|
|
|
说明:双击或选中下面任意单词,将显示该词的音标、读音、翻译等;选中中文或多个词,将显示翻译。
|
|
|
1) seismic stress field

地震应力场
1.
The study results show that the orientation of compressive principal stress is NE and the modern tectonic stress field is in keeping with neotectonic stress field and seismic stress field.
新构造应力场、现代构造应力场、地震应力场趋于一致。
2) seismic stress

地震应力
1.
Seismic porosity and seismic stress of rocks can be inverted with seismic and geological data based on the theory of two phase medium.
根据双相介质理论 ,使用地震、地质资料反演出地震孔隙率和岩石地震应力。
2.
The paper suggested that the generation of seismic stress is accompanied by the formation of “biaxial strain structure”.
讨论得出地震应力是随着“双向应变结构”的形成而产生的;地震应力主要有压缩应力、拉疏应力及剪切应力的复杂性;地震应力的传递与集中,在本质上就是应变的迁移与应变的转换;地震应力与区域构造应力有生成关系上的联系,也有作用对象与作用目的不同的区别。
3) source stress field

震源应力场
1.
The source mechanism, source stress field and source fault for the Chengjiang earthquake of M5.
利用地震波资料对澄江 5 2级地震序列的震源机制、震源应力场和震源断层作了分析研究。
4) crustal stress field

地应力场
1.
Multi-scale elasto-plastic calibration of the regression analysis of 3D initial crustal stress field;
三维初始地应力场的多尺度弹塑性校正
5) earth stress field

地应力场
1.
Study on the earth stress field in complex fault block——taking Xi-3 fault block in Beier Sag,Hailaer Basin as an example;
复杂断块构造的地应力场研究——以海拉尔盆地贝尔凹陷希3断块为例
2.
The obtained cognition was that the macro elements resulted in engineering accidents were closely related to the formation geologic characteristics of area geologic structure,formation lithology,petrophysical property,and the mechanism was represented by formation geologic factors, which were triggered by coupling actions,such as microscopic earth stress field,seepage field and temperature field.
为了进一步提高钻井工程异常预报的及时率、准确率,提升录井服务质量,应用数理统计方法对引起各类钻井工程事故发生的因素进行统计分析,获得了如下认识:导致工程事故发生的宏观因素主要与地层中区域地质构造、地层岩性、岩石物性等地质特性密切相关,其机理是通过地层内部微观的地应力场、渗流场、温度场等耦合作用引发地质因素变化表现出来。
6) Ground stress field

地应力场
1.
Study of finite element on egfects of faults on ground stress field;

断层对地应力场影响的有限元研究
2.
According to the comprehensive analysis on the results of engineering ground stress measurement and test hole deformation monitoring, general geological model, test hole excavation model and ground stress field distribution model are established.
在工程地应力测试和试验洞变形监测结果综合分析的基础上,建立地质概化模型,试验洞施工开挖模型、地应力场分布模型。
补充资料:铣刀片的应力场分析
【摘要】 铣削属断续切削,切削过程中刀片受力非常复杂,力的大小和方向随时变化,刀片的失效形式主要为冲击破损。因此,采用有限元法对铣刀片应力场进行分析,以寻求减少刀片破损的刀具最佳几何角度,对于铣刀片槽型的开发具有指导意义。
1.引言
铣削属断续切削,切削过程中刀片受力非常复杂,力的大小和方向随时变化,刀片的失效形式主要为冲击破损。因此,采用有限元法对铣刀片应力场进行分析,以寻求减少刀片破损的刀具最佳几何角度,对于铣刀片槽型的开发具有指导意义。 2.面铣切削加工坐标系统的建立 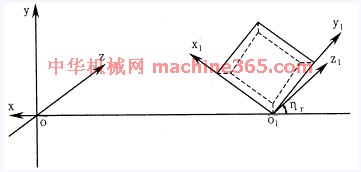
图1 面铣切削加工坐标系统
面铣切削加工坐标系统由刀体坐标系和刀片坐标系组成,如图1所示。 在刀体坐标系中,Y轴为铣刀轴线,X轴在基面内过刀尖与Y轴相交。在刀片坐标系中,y1轴通过主切削刃,x1轴通过副切削刃,刀片前刀面在x1o1y1平面内。铣刀半径为R=OO1,铣刀前角为g0,刃倾角为ls,主偏角为K,法向前角为gn。 面铣刀无论具有何种几何角度,都可看作是由刀体坐标系经过一次平移和三次旋转而成,可用矩阵表示为 
其中 A11=cosgnsinhr+singnsinlscoshr
A12=cosgncoshr-singnsinlssinhr
A13=singncosls
A21=-coslscoshr
A22=coslssinhr
A23=sinls
A31=-singnsinhr+cosgnsinlscoshr
A32=-singncoshr-cosgnsinlssinhr
A33=cosgncosls
tggn=tgg0cosls 
图2 切入冲击力的方向
3.切入冲击力方向的确定 铣削与车削的不同之处在于铣削为断续切削,存在着切入、切出过程,铣刀的破损主要是由机械冲击力引起的。因此,首先要确定铣刀切入瞬间冲击力的作用方向。铣削时,铣刀高速旋转,工件缓慢进给,若忽略进给运动(因进给运动速度仅为铣刀运动速度的约1/4),铣刀切入冲击力的方向应该在刀具相对工件运动的切线方向上。如图2所示。 由图1可知,切入冲击力方向为Z轴方向,力F分解到刀片坐标系中为 
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|










