1) epithermal neutron radiation field


超热中子辐射场
1.
The main moderating performances of above 3 kinds of materials used in constructing epithermal neutron radiation field are obtained,and the optimized moderating material,an Al-AlF_3 mixture with a mass fraction ratio w(Al)/(w(AlF_3)) of 2/3, is recommended for Tsinghua University experimental reactor.
研究给出了利用慢化材料实现超热中子辐射场的一般规律,并优选出适用于在该堆建立超热中子辐射场的最佳慢化材料是Al与AlF3质量百分数比为2∶3的Al-AlF3混合物。
2.
In order to get an Epithermal neutron radiation field for the using of Boron neutron capture therapy(BNCT),based on the Tsinghua University experimental reactor neutron source,the research pro- posed two engineering schemes through MC simulating method.
为得到满足硼中子俘获治疗(BNCT)系统所要求的超热中子辐射场,利用清华大学试验核反应堆中子源,采用蒙特卡罗(MC)计算方法,设计了两种产生超热中子辐射场的工程理论方案,并对这两种方案进行了分析与对比。
2) neutron radiation field


中子辐射场
1.
The typical workplace geometric model used in neutron radiation field simulation was established, neutron migration and transport in the radiation field was then simulated by MCNP 4C with data of plutonium isotope composition and neutron energy spectrum.
本文建立了工作场所中子辐射场模拟的几何模型,结合文献给出的钚材料同位素组成和中子能谱数据,采用MCNP 4C模拟了中子在辐射场的迁移和输运行为。
3) EpithennaI neutron radiation field


超热中子场
4) natural neutron flux


大气中子辐射场
1.
This paper describes the origins of natural neutron flux on the air-ground interface.


论述了地-空界面上天然宇宙中子流的来源;从理论上建立了描述地-空界面上大气中子辐射场的数学-物理模型。
5) fast neutron radiation field


快中子辐射场
1.
An fast neutron radiation field was gained.


本文以清华大学试验核反应堆为中子源源项,通过蒙特卡罗方法模拟的手段,设计出了实现快中子辐射场的理论技术方案,确定了此方案中各种材料的厚度,获得了典型快中子辐射场能谱。
6) Thermal radiation field


热辐射场
1.
Statistic properties of thermal radiation field in K-photon Jaynes-Cummings model;


K光子Jaynes-Cummings模型中热辐射场的统计特性
2.
Coherence properties of a two-level atom of the super Jaynes-Cummings model in thermal radiation field;
超Jaynes-Cummings模型中的原子置于热辐射场时的相干特性
3.
Dynamical properties of the V-type three-level atom and thermal radiation field in the Raman interaction;
V型三能级原子与热辐射场Raman相互作用时原子的动力学特性
补充资料:中子
| 中子 neutron 组成原子核的核子之一。中子是1932年B.查德威克用a粒子轰击 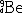 的实验中发现,并根据 E. 卢瑟福的建议命名的。中子电中性,其质量为 1.6749286 ×10-27千克(939.56563兆电子伏特),比质子的质量稍大,自旋为1/2,磁矩以核磁子作衡量单位为-1.91304275。自由中子是不稳定的粒子,可通过弱作用衰变为质子,放出一个电子和一个反电子中微子,平均寿命为896秒。中子是费米子,遵从费米-狄拉克分布和泡利不相容原理。中子和质子是同一种粒子的两种不同电荷状态,其同位旋为1/2 , 中子的同位旋第三分量I3=-1/2。中子是组 成原子核构成化学元 素 不可缺少的成分,虽然原子的化学性质是由核内的质子数目确定的,但是如果没有中子,由于带正电荷质子间的排斥力,就不可能构成除氢之外的其他元素。在轻核中含有几乎相等数目的中子和质子;在重核中,中子数则大于质子数,例如 的实验中发现,并根据 E. 卢瑟福的建议命名的。中子电中性,其质量为 1.6749286 ×10-27千克(939.56563兆电子伏特),比质子的质量稍大,自旋为1/2,磁矩以核磁子作衡量单位为-1.91304275。自由中子是不稳定的粒子,可通过弱作用衰变为质子,放出一个电子和一个反电子中微子,平均寿命为896秒。中子是费米子,遵从费米-狄拉克分布和泡利不相容原理。中子和质子是同一种粒子的两种不同电荷状态,其同位旋为1/2 , 中子的同位旋第三分量I3=-1/2。中子是组 成原子核构成化学元 素 不可缺少的成分,虽然原子的化学性质是由核内的质子数目确定的,但是如果没有中子,由于带正电荷质子间的排斥力,就不可能构成除氢之外的其他元素。在轻核中含有几乎相等数目的中子和质子;在重核中,中子数则大于质子数,例如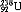 中共有146个中子和92个质子 。对于一定质子数的核,中子数可以在一定范围内取几种不同的值,形成一个元素的不同同位素。 中共有146个中子和92个质子 。对于一定质子数的核,中子数可以在一定范围内取几种不同的值,形成一个元素的不同同位素。中子不带电而具有磁矩。高能电子、μ子或中微子轰击中子的散射实验显示中子内部 的电荷和磁 矩有一定的分布,说明中子不是点粒子,而具有一定的内部结构 。 中子是由3个更深层次的粒子——夸克构成的。 中子是研究核反应很好的轰击粒子,由于它不带电,即使能量很低,也能引起核反应(见中子核反应)。中子还在核裂变反应中起重要作用。电中性的中子不能产生直接的电离作用,无法直接探测,只能通过它与核反应的次级效应来探测。 根据微观粒子的波粒二象性,中子具有波动性,慢中子的波长约10-10米,与晶体内原子间距相当。中子衍射是研究晶体结构的重要技术。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条