1) generalized instantaneous seismic attribute


广义瞬时地震波属性
2) seismic instantaneous attributes


地震瞬时属性
1.
A new method of extracting seismic instantaneous attributes based on empirical mode decomposition is discussed in this paper.
传统复地震道方法提取的地震瞬时属性存在物理意义不明确、对噪声敏感等不足,本文探讨基于经验模态分解的地震瞬时属性提取方法,得到不同尺度下的地震瞬时属性,由此得到的瞬时频率在数值上与地震主频对应较好。
3) instantaneous seismic attributes


瞬时地震属性
4) Seismic instantaneous attribute parameters


瞬时地震属性参数
5) instantaneous attribute


瞬时属性
1.
The quantitative analysis of static error and noise effect on instantaneous attribute.;


静校正误差和噪声对瞬时属性影响的定量分析
2.
It has also important application in seismic data analysis,for example,seismic spectral decomposition ,instantaneous attributes extraction,etc.
在地震勘探数据分析中也有重要的应用,如地震频谱分解,瞬时属性提取等。
6) instantaneous attributes


瞬时属性
1.
On the methods of seismic data instantaneous attributes estimate in time-frequency domain;
时频域内地震资料瞬时属性提取方法研究
2.
Starting from the equation of instantaneous parameters and scale energy in wavelet domain,the paper considered that the energy attribute and instantaneous attributes in wavelet scale domain can represent attenuation character of seismic signal in a certain scale scope and defined them as attenuation attributes of seismic wave in wavelet scale domain.
本文从小波域瞬时参数和尺度能量方程出发,提出小波尺度域的能量属性和瞬时属性在一定的尺度范围内可以表征地震信号的衰减特征,并把它们定义为小波尺度域地震波衰减属性。
3.
This paper introduces the concept of local seismic attributes, and compare with the Hilbert transform instantaneous attributes and wavelet transform methods in order to explain the local seismic attributes in an important role in the further exploration of its seismic data analysis.
本文介绍了局域化瞬时地震属性的概念,并与Hilbert变换属性提取瞬时属性和小波变换提取瞬时属性等方法进行了比较,从而说明局域化瞬时地震属性在属性提取中的重要作用,进一步探索了其在地震资料分析中的应用。
补充资料:地震波
| 地震波 seismic wave 由地震震源发出的在地球介质中传播的弹性波。地震发生时,震源区的介质发生急速的破裂和运动,这种扰动构成一个波源。由于地球介质的连续性,这种波动就向地球内部及表层各处传播开去,形成了连续介质中的弹性波。 地球介质,包括表层的岩石和地球深部物质,都不是完全弹性体,但因地球内部有很高的压力,地震波的传播速度很大,波动给介质带来的应力和应变是瞬时的,能量的消耗很小,因此可以近似地把地震波看作弹性波。 从震源发出的波动有两种成分: 一种代表介质体积的涨缩,称为涨缩波,其质点振动方向与传播方向一致,所以又称纵波。另一种成分代表介质的变形,称为畸变波,其质点振动方向与传播方向垂直,所以又称横波。纵波的传播速度较快,在远离震源的地方这两种波动就分开,纵波先到,横波次之。因此纵波又称P波,横波又称S波。在没有边界的均匀无限介质中,只能有P波和S波存在,它们可以在三维空间中向任何方向传播,所以叫做体波。但地球是有限的,有边界的。在界面附近,体波衍生出另一种形式的波,它们只能沿着界面传播,只要离开界面即很快衰减,这种波称为面波。面波有许多类型,它们的传播速度比体波慢,因此常比体波晚到,但振幅往往很大,振动周期较长。如果地震的震源较深,震级较小,则面波就不太发育。 波速随频率或波长而变化,这种现象叫做频散。在完全弹性的平行层介质中,由于各种类型的波的叠加,在地表观察到的面波频散是几何原因造成的。在地球内部,由于介质的不均匀性和非完全弹性,会导致体波的频散,这是物理原因造成的。由于频散,波形在传播过程中会发生变化。例如在震源处发出的一个脉冲,在远处就可以散成一个波列。 将地球介质看成完全弹性体只是一种近似。精密的观测表明,地震波在传播中的能量消耗有时是不能忽略的。在一定观测点,波的振幅A随时间t衰减可用A=Aoe-rx表示,r为时间衰减系数,Ao 为初始振幅。波传播x 距离后,因能量损耗而导致振幅的减小,可用 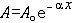 表示,a 为距离衰减系数。表示能量消耗的另一个重要参数Q称为品质因子,其定义是 表示,a 为距离衰减系数。表示能量消耗的另一个重要参数Q称为品质因子,其定义是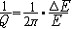
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|
|
| ©2011 dictall.com | |