1) optical parametric oscillation


光学参量谐振腔
1.
Generation of 4.0 μm optical parametric oscillation with periodically poled MgO∶LiNbO_3;


基于周期极化MgO∶LiNbO_3的4.0μm光学参量谐振腔的产生(英文)
2) optical parametric oscillator


光学参量振荡腔
1.
The dependence of the quantum correlation of twin beams generated from a non-degenerate optical parametric oscillator on the analysis frequency was theoretically studied with semi-classical method.
采用两对光纤构成的非平衡Mach-Zehnder干涉仪,对非简并光学参量振荡腔产生的20mW频率非简并孪生光束间的强度差与位相和的关联噪声进行测量,在分析频率为2MHz处测得关联噪声分别低于散粒噪声基准3·1和1·3dB,从实验上证实了在较低分析频率处孪生光束之间有较高量子纠缠。
2.
The phase squeezing of pump light reflected from triply resonant optical parametric oscillator (OPO) has been discussed by means of the semi classical theory.
利用半经典理论分析了由于级联非线性过程, 三模共振光学参量振荡腔反射场的相位压缩, 讨论了压缩与各参量的关系, 并与实验结果比较, 理论与实验基本吻
3) optical cavity


光学谐振腔
1.
The reflectivity of optical mirrors can be obtained by measuring linewidth of transmission spectrum of optical cavity and the fineness of Fabry-Perot (F-P) cavity.
谐振腔精细度法是通过测量光学谐振腔透射谱线宽度来实现对光学反射镜反射率的测定。
2.
The design of the BFEL optical cavity s 5 D precise remote control adjuster is described.


论述了北京自由电子激光 (BFEL)光学谐振腔真空机械五维精密遥控调节装置的设计考虑 。
3.
With the peak-seeking servo-controlled technology based on a residual error,an external optical cavity can keep in resonance with the frequency of Ti-sapphire laser in the experiment.
基于有差伺服调节技术,实现了外置光学谐振腔的共振频率与钛宝石激光器工作频率的锁定。
4) Resonator
[英]['rezəneɪtə(r)] [美]['rɛzə'netɚ]


光学谐振腔
1.
Based on our investigation results, some key problems and techniques concerning slab lasers, such as the thermal effects, pumping cavity and resonators, are analyzed physically.
结合作者部分工作,对板条激光器的热效应、聚光器和光学谐振腔等关键问题和技术进行了物理分析。
5) optical resonator


光学谐振腔
1.
Geometrical graphic method of designing optical resonator and its applications;


光学谐振腔设计的几何作图方法及其应用
2.
The numerical and graphical functions of MATLAB language are used in the design of the optical resonators.
本文将MATLAB的数值计算和图形功能用于光学谐振腔的设计中。
6) intracavity optical parametric oscillator


内腔式光学参量振荡器
1.
The threshold formula of a acousto-optically(AO) Q-switched Nd∶YAG intracavity optical parametric oscillator(OPO),side pumped by laser diode arrays,is studied.
讨论了激光二极管阵列(LDA)侧面泵浦声光调QNd∶YAG内腔式光学参量振荡器(OPO)的阈值特性;在相同的实验条件下,对比分析了KTA和KTP晶体参量激光输出特性。
补充资料:光学谐振腔
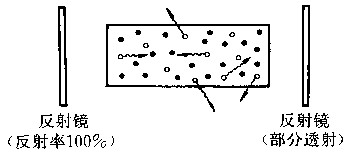
| 光学谐振腔 optical resonant cavity 光波在其中来回反射从而提供光能反馈的空腔。激光器的必要组成部分,通常由两块与工作介质轴线垂直的平面或凹球面反射镜构成。工作介质实现了粒子数反转后就能产生光放大。谐振腔的作用是选择频率一定、方向一致的光作最优先的放大,而把其他频率和方向的光加以抑制。如图,凡不沿谐振腔轴线运动的光子均很快逸出腔外,与工作介质不再接触。沿轴线运动的光子将在腔内继续前进,并经两反射镜的反射不断往返运行产生振荡,运行时不断与受激粒子相遇而产生受激辐射,沿轴线运行的光子将不断增殖,在腔内形成传播方向一致、频率和相位相同的强光束,这就是激光。为把激光引出腔外,可把一面反射镜做成部分透射的,透射部分成为可利用的激光,反射部分留在腔内继续增殖光子。光学谐振腔的作用有:①提供反馈能量,②选择光波的方向和频率。谐振腔内可能存在的频率和方向称为本征模,按频率区分的称纵模,按方向区分的称横模。两反射镜的曲率半径和间距(腔长)决定了谐振腔对本征模的限制情况。不同类型的谐振腔有不同的模式结构和限模特性。
|
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条