1) flexible manufacturing control software


柔性制造系统控制软件
2) FMS


柔性制造系统
1.
Measures to Improve the Work Efficiency of FMS;


提高柔性制造系统加工效率的措施
2.
A deadlock prevention policy for FMS using elementary siphons;


一种利用基本信标的柔性制造系统死锁控制器设计方法
3.
Review of Fault Diagnosis of Flexible Manufacturing System(FMS);


柔性制造系统(FMS)故障诊断技术研究综述
3) flexible manufacturing system


柔性制造系统
1.
Accurate localization of the organization in flexible manufacturing system(FMS)with PLC technology;
应用PLC技术实现柔性制造系统(FMS)中运输机构的准确定位
2.
Application of Adaptable Genetic Algorithms in Optimal Configuration of Flexible Manufacturing System;
自适应遗传算法在柔性制造系统优化配置中的应用
3.
Petri nets based dynamic optimal model for flexible manufacturing system;


基于Petri网的柔性制造系统动态优化模型
4) flexible manufacturing system (FMS)


柔性制造系统(FMS)
5) flexible manufacturing systems


柔性制造系统
1.
Based on the system of electric power supply for flexible manufacturing systems (FMS), a study has been carried out on the intelligent safety examination, monitoring and maintenance of its running environment.
以柔性制造系统 (FMS)的供电系统为主要对象 ,对FMS运行环境的智能安全检测监控与维护进行探索研究 。
2.
The flexible manufacturing systems considered in the paper consist of possible unreliable workstations, whose inputs may be random.
对于具有随机输入和随机需求的一类不可靠柔性制造系统 ,利用转移率一致化技术和随机动态规划方法 ,给出了输入率和服务率分配的最优反馈控制策略 ,指出系统的最优控制具有bang bang形式的开关结构 ,数值例子验证了文中的结
3.
Here, the total productivity of the systems as a measure of performance of FMS, we use it to evaluate the performance of flexible manufacturing systems of alternative designs.
运用“系统总生产率Ps”对柔性制造系统设计方案进行了评估。
6) flexible manufacturing system(FMS)


柔性制造系统(FMS)
1.
The criteria system and selection principle for Flexible Manufacturing System(FMS) s synthetic evaluation are analyzed,the synthetic evaluation algorithm of FMS based on fuzzy mathematics is established,and the main problems of the algorithm are discussed.
分析了柔性制造系统(FMS)综合评价的指标体系及选取原则,基于模糊数学建立了FMS的综合评价模型,并对模型中的主要问题作出讨论。
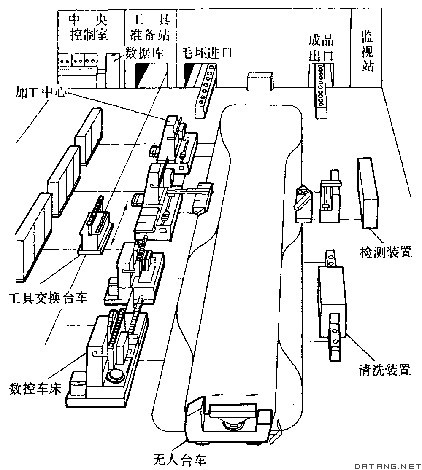
补充资料:柔性制造系统
| 柔性制造系统 flexible manufacturing system 由统一的信息控制系统、物料储运系统和一组数字控制加工设备组成的,能适应加工对象变换的自动化的机械制造系统。英文缩写FMS。系统兼有加工制造和部分生产管理的功能,能缩短生产周期,减少劳动力,提高设备的利用率和产品质量的一致性。 1967年,英国莫林斯公司首次根据D.T.N.威廉森提出的FMS基本概念研制“系统24”,主要设备是6台模块化结构的多工序数字控制机床。同年美国的怀特·森斯特兰公司建成 Omniline I系统,由8台加工中心和2台多轴钻床组成。1976年,日本发那科公司展出了由加工中心和工业机器人组成的柔性制造单元,为发展柔性制造系统提供了重要的设备形式。1982年,日本发那科公司建成自动化电机加工车间,由60个柔性制造单元(包括50个工业机器人)和1个立体仓库组成,另有2台传送毛坯机工件的自动引导台车和1个无人化电机装配车间,它们都能连续24小时运转。 柔性制造系统一般由数字控制加工设备(如加工中心和数控车床等)、物料(如毛坯、工件、刀具、夹具、量检具、切屑等)贮运系统和信息控制系统(如各种专用计算机和专门应用软件)、监视测量系统等组成。
根据机床和搬运系统的相互关系,柔性制造系统有直线型、循环型、网络型和单元型等布局形式。其中直线型加工顺序不能改变,易于管理,多用于加工工件品种少、柔性要求小的制造系统。单元型柔性较大,易于扩展,但调度作业的程序设计比较复杂。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条