1) approximative modelling


近似模化
1.
: Concerning model experiment, the authors introduces the methods for the seeking of similarity criterion, the approximative modelling and the verification of model experiment, and practical similarity method is presented for the research of model experiment.
针对模型实验,较详细地介绍了寻求相似准则的方法、近似模化的具体方法和模型实验的验证方法,为今后从事模型实验研究工作提供了实用的相似方法。
2) reduced network approximation modeling


简化近似模型
3) approximate model


近似模型
1.
Based on approximate models and genetic arithmetic,a scheme for the plane with multi-flaps was proposed to implement the multidisciplinary design optimization(MDO) of full-envelope flight control law and control effectors geometry & their placement.
基于近似模型和遗传算法,针对多操纵面布局飞机提出一种对全包线飞行控制律和操纵效率器几何形状与位置进行多学科优化的设计方法。
2.
In this approach, uniform design method was employed to generate the geometric information of samples, whose performances are calculated by CFD technique; the relationship between the geometric information and its performances of samples is mapped by the approximate model constructed by parallel artificial networks (PANN); genetic algorithms is employed to find .
均匀设计方法用来生成试验样本点几何信息,各样本点性能评估分析则借助CFD技术来完成,样本点几何信息与其性能之间的关系则采用并行神经网络所映射的近似模型来给出,最后由遗传算法来对该近似模型进行全局寻优,并将其优化得到的相应结果加入样本点集中,重复最后两步,直到满足设定的终止准则。
3.
In the light of the huge amount of time-consuming CFD (computational fluid dynamics) calculations during the numerical optimization of a turbo-machinery unit,developed was an optimized design method based on an approximate model.
针对叶轮机械数值优化过程中常常需要大量耗时的CFD计算,发展了一种基于近似模型的优化设计方法。
4) approximation model


近似模型
1.
To reduce huge computation of the traditional stochastic optimization methods for engineering optimization,approximation model methods with acceptable accuracy for engineering design are developed based on the statistical theory.
针对在工程中完全采用随机类优化方法寻优时计算量过大的问题,应用统计学的方法发展了计算量小、在一定程度上可以保证设计准确性的近似模型方法。
2.
Based on the original algorithm, the Kriging model is employed as an approximation model for Bayesian analysis.
介绍了克里金模型的基本理论,并采用以克里金模型为近似模型的贝叶斯分析算法,对函数关系复杂、难以计算情况下的全局优化问题进行求解。
3.
The paper presents an algorithm combining square response surface and Radial Basis Function Neural Network(RBFNN) to solve the problem that RBFNN is often difficult to meet the precision request of approximation model.
用径向基神经网络方法构造近似模型常常难以满足精度要求,提出了一种把二次响应面与径向基神经网络相结合的算法。
5) approximate simulating


近似模拟
1.
The approximate simulating method was presented according to li.


”根据技术条件限制,提出了地面热平衡实验时座舱内空气对流换热的近似模拟方案,阐述了近似实验时座舱内空气状态的确定方法。
6) approximate modeling


近似建模
1.
Investigation and comparison of approximate modeling of a complex system;


系统近似建模技术的研究与比较
2.
These include layout design process modeling,functional feature-based components and container approximate modeling,representation of layout knowledge and layout constraints and application of layout approaches.
针对工程布局设计的复杂性,提出了开放式的工程布局设计CAD系统的结构框架,讨论了实现该系统的关键方法,包括自动化设计进程建模、基于功能特征的待布物和布局空间几何近似建模、布局知识和布局约束的表达、布局方法应用。
补充资料:SL1126内燃机零部件数字化建模
1、 SL1126内燃机总成
SL1126内燃机是由机体总成、缸盖总成、运动机构总成,其它机构总成等组成,见图I。
(1)机体总成主要由:机体、油底壳、风扇、油标、同步齿轮室盖、主副曲轴轴承盖、标尺及相应的标准零件。在机体总成中,机体是主要的设计零件。
(2)气缸盖总成主要包括的零件有:气缸盖、缸盖罩、喷油嘴、机油筒、空气滤清器等零件;其中气缸盖是主要设计零件。
(3)运动机构总成由活塞,滑块,活塞销,连杆,连杆配件,主、副曲轴总成,正视齿轮总成,凸轮轴总成以及气门挺杆总成等组成。
(4)其他机构总成有:机油泵总成,喷油泵总成等组成。
SL1126内燃机是由机体总成、缸盖总成、运动机构总成,其它机构总成等组成,见图I。
(1)机体总成主要由:机体、油底壳、风扇、油标、同步齿轮室盖、主副曲轴轴承盖、标尺及相应的标准零件。在机体总成中,机体是主要的设计零件。
(2)气缸盖总成主要包括的零件有:气缸盖、缸盖罩、喷油嘴、机油筒、空气滤清器等零件;其中气缸盖是主要设计零件。
(3)运动机构总成由活塞,滑块,活塞销,连杆,连杆配件,主、副曲轴总成,正视齿轮总成,凸轮轴总成以及气门挺杆总成等组成。
(4)其他机构总成有:机油泵总成,喷油泵总成等组成。
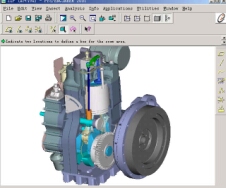
图I SL1126内燃机总成
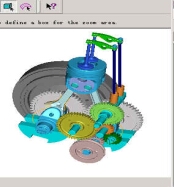
图II 内燃机运动机构总成
2、自顶向下设计的参数化技术
在CAD中,参数化技术是采用参数预定义的方法建立图形的集合约束集,指定一组尺寸作为参数使其与几何约束集相关联,并将所有的关联式融入到应用程序中,然后以人机交互方式修改参数尺寸,通过参数化尺寸驱动实现对设计结果的修改。参数化设计过程中,参数与设计对象的控制尺寸有明显的对应关系,并具有全局相关性。参数化设计不同于传统的设计,它储存了设计的整个过程,能设计出一族而非单一的在形状和功能上具有相似性的产品模型。正是有了这种参数化建模技术,才使得数据的改变在不同层次(如不同的子装配系统和不同的零件)之间的传递变得唯一个即时。这样,才有了真正意义上的自顶向下设计及以这种设计为基础的并行设计,后者是团队设计的基础。
下面以主同步齿轮零件三维参数化为例:
下面为渐开线方程:
alpha=20
m=4
z=46
r0=0.5*m*z*cos(20)
t0=t*40
x0=(cos(t0)+t0*pi/180*(sin(t0)))*r0
y0=(sin(t0)-t0*pi/180*(cos(t0)))*r0
theta=-(tan(alpha)-alpha*pi/180)*180/pi-90/z
x=x0*cos(theta)-y0*sin(theta)
y=x0*sin(theta)+y0*cos(theta)
z=0
其中alpha为压力角, m为模数, z为齿数, r0为基圆半径。

图III 齿轮总成
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条