1) nitrogen agronomic efficiency


氮肥农学利用率
1.
The relationship between nitrogen agronomic efficiency and agronomic characteristics was investigated using 16 mid-season hybrid rice combinations on two levels of nitrogen application.
以16个杂交中稻组合为材料,在正常施氮和不施氮2个施氮水平下研究了杂交中稻氮肥农学利用率与植株地上部农艺性状的关系。
2) agronomic nitrogen use efficiency


氮素农学利用率
3) Nitrogen use efficiency


氮肥利用率
1.
Effect of coated compound fertilizer on yield,nitrogen use efficiency and soil available nitrogen in summer maize;
包膜复合肥对夏玉米产量、氮肥利用率与土壤速效氮的影响
2.
A statistical model of nitrogen use efficiency for rice and wheat crops;


一个稻麦作物氮肥利用率的统计模型
3.
Effect of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on growth and fertilizer nitrogen use efficiency of double rice in southern China
控释氮肥对双季水稻生长及氮肥利用率的影响
4) N use efficiency


氮肥利用率
1.
Effect of N fertilizer and N use efficiency under different N levels of application in high-fertility paddy field.;
高肥力稻田不同施氮水平下的氮肥效应和几种氮肥利用率的研究
2.
The N use efficiency(NUE) and fate of N fertilizers applied to open field vegetables including green cabbage,Chinese cabbage and tomato were investigated by using field plot and microplot experiments.
采用田间小区和微区试验相结合,研究了小青菜、大白菜和番茄3种露地蔬菜的氮肥利用率及其氮素去向的差异。
3.
The main results are as follows:(1) Yield,water consumption and water use efficiency(WUE) were increased by the increment of N application rate,while N use efficiency(NUE) was decreased.
研究了华北平原夏玉米季施用不同类型氮肥对当季与后作冬小麦及周年产量与水、氮利用的影响,结果表明:(1)随施氮量增大,夏玉米产量、耗水量与水分利用效率(WUE)增大,氮肥利用率(NUE)降低。
5) fertilizer-N use efficiency


氮肥利用率
1.
The effect of applying N-fertilizer or not in wheat on soil fertility and grain yield and fertilizer-N use efficiency (FNUE) of rice in the wheat-rice cropping system were studied.
通过对前茬作物小麦设置施用氮肥与不施用氮肥处理研究它对土壤肥力及后茬作物水稻产量和氮肥利用率的影响。
6) Nitrogen utilization efficiency


氮肥利用率
1.
In order to increase crop production and maximize nitrogen utilization efficiency, field experiments were conducted to investigate the effect of urea and delayed release coated urea under different conditions (with different dose and applied methods) on the growth and nitrogen uptake of transplanted rice.
结果表明,延迟释放型包衣尿素在比普通尿素施氮量(N150kg/hm2)减少30%(N105kg/hm2)和50%(N75kg/hm2)时,对水稻生长不会产生任何不良影响;由于包衣尿素在田间的养分释放动态与水稻对氮素的吸收规律吻合,施用包衣尿素的水稻产量、吸氮量和氮肥利用率均显著高于普通尿素处理,其中水稻产量增加12 7%~14 4%,吸氮量增加27 5%~32 7%;普通尿素和氮肥用量减少30%和50%的包衣尿素3个处理的氮肥利用率分别为19 9%、58 8%和89 9%。
2.
In Tai Lake Watershed of south Jiangsu province the studies on rice yield, nitrogen utilization efficiency, nitrogen leaching amount at different nitrogen fertilizer doze in paddy rice field were made.
在苏南太湖流域,对不同氮肥施用水平下水稻的产量、氮肥利用率及氮肥水环境损失进行了研究。
3.
Based on the long-term field experiments,the relationships between soil nitrogen balance,nitrogen utilization efficiency(NUE) and soil nitrate were studied.
利用长期肥料试验资料研究了土壤氮素平衡、氮肥利用率和土壤硝态氮之间的相互关系。
补充资料:氮肥
| 氮肥 nitrogen fertilizer 具有氮( N)标明量的单元肥料。施于土壤或植物可提高植物的氮营养水平。按氮的化学形态可分为三大类:①铵态氮肥 ,氮以 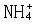 形态存在。主要有氨水 、液氨、碳酸氢铵、硫铵、氯化铵等。②硝态氮肥,氮以 形态存在。主要有氨水 、液氨、碳酸氢铵、硫铵、氯化铵等。②硝态氮肥,氮以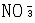 形态存在。主要有智利硝石(硝酸钠)、硝酸钙;同时含有 形态存在。主要有智利硝石(硝酸钠)、硝酸钙;同时含有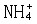 和 和 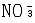 的氮肥有硝酸铵、硫硝酸铵、硝酸铵钙等。③酰胺态氮肥,氮以酰胺基形态存在。主要有尿素等。中国常用的氮肥有尿素、氨水、碳酸氢铵、硝酸铵、硫铵、氯化铵和含氮复合肥料。 的氮肥有硝酸铵、硫硝酸铵、硝酸铵钙等。③酰胺态氮肥,氮以酰胺基形态存在。主要有尿素等。中国常用的氮肥有尿素、氨水、碳酸氢铵、硝酸铵、硫铵、氯化铵和含氮复合肥料。氮肥施入土壤后,其中的氮素被当季植物吸收,一部分通过微生物的同化和粘粒矿物的固定等作用而残留在土壤中;还有一部分则通过各种途径,如氨的挥发、反硝化作用、淋洗作用和径流等离开土壤 -植物系统而损失掉 。土壤氮素含量、形态及其转化和供氮能力与氮肥肥效关系极大。土壤中氮分为无机态和有机态 2类 。无机态氮中,粘土矿物固定态的铵约占土壤全氮量的 2% ~ 3%,能被植物直接吸收利用,称有效态氮。有机态氮约占土壤表土全氮量的 90%或更高,经微生物分解转化为铵态氮和硝态氮后,易为作物吸收。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条