1) basie controlling principle


基本控制原理
2) basic principles and law of controlling


基本原理及控制规律
3) basic principle of refrigeration


制冷基本原理
4) basic principle


基本原理
1.
Engineering project management and its basic principles;


工程项目管理及基本原理概述
2.
From quantum mechanics and relativity to the basic principles of physics and development of the Noether s theorem;
从量子力学-相对论到物理学的基本原理和Noether定理的推广
3.
On Basic Principles of Civil Adversarial Procedure;


民事争讼程序基本原理论
5) principle
[英]['prɪnsəpl] [美]['prɪnsəpḷ]


基本原理
1.
The principle,simulation procedure and widely used potential functions of molecular dynamics simulation technology were introduced,and the latest achievements in the research of melt structure and future development of the technology were summarized as well.
介绍了分子动力学模拟技术的基本原理、模拟过程及广泛使用的原子间相互作用势函数,综述了该方法在研究金属熔体结构方面的最新成果及今后的发展方向。
2.
This paper introduces the principles and characteristics of differential protection device 7UT512 and it s application in Dong-jinag Water Source Engineering.
文章主要阐述了西门子差动保护装置 7UT5 12的基本原理、特性及其在深圳市东江水源工程的应
3.
The work principle,structure,and assembly of the reflectometry interference spectroscopy(RIFS) biosensor are introduced in this paper.
综述了光反射干涉生物传感器的工作基本原理,仪器结构的组成及各部件,并给出了光反射干涉生物传感器检测免疫学反应的图例。
6) fundamental principle


基本原理
1.
This paper introduces the fundamental principle and features of supercritical CO2 extraction, and sums up its application in perfume, medicine, food and other industries.
介绍了超临界二氧化碳萃取技术的基本原理和特点,综述了该技术在香料、医药、食品等工业中的应用。
2.
It also analyses the fundamental principle , technology features and developing tendency of rotary forging.
介绍了摆动辗压技术的发展历程,分析了摆动辗压的基本原理及工艺特点,论述了摆动辗压技术的发展趋势,并在此基础上指出了目前我国摆动辗压技术存在的差距。
3.
The fundamental principle of strength reduction is adopted in RFPA(rock failure process analysis) code;and a RFPA based numerical code RFPA-SRM (strength reduction method) is developed for rock and soil engineerings.
将强度折减法的基本原理引入到岩石破裂过程分析RFPA方法中,建立RFPA-SRM岩土工程稳定性强度折减分析方法。
补充资料:Delcam改写高速加工基本原理
Delcam的加工软件PowerMILL长期以来被业界赞誉为产生高速加工NC程序的一流系统。Delcam在高速加工方面的经验越来越明显地证明,高速加工不能仅仅依赖于提高主轴转速来实现。刀具咨询商H.R.Pearce和刀具生产厂家Mitsubishi Carbide的合作研究结果表明,用户必须改变其对整个加工过程基本原理的认识,方可真正看到任何在高速加工设备方面投资所得到的效果。

加工策略的基本点是:尽可能地保持刀具负荷的稳定,从而最大限度地延长刀具的使用寿命;尽可能地减少任何切削方向的突然变化,从而尽量减少切削速度的降低。要满足上述的这些条件,则在粗加工中,必须使用偏置加工策略,而不是使用传统的平行加工策略。在可能的情况下,都应从工件的中心开始向外加工,以尽量减少全刀宽切削。
以前对高速加工的要求是,必须同时保证使用比传统加工方法小的行距和下切步距。最新切削刀具技术的发展,使得下切步距大小不再受到限制。
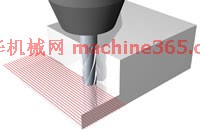
现在在粗加工过程中,可使用带有4到6个刃槽,可使用刀具侧面切削的球头刀来进行深切加工。然而,在这种情况下,行距仍然需相对的小。同样,使用刀具的侧面进行加工,在精加工陡峭壁时,可通过从底部向上加工来优化精加工刀具路径。
粗加工中最好使用顺铣,因为使用顺序可减少刀具磨损。尽管这种加工方法确实存在许多不必要的刀具空程移动,但此时,切削移动速度的提高,足以弥补空程移动的损失。当切削厚度小于0.3mm时,在精加工过程中可安全地组合使用顺铣和逆铣来进行加工。

切入和切出工件时,无论是粗加工还是精加工,都应使用使用圆弧切入和切出方法来切入或离开工件。应尽量避免垂直下刀,直接接近零件表面,因为这样会降低切削速度,同时会在零件表面上留下很多刀痕。
切削角落时,刀具半径应相对小于角落半径,以保持最大接触距离小于切削刀具周长的30%以下。这样可使刀具得到足够的冷却,同时避免刀具进入角落时刀具负荷的突然增加。
对许多形状来说,精加工最有效的策略是使用三维螺旋策略。使用这种策略可避免使用平行策略和偏置精加工策略中会出现的频繁的方向改变,从而提高加工速度,减少刀具磨损。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条