1) electrically large


电大尺寸
1.
A coupling model of antenna and an adaptive multilevel fast multipole algorithm(AMLFMA) are introduced for the analysis of the broad band coupling of antennae on electrically large targets.
为求解电大尺寸载体天线间的宽带干扰耦合度,建立了天线间干扰耦合分析模型,提出了自适应多层快速多极子算法作为求解该耦合分析模型的核心算法。
2.
Therefore it can be used to compute EM scattering of electrically large object and multiple objects.
推导和计算实例表明 :此种算法是精确的和高效的 ,它在计算速度和存储量上明显优于传统矩量法 ,因而可用于计算电大尺寸物体 ,并可同时计算多个物体的电磁散
3.
The fast multipole method (FMM) and the multilevel fast multipole algorithm(MLFMA) are new efficient methods for analysis problems of electrically large objects.
快速多极子方法(FMM)和多层快速多极算法(MLFMA)是研究电大尺寸目标问题的新型的快速高效数值算法。
2) electrical large


电大尺寸
1.
Next,the RCS of conductor sphere was calculated by FMA,and pointed out applied prospect of the method,which was greatly superior over MM in the calculation speed and memory requirement by analysis,and was suit for solution to electrical large object s scattering.
通过分析表明该方法在计算速度和存储要求方面比矩量法有明显优势 ,适合于在现有计算机条件下求解电大尺寸目标的散射问题 。
3) very large electric-dimension


超电大尺寸
4) electrically large structures


电大尺寸物体
1.
A new Multigrid-FFT (MGFFT) algorithm, combined multigrid method with FFT, ispresented in this paper for analyzing scattering from electrically large structures.
采用多重网格法(MG)分析电大尺寸物体的电磁散射,这种MG方法与已有的几种多重矩量法有本质的不同,与其他多层方法相比,它是一种高效率的迭代方法。
5) electrically large aperture


电大尺寸口径面
1.
The solution of electromagnetic scattering from objects with open cavities is very important and challenging,especially when the cavity has an electrically large aperture.
含腔目标,尤其是含电大尺寸口径面腔体目标的电磁散射是目标散射问题中极其重要和极具挑战的问题。
6) electrically large problem


电大尺寸问题
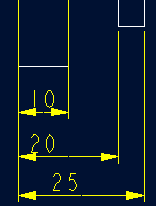
补充资料:工程图标准尺寸及坐标尺寸
标准标注类型,是我们常用的标注类型。而坐标标注是便于数控加工采用的另一中标注形式。PRO/E可以将两种标注方式进行转换。
· 3.2 标准标注到坐标标注的转换
注意: 转化为坐标标注的尺寸必须是线性标注的,下列尺寸不能转化为坐标标注:
- 被显示成线性尺寸的直径
- 中心线尺寸
- 选择MODIFY DRAW > Dim Params > Dim Type > Ordinate Dim > Create Base.
- 选择作为参考基准线的尺寸
- 选择基准的引出线,该点为0点
- 选择 MOD DIM TYPE > Lin to Ord .
- 选择线性尺寸:注意:必须选择具有相同基准的尺寸
 ========>>>>
========>>>>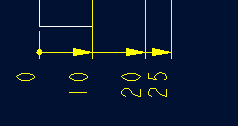
1. 选择 DIM PARAMS > Diam Dim Type .
2.点击Ord to Lin 
3.选择尺寸即可
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条