1) wind-induced response


风致动力响应
1.
A new load-dependent Ritz vector method is presented for wind-induced response analysis of large span roofs which is denoted as the Ritz-POD method.
目的提出在频域内分析大跨度屋盖结构风致动力响应的新方法———Ritz-POD法,克服传统Ritz向量叠加法的不足,完善Ritz向量叠加法在大跨度屋盖结构风振响应分析中的应用问题。
2) wind-induced dynamic response


风致动力响应
1.
Due to widespread damage of expressway toll canopy,numerical simulation analysis of FSI for wind-induced dynamic response using ADINA is conducted in this paper.
流体-结构耦合作用的力学问题是当前计算风工程领域的研究重点,针对当前高速公路收费站雨蓬结构风灾破坏的普遍性,本文采用 ADINA 有限元软件对该类结构进行了流体-结构耦合风致动力响应数值模拟计算,得出了该类结构的风振系数和体型系数,可供工程参考使用。
3) wind-induced responses


风致动态响应
4) wind-induced response


风致响应
1.
Block Ritz method of computation for wind-induced response of single-layer latticed domes;
单层球面网壳结构风致响应计算的块里兹向量法
2.
Application of POD to calculation of wind-induced response of large roofs;


POD在大跨屋盖风致响应计算中的应用
3.
Theoretical method and wind tunnel tests were carried out to investigate wind-induced response for closed type roof structure.
为了研究封闭式屋盖结构的风致响应特性,用理论方法与风洞试验进行定性与定量分析。
5) wind induced response


风致响应
1.
An experimental study on the wind induced response and aerodynamic damping of Guangzhou West Tower
广州西塔风致响应和气动阻尼特性的试验研究
2.
Simplifying the computational process of wind induced responses of tall buildings is very important for practical purpose and code applications.
简化高层建筑风致响应的计算对实际工程和规范应用均具重要意义。
3.
Computational methods and representative characteristics of wind induced responses and equivalent static wind loads of tall buildings are discussed in detail.
将结构风致响应分解为平均响应、动力响应的背景分量和共振分量,给出了相应的计算公式;还给出了背景和共振等效静力风荷载的计算公式,提出了等效静力风荷载组合的一种简便方法,并讨论了计算背景分量的QML法和LRC法的差异。
6) wind-induced dynamic response


风致响应
1.
Random wind-induced dynamic response of long-span roof to thunderstorm downbursts in the time domain;
冲击风作用下大跨屋盖多模态随机风致响应研究
2.
Random discrete wind-induced dynamic response of long-span roof in disaster windy environments;
灾害天气下大跨屋盖多模态随机离散风致响应研究
3.
The wind-induced dynamic responses of the structure were obtained in the time domain, including Mean nodal displacement, RMS displacement and RMS acceleration.
该文以某一大型薄壁钢管构架为工程背景,结合多阶模态力法和模态解耦原理,提出了多模态显式积分法,并推导了结构风致响应与风振系数的计算公式。
补充资料:动力机械:内燃机动力学
研究内燃机运转中的力学现象的科学。其主要任务是研究分析内燃机运转时各主要零件的运动规律及其受力情况﹐用以作为内燃机零件设计﹑计算的依据。它还研究这些力对内燃机动力装置的影响及其消减方法。内燃机动力学的主要内容为曲柄连杆机构运动学﹑曲柄连杆机构动力学和内燃机平衡分析等。
曲柄连杆机构运动学 研究曲柄﹑连杆﹐尤其是活塞的运动规律。活塞作周期性往复运动时的位移 、速度
、速度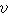 和加速度
和加速度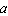 可用下述各式近似求算
可用下述各式近似求算
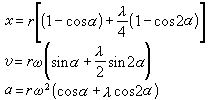
式中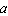 为曲轴转角﹔
为曲轴转角﹔ 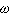 为曲轴旋转角速度﹔
为曲轴旋转角速度﹔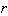 为曲柄半径﹔
为曲柄半径﹔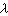 为曲柄半径
为曲柄半径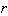 与连杆长度
与连杆长度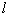 之比﹐即
之比﹐即 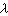 =
= 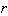 /
/ 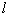
曲柄作回转运动﹐连杆作复杂的平面运动。连杆的运动往往被简化分解为随活塞组的往复运动和随同曲柄的旋转运动。
曲柄连杆机构动力学 研究分析曲柄连杆机构(见曲柄滑块机构)在运动中力的生成﹑传递和输出。作用在曲柄连杆机构上的力有曲柄连杆机构运动时产生的往复惯性力和离心惯性力﹐以及内燃机气缸内的气体压力。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条