areas of all the country i.
研究超浅层地震在乌鲁木齐城市活断层探测中规范的数据采集、处理技术具有一定的代表性与应用价值;可为今后本地区及全国其他环境相近地区的活断层探测提供重要的参考。
4) Lanzhou city


兰州市
1.
Research on hazardous waste management information system based on GIS——A case of hazardous waste management information system of Lanzhou City;
基于GIS的危险废物管理信息系统设计研究——以兰州市危险废物地理信息系统为例
2.
Dynamic Analysis to the Sustainable Development of Cities in Northwest Semi-arid Areas: A Case Study of Lanzhou City;
西北半干旱区城市可持续发展状况动态分析——以兰州市为例
3.
Regularities and prevention-controlling measures of air pollution in Lanzhou City;


兰州市大气污染规律及治理对策
5) Lanzhou
['lɑ:n'dʒəu]


兰州市
1.
Magnetic Characteristics of Street Dust in Lanzhou and Its Environmental Significance;


兰州市街道尘埃磁学特征及其环境意义
2.
Mineral Compositions of Individual Particles in the Inhalable Particulate Matter in the Lanzhou Air during Heating Period;
兰州市取暖期可吸入颗粒物中单颗粒矿物组成特征
3.
Magnetic Property of Lanzhou Dustfall and Its Implication in Urban Pollution;


兰州市大气降尘环境磁学特征研究
6) Lanzhou City


兰州市区
1.
Formative Causes of Landslide and Debris Flowin Lanzhou City and Preventives;


兰州市区滑坡泥石流危害、成因及其防治对策
2.
Objective:To investigate the rate and the type of Shigella spp infection among the patients suffered with the diarrhea in Lanzhou city.
目的:调查兰州市区腹泻患者中志贺菌的感染率和感染型别;确定兰州市区分离志贺菌株的毒力基因型;测定不同毒力基因型志贺菌的毒力,以探讨毒力与毒力基因型的关系。
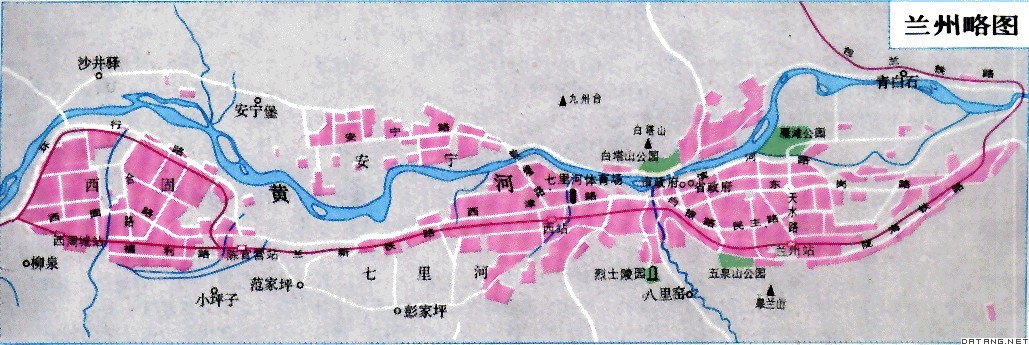
补充资料:兰州市
| 兰州市 中国甘肃省省会,全省政治、经济和科学文化中心。别称金城。位于甘肃省中部,处于中国版图的几何中心。面积1.44万平方千米,其中市区2122平方千米。辖永登县、皋兰县、榆中县3县。1992年人口258万 ,其中市区人口132万 。有汉、回、藏、满、东乡、蒙古、土等36个民族,其中,汉族占 96.44% 。兰州市区习惯上指南北介于皋兰山和北山之间,东起桑园峡 ,西至岸门的黄河谷地部分 ,城区面积163平方千米。汉昭帝始元六年(前81)置金城郡,治允吾(今永靖大川)。至西魏时四次迁都治于今城关区(汉置金城县)。隋文帝开皇三年(583 )废金城郡置兰州总管府 ,以地处皋兰山北麓而得名。后州、郡数次易名。唐复置兰州,1667年始作省会。1941年将皋兰县城郊划出设兰州市。
自然资源丰富。黄河横贯市区,水资源丰富,境内分布着各类矿产地155处,共35个矿种,其中煤、水泥灰岩 、石英岩及玻璃用石英砂等分布广、储量大,已构成省内优势资源。此外有金、石膏、芒硝、多金属(含铜、铅、锌、银等)、石油、白云岩、熔剂灰岩、辉绿岩、大理石等矿产。农作物中粮食作物有小麦、玉米、豆类、马铃薯等,经济作物有蔬菜、油料、麻类、烟叶、药材等,野生植物有松、桦、杨、柳、杉、榆、槐等,还有驰名的蕨菜、发菜等。盛产西瓜、籽瓜、白兰瓜、麻醉瓜、蜜桃、杏、冬果梨、软儿梨、苹果等,素有瓜果城之美称。另外还有玫瑰、水烟、百合、黑瓜子等土特产。兰州是黄河上游最大的一座门类齐全、规模宏大的现代化工业城市,已形成了一个以石油、化工、机械、冶金为主体的重工业,包括毛纺、制药、塑料、制革、食品等具有地方特色的轻工业及煤炭、建材等工业的产业结构比较齐全的工业体系。1993年国民生产总值 109.55 亿元 。是西北最大的交通枢纽,也是欧亚大陆桥上的一个重要的中心城市 ,中国东西大动脉陇海线和兰新线以及包兰 、兰青4条铁路干线在此交会;西兰、甘新、甘青等干线公路纵横过境;民航辟有通往香港、哈尔滨、北京、上海、福州、广州、武汉、南京、西安、成都、昆明、乌鲁木齐及敦煌等十几条航线。名胜古迹有黄河中山铁桥、庄严寺、泰和铁钟、铜接引佛、金天观、白塔寺、黄河水车、汉代铜车马俑、白衣寺塔、五泉山、白塔山、金城盆景园、雁滩公园、石佛沟、吐鲁沟、石门度假村、兴隆山、省博物馆及八路军驻兰州办事处等 。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条