1) nonidcal solution theory


非理想溶液理论
2) nonideal solution


非理想溶液
1.
The mathematical model for optimum design of distillation for binary nonideal solution was established, based on the annual cost of distillation system including the distillation column, condensator and reboiler.
建立二元非理想溶液精馏优化设计数学模型 。
3) ideal solution


理想溶液
1.
In this paper,concepts for the force field condition and shape change of molecules were put forward by deducing relationship between gas phase pressure and molecular force,and therefore a new explanation for the ideal solution was carried out macrocosmically.
本文推演了理想溶液中气相压力与分子间力的关系,提出了力场环境及分子变形的概念。
2.
There are two kinds of standard states for ideal solution.


对于理想溶液 ,可以选择两种标准状态 ,推导了不同标准状态下 ,溶质的化学势表达式 。
4) IAST


理想吸附溶液理论
1.
The adsorption isotherms of CH_4/CO_2 dioxide binary gas on Jincheng and Lu'an coal were studied,and experimental data were predicted with expended Langmuir and ideal adsorbed solution theory(IAST) in conjunction with pure gas isotherm models viz.
研究了晋城煤和潞安煤对CO2和CH4及其二元混合气体的等温吸附特性,利用扩展Langmuir和理想吸附溶液理论结合纯气体等温吸附模型Langmuir,DA,DR,BET对吸附实验数据进行预测,并检验了实验数据的预测准确度。
5) solution theory


溶液理论
1.
A method of gas-liquid-solid three phases equilibrium calculation is presented based on an equation of state and solution theory.
用状态方程和溶液理论建立了气 -液 -固三相相平衡计算方法。
2.
Basis on chromatographic theory and solution theory,the retention equation of RP HPLC was derived.
根据色谱理论和溶液理论推导出反相高效液相色谱保留值方程。
6) theory of solution


溶液理论
1.
In the present paper,a theory of solution for molecular aggregation is proposed based on both classical thermodynamic and molecular thermodynamic principles.
本文应用经典热力学和分子热力学方法建立了分子聚集溶液理论。
补充资料:理想溶液
| 理想溶液 ideal solution 溶液中的所有组分在全部浓度范围内都严格遵守拉乌尔定律的溶液。同分异构体和有机物中的同系物等都能近似构成理想溶液。在理想溶液中,同种分子的分子间力和异种分子的分子间力平均来说都是相等的,即每一种物质的分子与其他分子的相互作用都与纯态时的相互作用相同。因为理想溶液中的所有组分都服从拉乌尔定律,所以它们的化学势具有完全相同的表示形式:  式中μB为溶液中任一组分B的化学势;T为溶液的热力学温度;p为溶液的压力;xB为B的物质的量分数。 式中μB为溶液中任一组分B的化学势;T为溶液的热力学温度;p为溶液的压力;xB为B的物质的量分数。 为标准压力,习惯上取 为标准压力,习惯上取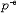 =101.325千帕; =101.325千帕;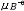 为标准压力下与溶液同温的纯B液体的化学势;Vm,B为纯B的摩尔体积。 为标准压力下与溶液同温的纯B液体的化学势;Vm,B为纯B的摩尔体积。在一定温度和压力下将多种纯液体相混合形成理想溶液,则该过程具有如下特性: ①无热效应,即: ΔminH=0(1)式中ΔminH是上述过程的混合焓。配制理想溶液时不吸收或放出热量,这是由于混合前后无分子间力的变化,使每一种物质在溶液中的偏摩尔焓与纯态时的摩尔焓完全相等,因而整个过程没有焓变。 ②无体积效应,即: ΔmixV=0(2)式中ΔmixV是上述过程的混合体积。配制理想溶液时总体积不发生变化,这是由于每一种物质在溶液中的偏摩尔体积完全等于其纯态时的摩尔体积。 ③混合熵,即: 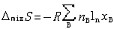 (3)式中ΔmixS是上述过程的混合熵;nB是任一组分B的物质的量;xB是B的物质的量分数;R是摩尔气体常数。 (3)式中ΔmixS是上述过程的混合熵;nB是任一组分B的物质的量;xB是B的物质的量分数;R是摩尔气体常数。④混合吉布斯函数,即: 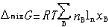 (4)式中ΔmixG是上述过程的混合吉布斯函数。式(1)~(4)表明,理想溶液的配制过程是一个无功、无热、熵增加、吉布斯函数减少的过程。 (4)式中ΔmixG是上述过程的混合吉布斯函数。式(1)~(4)表明,理想溶液的配制过程是一个无功、无热、熵增加、吉布斯函数减少的过程。理想溶液的概念及研究具有重要实际意义和理论价值。在处理任意非理想溶液时总是采用与理想溶液相对比的方法。可通过测量实际溶液的ΔmixH或ΔmixV值,发现它与理想溶液的差异,进而讨论和研究溶液的具体性质和规律。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条