1) Metal diffraction grating


金属衍射光栅
2) grating diffraction


光栅衍射
1.
Comparison of amplitude vector method and half-wave spectrum method to analyze grating diffraction;
振幅矢量法与半波带法分析光栅衍射的比较
2.
Analyses of grating diffraction by computer simulation;


光栅衍射现象的计算机仿真分析
3.
Testifying secondary maximum among slits interference item of grating diffraction is symmetrical with Fresnel Zone Plate Method;
光栅衍射缝间干涉因子次极大强度对称性的菲涅耳半波带法证明
3) Diffraction grating


衍射光栅
1.
Study of the photoelectric ruling control on the fabricating of the high density diffraction grating;
制作高密度衍射光栅的光电式刻划控制的研究
2.
Super-fine Diamond Tools for Ruling Diffraction Gratings;


超精密金刚石刀具──衍射光栅刻划刀
3.
The second kind angular dispersion and the analysis of characteristics of diffraction grating;
衍射光栅的第二类角色散及其特性分析
5) diffraction gratings


衍射光栅
1.
The large-size diffraction gratings have become the key unit of some major engineering.


近年来大面积衍射光栅已成为许多大型高技术工程项目的关键元件 ,它的获取方法也一直是光栅界探求的目标 ,本文简要回顾衍射光栅研制技术的发展历史 ,介绍了衍射光栅的发展趋势以及国内外研制大面积衍射光栅的技术现状 ,说明了拼接光栅的原理、方法以及利用这种方法来获取大面积衍射光栅的诸多优点。
2.
An asymptotic formalism used in the scalar domain is derived for studying the behavior of threedimension diffraction gratings used in small groove pitch and near normal incidence for soft X-ray.
利用标量区衍射理论分析了正交二元矩形软X射线衍射光栅的光学特性,给出了理论设计的初步结果。
3.
In this paper the study on the dispersion theory, design, manufacture techniques, and efficiency test methods of diffraction gratings were made in a deep way.
本文对衍射光栅色散理论与光栅设计、制作工艺和效率检验方法做了较为深入的研究。
6) diffractive grating


衍射光栅
1.
Construction and application of diffractive grating analysis program;


衍射光栅分析软件构建与使用
2.
In such system the transform lens and diffractive grating play an important role in determining the combining system s efficiency.
传输透镜及衍射光栅是决定组束系统效率的关键部件,通过理论分析和数值仿真,结果表明透镜焦距25cm、光栅频率200mm-1对组束系统是较为合适的。
3.
The author educes the conclusions below: the light intensity distributions of diffractive grating are consistent with the light intensity distributions of the fraunhofer single slit diffraction when d→0.
光栅衍射花样是由夫琅禾费衍射对多光束干涉调制的结果,本文讨论了光栅长度不变,随着光栅常数d的减少,通过缝数N的增加,保持Nd为常数时衍射光栅的光强分布,并得出,当d→0时,衍射光栅的光强分布与单缝夫琅禾费衍射的光强分布形式一致。
补充资料:衍射光栅
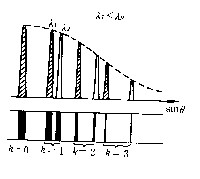
| 衍射光栅 diffraction grating 能等宽等间隔地分割入射波前的、具有空间周期性结构的光学元件。常作为色散元件来分离不同波长的谱线。光栅分透射光栅和反射光栅两类。透射光栅按透射率函数的不同可分为普通的矩形透射率光栅和正弦光栅两种。闪耀光栅是反射光栅的一种,有较高的能量利用率,凹面反射光栅能自动聚焦成像。根据制作方法的不同,可分划线光栅、复制光栅和全息光栅3种。 所有光栅的基本原理均相同。以平面透射光栅为例,在平板玻璃上用金刚石刻刀刻划等宽等间距的平行刻线,未刻部分能透光,刻划部分因漫反射而不透光,这等效于大量等宽等间距的平行狭缝。设缝宽为a,不透光部分宽度为b,则相邻两缝的间距d=a+b称光栅常数。是光栅的重要参量。光栅的实验装置如图1 ,单色缝光源与光栅的狭缝平行,放置在透镜L1的物方焦面内,从L1射出的平行光垂直入射到光栅上,光栅的每条狭缝都将产生单缝衍射,衍射角为θ的所有衍射光被透镜L2会聚于幕上的P处 ,相干叠加的结果决定了P处的总光强 。幕上干涉主极大的位置由下述光栅方程给定: dsinθ=kλ (k=0±1,±2,……)整数k称干涉级,λ为波长。不同波长的主极大位置不同,故光源为复色光时,不同波长成分的主极大彼此分离而成光谱,称光栅光谱。各级主极大的强度要受到单缝衍射的限制,级次愈高强度愈弱,但不同谱线分得愈开,如图2所示。图中虚线表示单缝衍射的分布曲线。注意到所有波长的零级干涉主极大均重合在一起,并落在单缝衍射的中央极大处,无色散的零级主极大占了大部分能量,能量利用率较低。反射式闪耀光栅可把衍射中央极大闪耀到某一级光谱处,大大提高了能量利用率。
波长差相差一个单位的两谱线分开的角间距称为光栅的角色散率,用来描述光栅分开谱线的能力,它由下式给出: 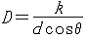
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|
||||
| ©2011 dictall.com | ||||