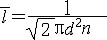1) average free energy


平均自由能
2) mean Gibbs free binding energy


平均结合自由能
1.
The equations which are used for calculating the mean Gibbs free binding energy (△G_(bi)) and adsorption energy (△G_(ad)) between cations and soil clay particles were introduced in this dissertation.
本文介绍了阳离子与土壤黏粒间平均结合自由能和平均吸附自由能的计算公式,再用悬液Wien效应法研究了重金属阳离子(Zn~(2+)、Cd~(2+)、Cu~(2+)、pb~(2+)、Cr~(3+))及其它离子(Na~+、K~+、NH_4~+、Ca~(2+))与主要黏土矿物(蒙脱土、高岭土等)和主要的恒电荷土壤(黄棕壤、棕壤、黑土等)黏粒间的相互作用及能量关系。
3) mean free path


平均自由程<能>
4) Mean free adsorption energy


平均吸附自由能
6) mean free path


平均自由程
1.
Relation between temperature and mean free path in the Franck-Hertz experiment


弗兰克-赫兹实验中温度与电子平均自由程的关系
2.
The relationships of the compressing strength and abrasion resistance of PCBN and the mean free path of CBN particles in it's microstructure were studied.
根据Gorland强度理论中平均自由程与材料性能的关系,通过一系列的试验和回归分析,研究了PCBN的内部结构,成份组成与其抗压强度和磨耗比之间的关系,建立了CBN粒度、结合剂掺入量与PCBN平均自由程、抗压强度、耐磨性之间的关系式,对提高PCBN的性能具有重要的指导价值。
3.
dopant content are consi-dened as the relationships between the properties and the mean free path ofdiamond,since this mean free path depends on both the diamond particle size and the dopant content.
在性能与平均自由程的关系曲线中存在性能最佳值。