1) slowness of seismic wave


地震波慢度
2) seismic slowness


地震慢度
3) seismic velocity


地震波速度
1.
Characteristics and effect factors of seismic velocity in metamorphic rock area:An example from CCSD borehole area;
变质岩区地震波速度的特点及其影响因素——以中国大陆科学钻探孔区为例
2.
This paper illustrates the relationship between synergetic acoustic logging velocity and seismic velocity by the theory of wave mechanics,and the exact interval velocity for structure mapping by variable velocity is computed.
从波动力学的角度出发,研究建立声波速度和地震速度的关系,提出了利用合成声波测井速度求取地震波速度的方法,并用于地震勘探变速成图,从而使构造图的精度大幅度提高。
4) seismic wave velocity


地震波速度
1.
Based on overlaying velocity data, mudstone thickness was predicted by using the rules of seismic wave velocity changes of itself and inherent relations between lithological properties, mudstone porosity was transformed by using interval velocity, thus vitrinite reflectance of source rocks was further predicted, therefore mature hydrocarbon source rock area was determined, and bases were p.
根据叠加速度谱资料,利用地震波速度参数自身的变化规律与地下岩性之间的内在联系,预测了泥岩厚度;利用层速度,进行泥岩孔隙度转换,从而进一步预测烃源岩镜质体反射率,最终定量地圈定凹陷主力烃源岩的成熟区,为区带评价优选提供了依据。
2.
Because of large variation range on the seismic wave velocity and complex structure in Ciyutuo Oilfield,it s necessary to research the seismic wave velocity so as to offer accurate tectonic basis for geometric arrangement of wells.
在地震地质解释过程中,地震波速度是地震解释资料中重要的参数。
3.
Through the study of horizontal slice,slice along layer and vertical slice,it focused on the variation rules of seismic wave velocity vertically and horizontally in Jiangling Depression,and also analyzed the cause of horizontal change of seismic w.
地震波速度是地球物理勘探和开发中最重要的一个参数。
5) the intensity of earthquake wave


地震波强度
6) slow earthquake


慢地震
1.
The identification and location,generation of slow earthquake and their physical mechanism of occurrence are summarized.
综述了慢地震的定义,慢地震观测、识别和定位,以及慢地震的机制和传播等问题。
2.
The slow earthquake event occurred before west to Kunlun Mountain Pass earthquake of M S 8.
笔者认为 ,该慢地震事件是M 8 1大震前中昆仑断裂临震预滑动引起的。
补充资料:地震波
| 地震波 seismic wave 由地震震源发出的在地球介质中传播的弹性波。地震发生时,震源区的介质发生急速的破裂和运动,这种扰动构成一个波源。由于地球介质的连续性,这种波动就向地球内部及表层各处传播开去,形成了连续介质中的弹性波。 地球介质,包括表层的岩石和地球深部物质,都不是完全弹性体,但因地球内部有很高的压力,地震波的传播速度很大,波动给介质带来的应力和应变是瞬时的,能量的消耗很小,因此可以近似地把地震波看作弹性波。 从震源发出的波动有两种成分: 一种代表介质体积的涨缩,称为涨缩波,其质点振动方向与传播方向一致,所以又称纵波。另一种成分代表介质的变形,称为畸变波,其质点振动方向与传播方向垂直,所以又称横波。纵波的传播速度较快,在远离震源的地方这两种波动就分开,纵波先到,横波次之。因此纵波又称P波,横波又称S波。在没有边界的均匀无限介质中,只能有P波和S波存在,它们可以在三维空间中向任何方向传播,所以叫做体波。但地球是有限的,有边界的。在界面附近,体波衍生出另一种形式的波,它们只能沿着界面传播,只要离开界面即很快衰减,这种波称为面波。面波有许多类型,它们的传播速度比体波慢,因此常比体波晚到,但振幅往往很大,振动周期较长。如果地震的震源较深,震级较小,则面波就不太发育。 波速随频率或波长而变化,这种现象叫做频散。在完全弹性的平行层介质中,由于各种类型的波的叠加,在地表观察到的面波频散是几何原因造成的。在地球内部,由于介质的不均匀性和非完全弹性,会导致体波的频散,这是物理原因造成的。由于频散,波形在传播过程中会发生变化。例如在震源处发出的一个脉冲,在远处就可以散成一个波列。 将地球介质看成完全弹性体只是一种近似。精密的观测表明,地震波在传播中的能量消耗有时是不能忽略的。在一定观测点,波的振幅A随时间t衰减可用A=Aoe-rx表示,r为时间衰减系数,Ao 为初始振幅。波传播x 距离后,因能量损耗而导致振幅的减小,可用 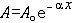 表示,a 为距离衰减系数。表示能量消耗的另一个重要参数Q称为品质因子,其定义是 表示,a 为距离衰减系数。表示能量消耗的另一个重要参数Q称为品质因子,其定义是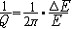
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|
|
| ©2011 dictall.com | |