1) extended schrdinger equation


推广薛定谔方程
2) Schrdinger equation


薛定谔方程
1.
Application of time-splitting and wavelet based space-time adaptive method to solving Schrdinger equations;
时间分裂空间小波自适应方法在薛定谔方程中的应用
2.
In the field of force with nucleus as the center we set up the radial Schrdinger equation of alkaline metal atom, change it into the same form as the radial equation of hydrogen atom, compare it with the energy level of hydrogen atom, get the energy level formula of alkaline metal atom and discuss the fission law of alkaline metal atom energy level at the same time.
在以原子核为中心的力场中 ,建立碱金属原子的径向薛定谔方程 ,再将方程变成与氢原子径向方程相同的形式 ,类比氢原子的能级 ,得出了碱金属原子的能级公式 ,进而讨论了碱金属原子能级的分裂规
3.
Analysis on spatial modulation instability about nonlinear Schrdinger equation in the case of considering 3-dimensional(3D) 3-component(3C),which is the cause of self-focus.
在考虑三维三分量[1]的情况下对非线性薛定谔方程进行同时考虑横向和纵向的空间调制不稳定性分析,其空间调制不稳定是导致自聚焦的原因。
3) Schrodinger equation


薛定谔方程
1.
The Steady-State Solution and Non-Steady-State Solution to the Schrodinger Equation;


薛定谔方程的定态解与非定态解
2.
The numerical value calculation of schrodinger equation;


薛定谔方程的数值计算设计
3.
The atom s probability in crystal was investigated by using the one-dimensional linearity resonance model and the Schrodinger equation.
在一维线性谐振子模型基础上,应用薛定谔方程分析了晶体中原子的概率分布;将晶体中原子的概率分布定义为原子云,解释了物理气相沉积法制备薄膜时残余应力产生的原因,建立了薄膜残余应力产生机理的理论模型。
4) Schrdinger equation


薛定谔方程
1.
The Schrdinger equation is given directly from the classical Hamiltonian function of a damping harmonic oscillator,and its solution is obtained by the separation of variables.
写出阻尼谐振子的哈密顿函数,对其直接量子化,用分离变量法得出了薛定谔方程的解。
2.
In this article the distribution functions are constructed with the solution of the Schrdinger equation in phase space and it is found that the constructions of various distribution functions are not the same.
利用推广后的T-F相空间中的薛定谔方程的解来构造分布函数。
3.
Using the method of structuring radial wave function for hydrogen atom,we have given the coefficients of the power-polynomial of the radial wave function for hydrogen atom by solving the Schrdinger equation.
用构造氢原子径向波函数的方法,通过解薛定谔方程给出氢原子径向波函数幂多项式的系数。
5) Schrdinger equation


薛定谔方程
1.
An explicit analytical solution of the Schrdinger equation for a detuned quantum frequency conversion system;
失谐量子频率转换系统薛定谔方程的显式解析解
2.
A concise method to solve Schrdinger equation with given potential: method of Cole-Hopf transformation;
一种简捷求解定态薛定谔方程的方法:科尔-霍普夫变换法
3.
The variable separation approach and study on solving the variable-coefficient nonlinear Schrdinger equation;
变量分离法与变系数非线性薛定谔方程的求解探索
6) Schrdinger equation


薛定谔方程
1.
The Relative Error on Solving Schrdinger Equation of Wave Function of Particle Spin with Symposium;
粒子自旋薛定谔方程辛算法解的相对误差研究
补充资料:薛定谔方程
薛定谔方程 E.薛定谔提出的量子力学基本方程 。建立于 1926年。它是一个非相对论的波动方程。它反映了描述微观粒子的状态随时间变化的规律,它在量子力学中的地位相当于牛顿定律对于经典力学一样,是量子力学的基本假设之一。设描述微观粒子状态的波函数为Ψ(r,t),质量为m的微观粒子在势场U(r,t)中运动的薛定谔方程为 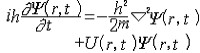 。在给定初始条件和边界条件以及波函数所满足的单值、有限、连续的条件下,可解出波函数Ψ(r,t)。由此可计算粒子的分布概率和任何可能实验的平均值(期望值)。当势函数U不依赖于时间t时,粒子具有确定的能量,粒子的状态称为定态。定态时的波函数可写成 。在给定初始条件和边界条件以及波函数所满足的单值、有限、连续的条件下,可解出波函数Ψ(r,t)。由此可计算粒子的分布概率和任何可能实验的平均值(期望值)。当势函数U不依赖于时间t时,粒子具有确定的能量,粒子的状态称为定态。定态时的波函数可写成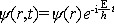 式中Ψ(r)称为定态波函数,满足定态薛定谔方程 式中Ψ(r)称为定态波函数,满足定态薛定谔方程 ,这一方程在数学上称为本征方程,式中E为本征值,是定态能量,Ψ(r)又称为属于本征值E的本征函数。 ,这一方程在数学上称为本征方程,式中E为本征值,是定态能量,Ψ(r)又称为属于本征值E的本征函数。量子力学中求解粒子问题常归结为解薛定谔方程或定态薛定谔方程。薛定谔方程广泛地用于原子物理、核物理和固体物理,对于原子、分子、核、固体等一系列问题中求解的结果都与实际符合得很好。 薛定谔方程仅适用于速度不太大的非相对论粒子,其中也没有包含关于粒子自旋的描述。当计及相对论效应时,薛定谔方程由相对论量子力学方程所取代,其中自然包含了粒子的自旋。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条