2) efficiency of pile groups


地震波瞬态响应
3) seismic response


地震响应
1.
Analysis on seismic response of special cavernous structure of carbonate;


碳酸盐岩特殊孔洞型构造地震响应特征分析
2.
Research on petrophysical parameters and seismic response models of He 8 formation;


盒8地层岩石物理参数及地震响应模型研究
3.
Sedimentary facies and seismic responses in the Upper Jurassic Suining Formation,Luodai Gas Field;
洛带气田上侏罗统遂宁组沉积相及含气地震响应特征
4) earthquake response


地震响应
1.
Non-classical mode superposition method for earthquake response of a reinforced concrete building with a steel tower atop it;
非经典振型分解法求混凝土房屋及其上钢塔的地震响应
2.
Magneto-rheological(MR) dampers semi-active control of earthquake response for elevated bridge;
高架桥梁地震响应磁流变阻尼器(MR)半主动控制
3.
Dynamic property and earthquake response analysis of cable-strut-supported shell structure;
张弦网壳结构的自振特性及地震响应分析
5) seismic responses


地震响应
1.
Nonlinear seismic responses of arch dams with joins;


带横缝拱坝的非线性地震响应
2.
Study on the Seismic Responses and Shock Absorption Technique of Self-anchored Suspension Bridges;
自锚式悬索桥地震响应分析和减震措施研究
3.
The three dimensional FEM models are constructed to analyze the effects of raft thickness on the vibration characteristics and seismic responses of the twin-towers high-rise building structures with enlarged base,and the dynamic soil-structure interaction is incorporated in the analysis as well.
考虑土-结构动力相互作用,建立了双塔楼大底盘高层建筑动力响应分析的三维有限元模型,研究了筏板厚度变化对结构振动特性和地震响应的影响。
6) response of earthquake


地震响应
1.
This dissertation take example of Rongzhou Bridge in Yibin acrossing Jinsha river, according to the variety of construction load, calculation and analysis of the construction process is performed with the help of the FEM software, the whole process of construction is simulated and the response of earthquake is analysed.
本文以宜宾金沙江戎州大桥为实例,根据施工加载程序的变化,运用有限元软件对该拱桥的施工过程进行了计算分析,对这座拱桥的施工全过程进行模拟仿真,并在此基础上对该桥进行地震响应分析。
补充资料:地震波
| 地震波 seismic wave 由地震震源发出的在地球介质中传播的弹性波。地震发生时,震源区的介质发生急速的破裂和运动,这种扰动构成一个波源。由于地球介质的连续性,这种波动就向地球内部及表层各处传播开去,形成了连续介质中的弹性波。 地球介质,包括表层的岩石和地球深部物质,都不是完全弹性体,但因地球内部有很高的压力,地震波的传播速度很大,波动给介质带来的应力和应变是瞬时的,能量的消耗很小,因此可以近似地把地震波看作弹性波。 从震源发出的波动有两种成分: 一种代表介质体积的涨缩,称为涨缩波,其质点振动方向与传播方向一致,所以又称纵波。另一种成分代表介质的变形,称为畸变波,其质点振动方向与传播方向垂直,所以又称横波。纵波的传播速度较快,在远离震源的地方这两种波动就分开,纵波先到,横波次之。因此纵波又称P波,横波又称S波。在没有边界的均匀无限介质中,只能有P波和S波存在,它们可以在三维空间中向任何方向传播,所以叫做体波。但地球是有限的,有边界的。在界面附近,体波衍生出另一种形式的波,它们只能沿着界面传播,只要离开界面即很快衰减,这种波称为面波。面波有许多类型,它们的传播速度比体波慢,因此常比体波晚到,但振幅往往很大,振动周期较长。如果地震的震源较深,震级较小,则面波就不太发育。 波速随频率或波长而变化,这种现象叫做频散。在完全弹性的平行层介质中,由于各种类型的波的叠加,在地表观察到的面波频散是几何原因造成的。在地球内部,由于介质的不均匀性和非完全弹性,会导致体波的频散,这是物理原因造成的。由于频散,波形在传播过程中会发生变化。例如在震源处发出的一个脉冲,在远处就可以散成一个波列。 将地球介质看成完全弹性体只是一种近似。精密的观测表明,地震波在传播中的能量消耗有时是不能忽略的。在一定观测点,波的振幅A随时间t衰减可用A=Aoe-rx表示,r为时间衰减系数,Ao 为初始振幅。波传播x 距离后,因能量损耗而导致振幅的减小,可用 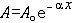 表示,a 为距离衰减系数。表示能量消耗的另一个重要参数Q称为品质因子,其定义是 表示,a 为距离衰减系数。表示能量消耗的另一个重要参数Q称为品质因子,其定义是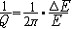
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|
|
| ©2011 dictall.com | |